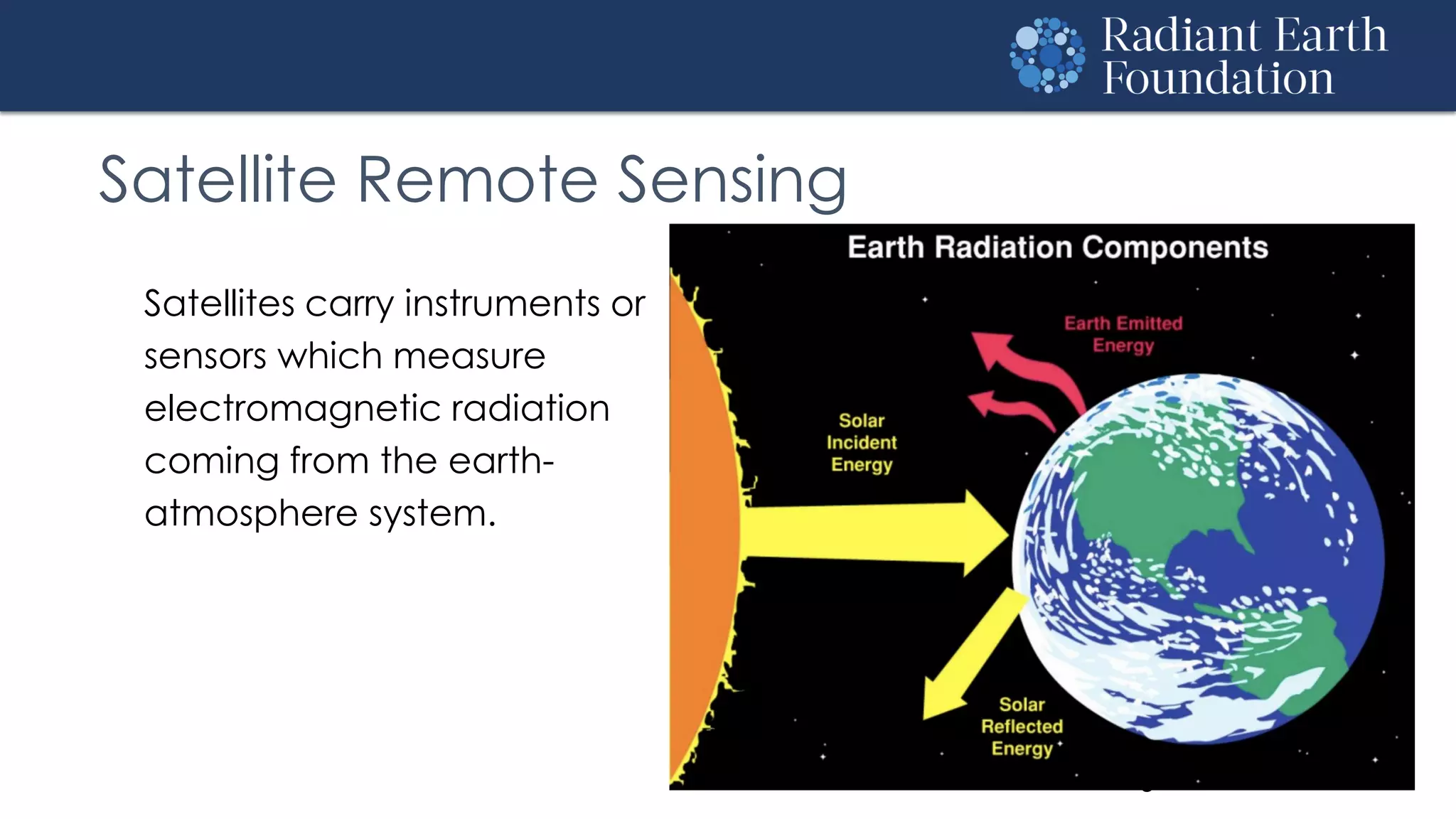
