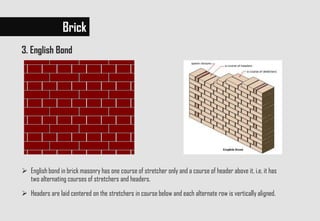
This document provides information about brick and stone building materials. It discusses the brief history of bricks, the types of bricks including sun-dried, burnt bricks in various classes. It also describes different brick bonds, standard brick sizes used in various countries and the types of stones including sedimentary, metamorphic and igneous stones. The key types of sedimentary stones discussed are limestone, sandstone, soapstone and fossil stone.