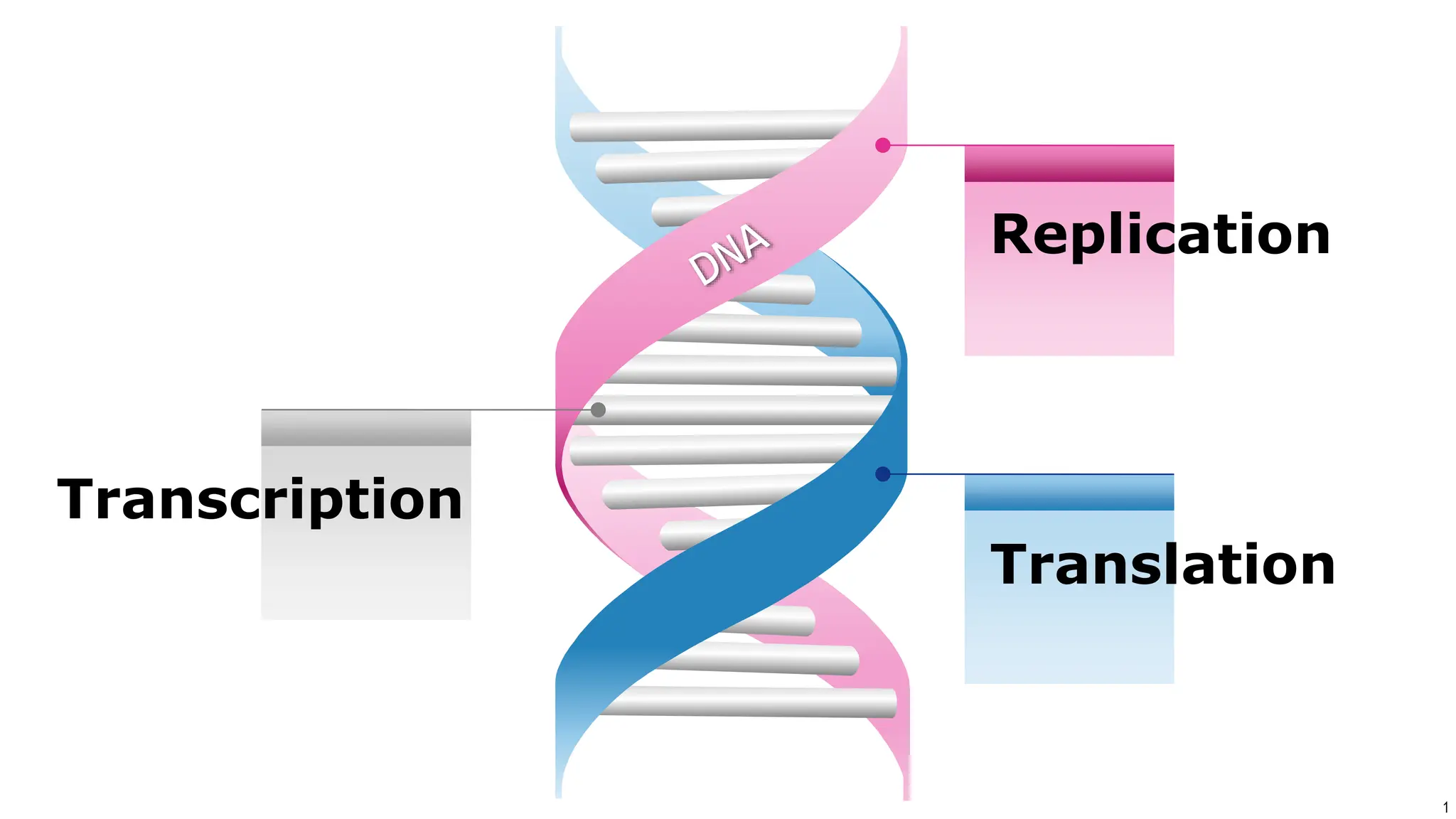
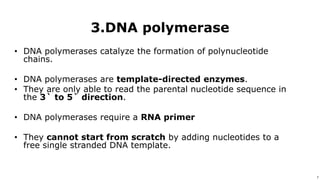
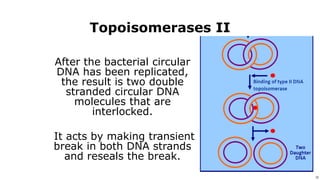
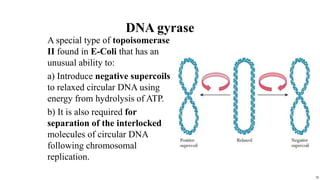
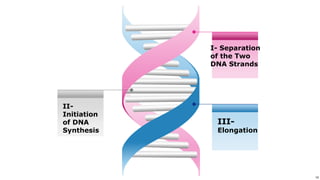
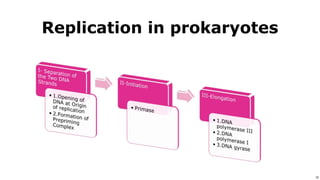
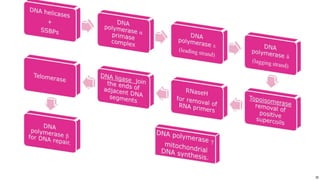
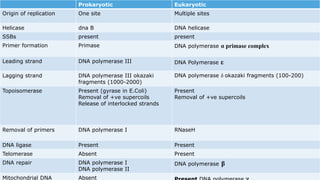
DNA replication occurs during S phase of the cell cycle and involves semi-conservative replication where each daughter DNA molecule contains one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. It requires several enzymes including DNA helicase, primase, DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, and DNA topoisomerases. DNA helicase unwinds the double helix and primase forms an RNA primer. DNA polymerase then synthesizes DNA in the 5' to 3' direction along the template strand. DNA ligase joins the fragments and topoisomerases resolve supercoiling issues introduced during replication.