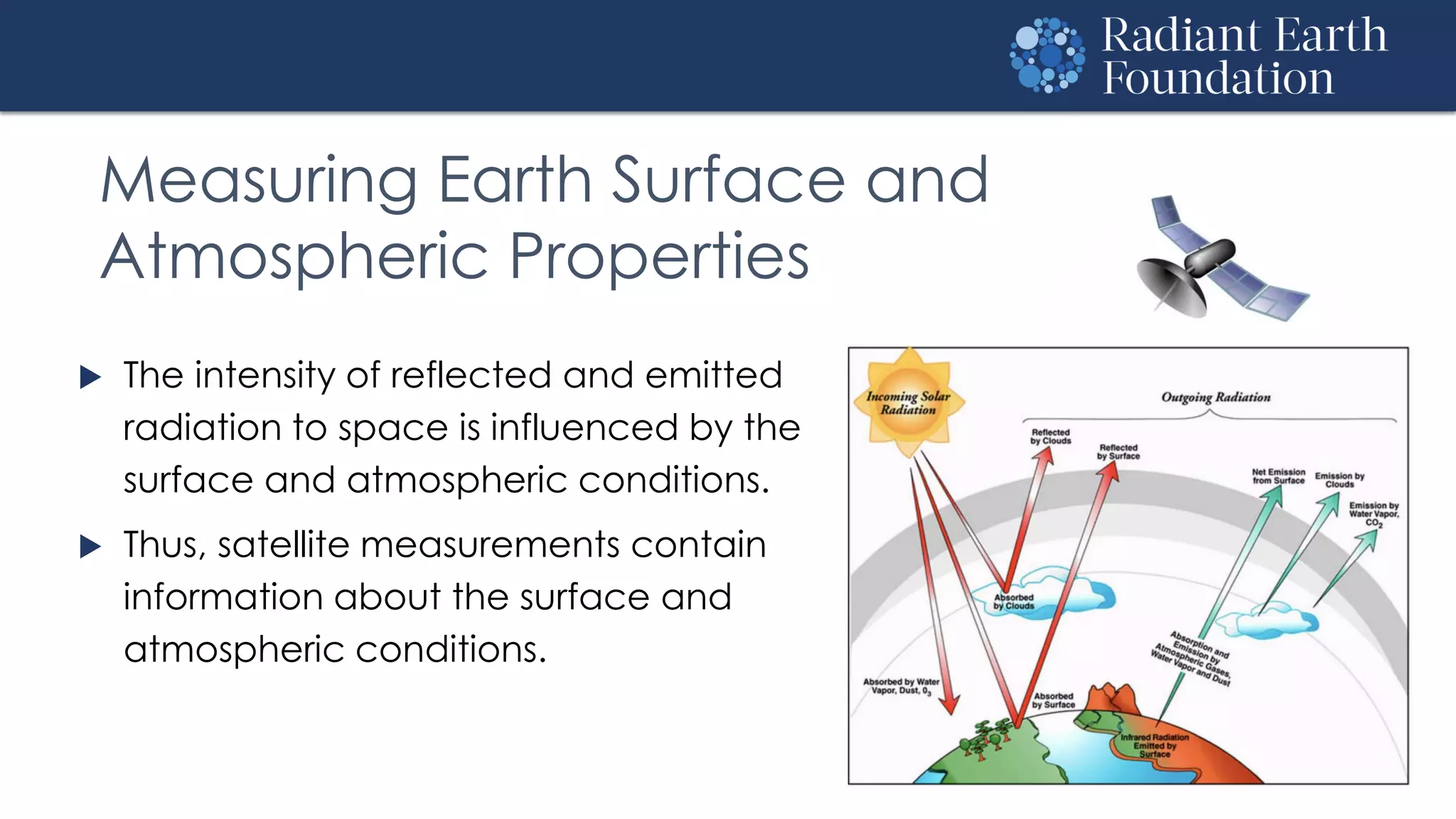
