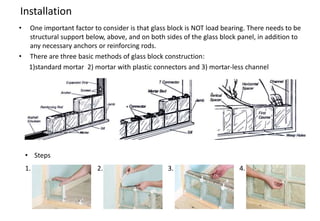
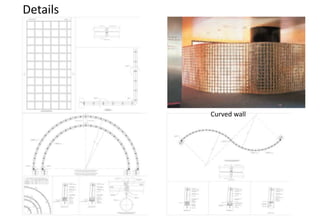
Glass blocks are a unique building material developed in the 1900s to provide natural light. They come in various sizes, styles, and colors and can be used as non-load bearing walls, windows, or partitions. Glass blocks allow natural light to pass through while providing privacy, security, durability, and insulation. They have numerous advantages for both residential and commercial buildings.