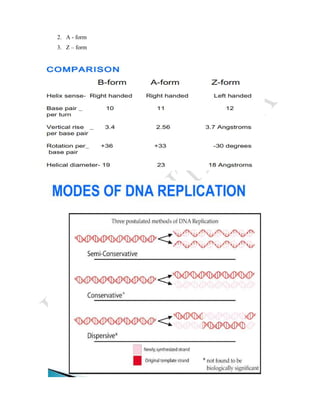
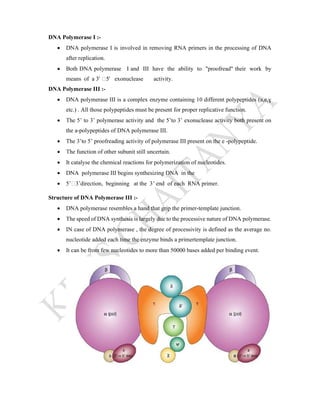
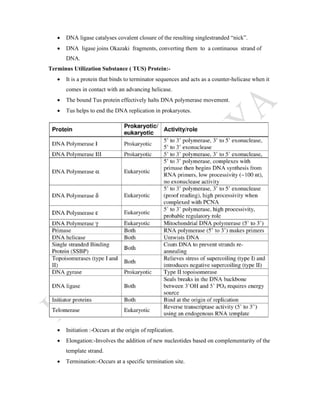
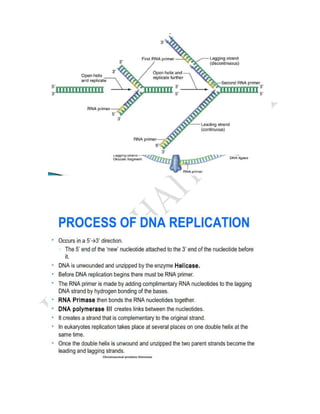
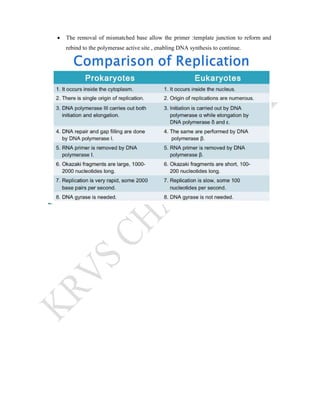
DNA replication is the process by which DNA copies itself. It involves unwinding the double helix and using each strand as a template to synthesize new complementary strands. Key enzymes involved include helicase, primase, DNA polymerase III, and ligase. DNA polymerase III is responsible for adding nucleotides to the new strands, while helicase unwinds the DNA and primase adds RNA primers. The process is semi-conservative, producing two DNA molecules each with one original and one new strand. Replication occurs through initiation, elongation, and termination stages and proofreading ensures high-fidelity copying of the genetic material.