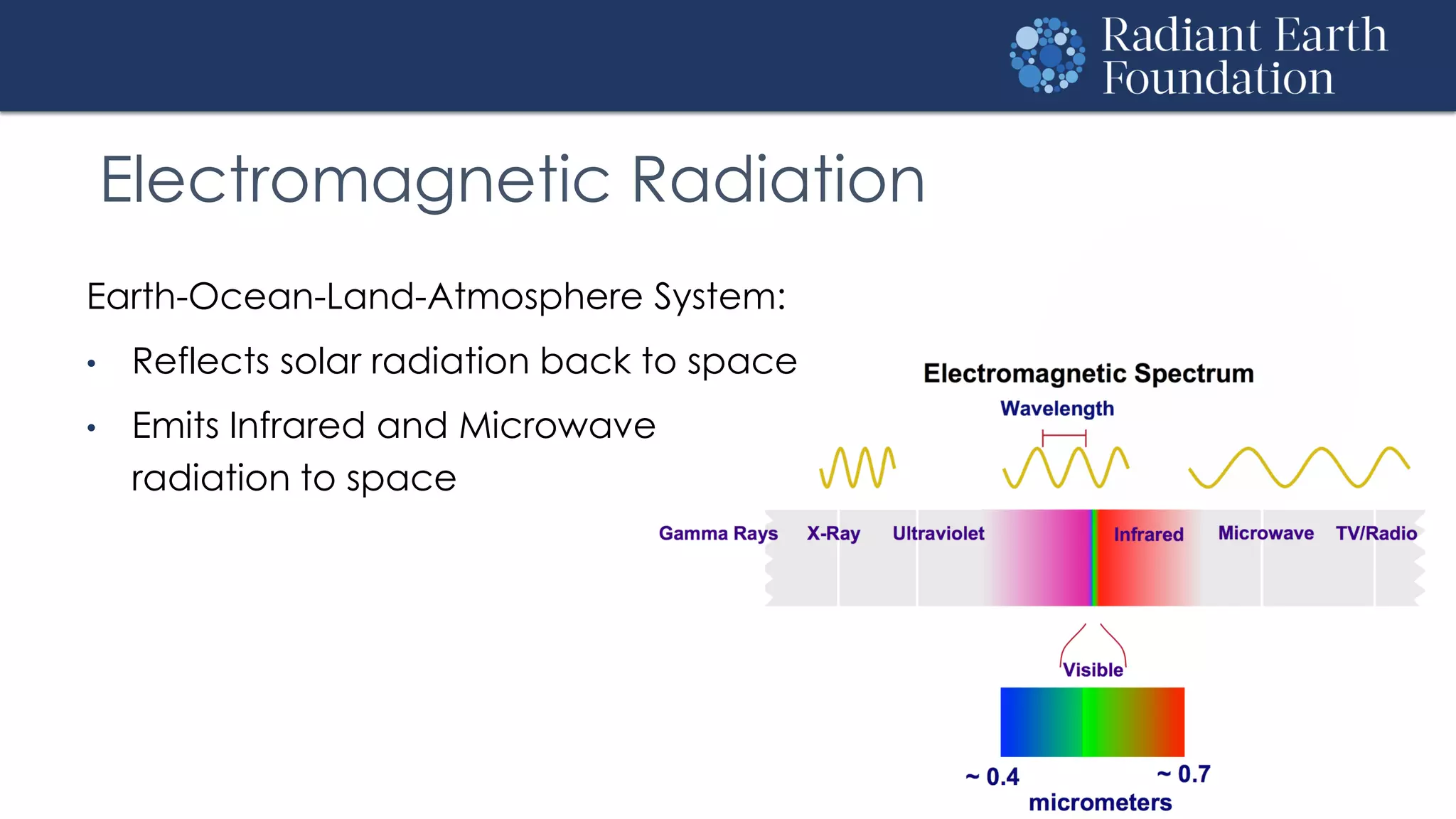
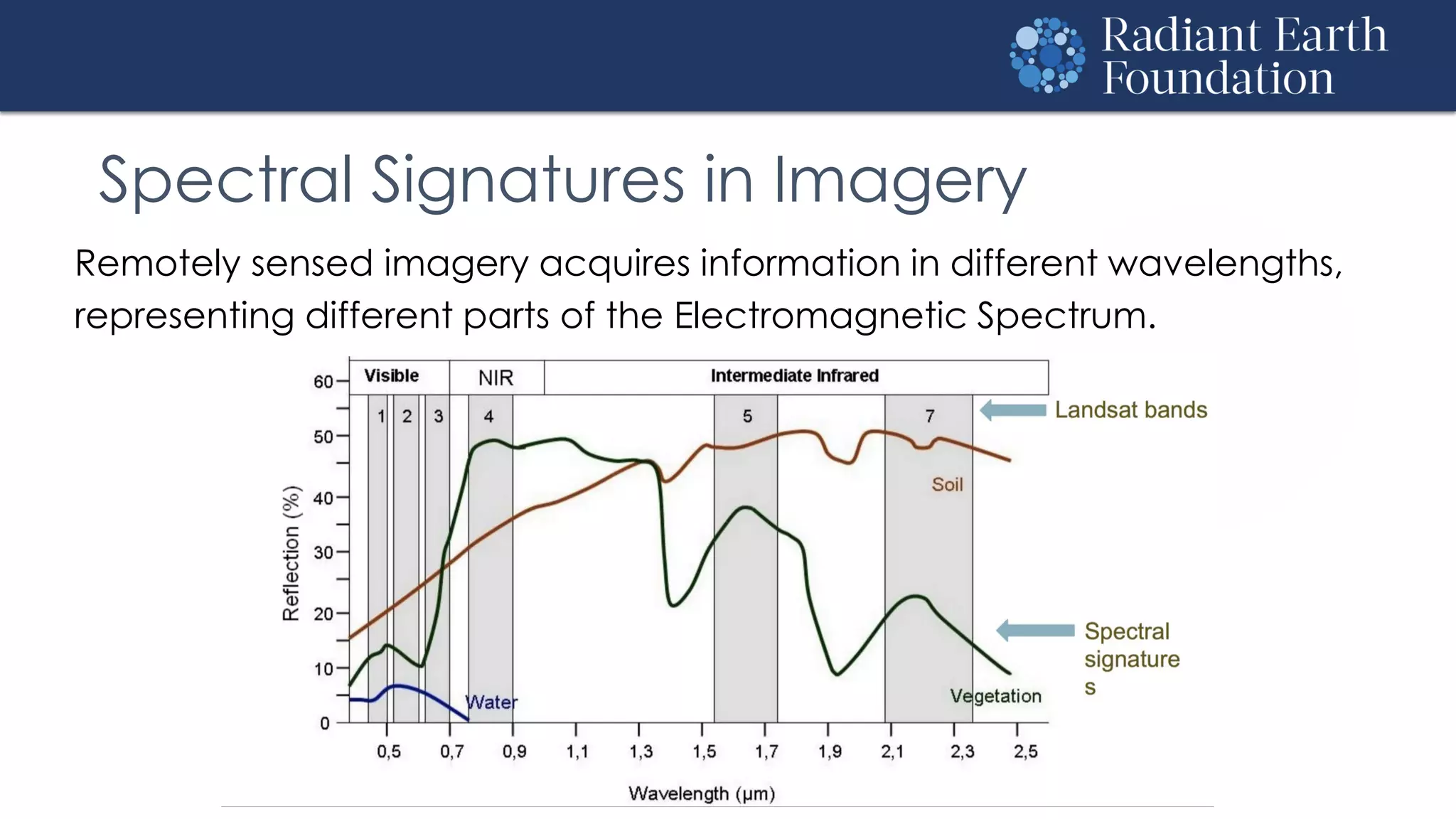
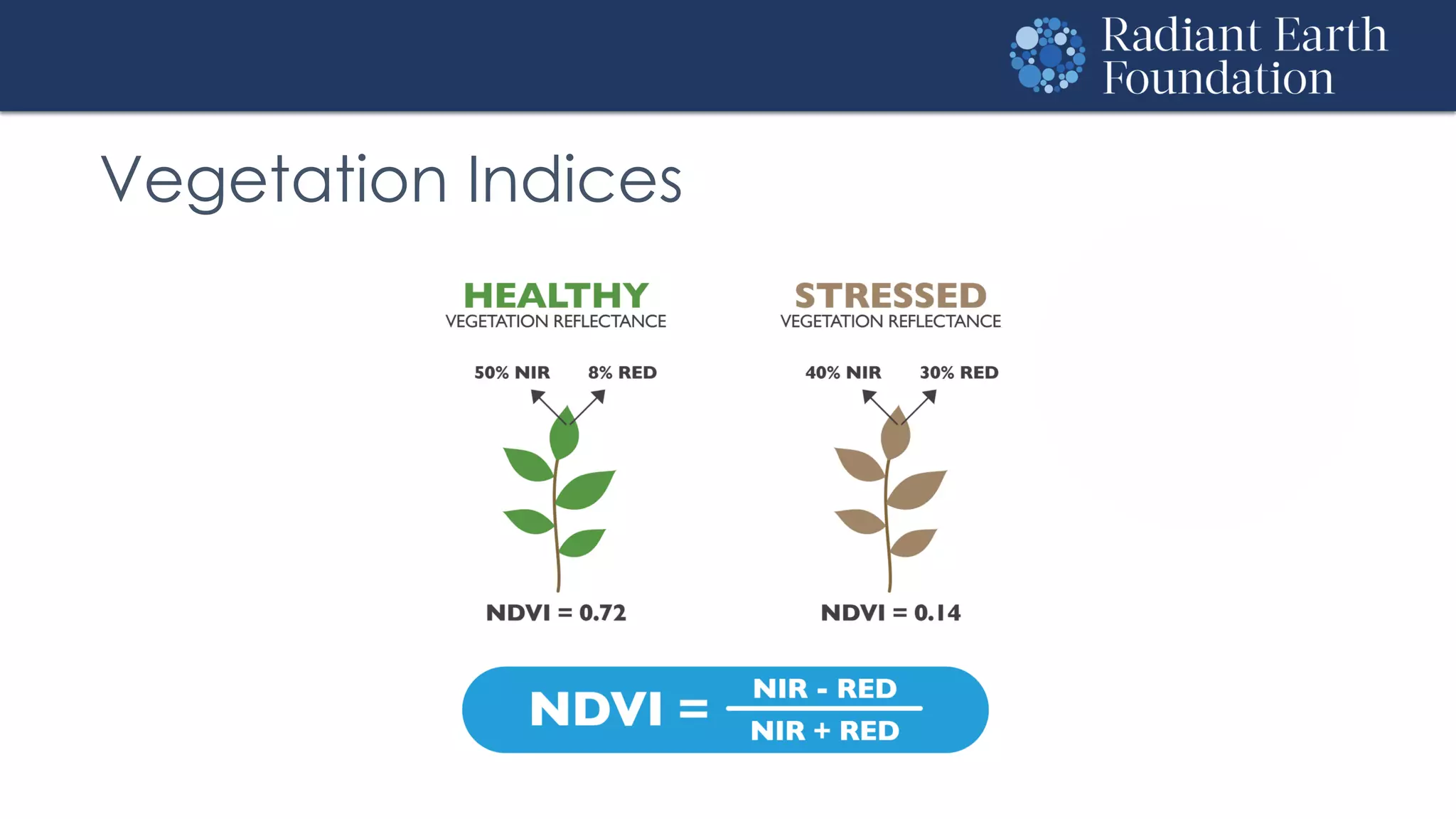
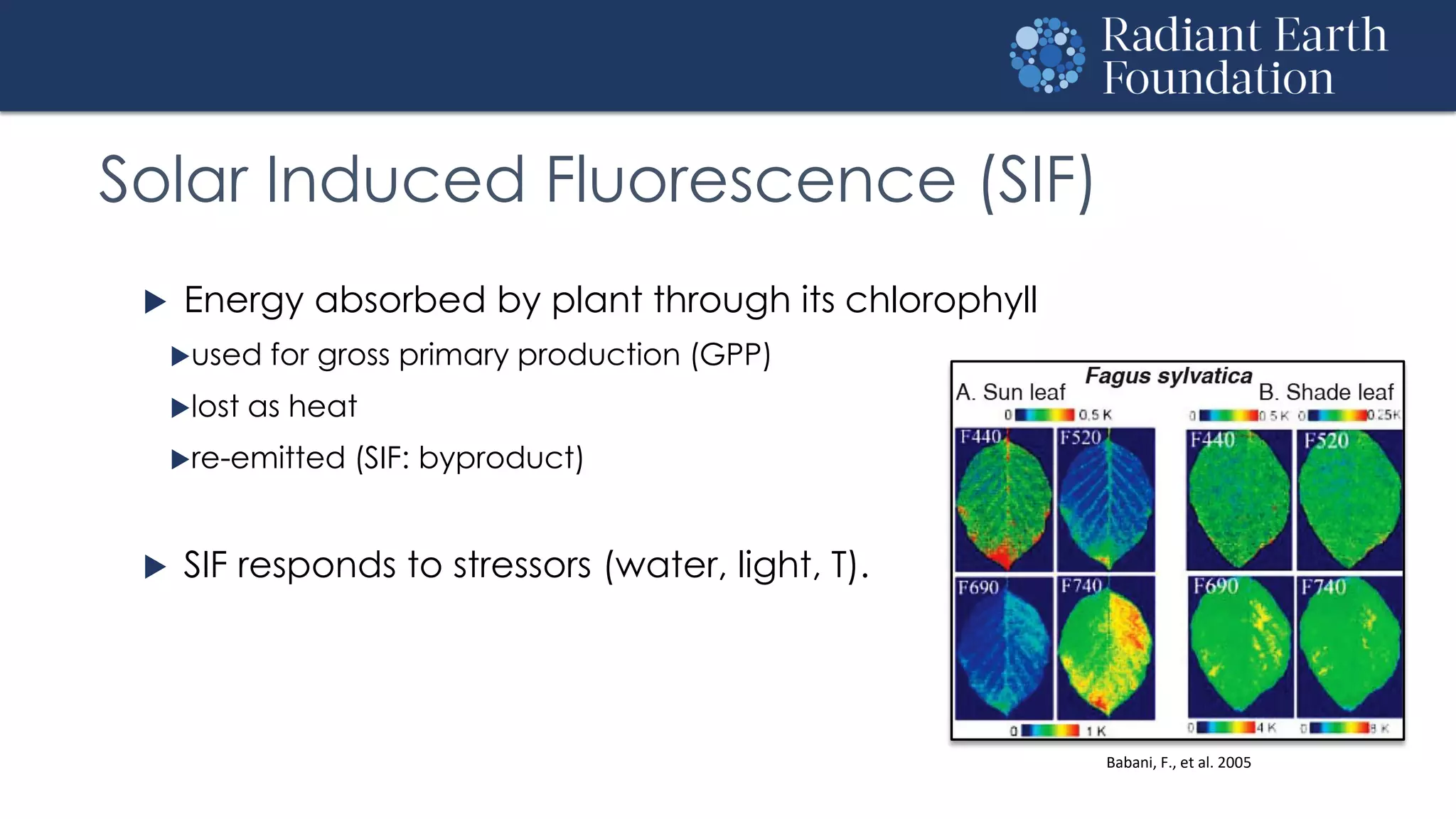
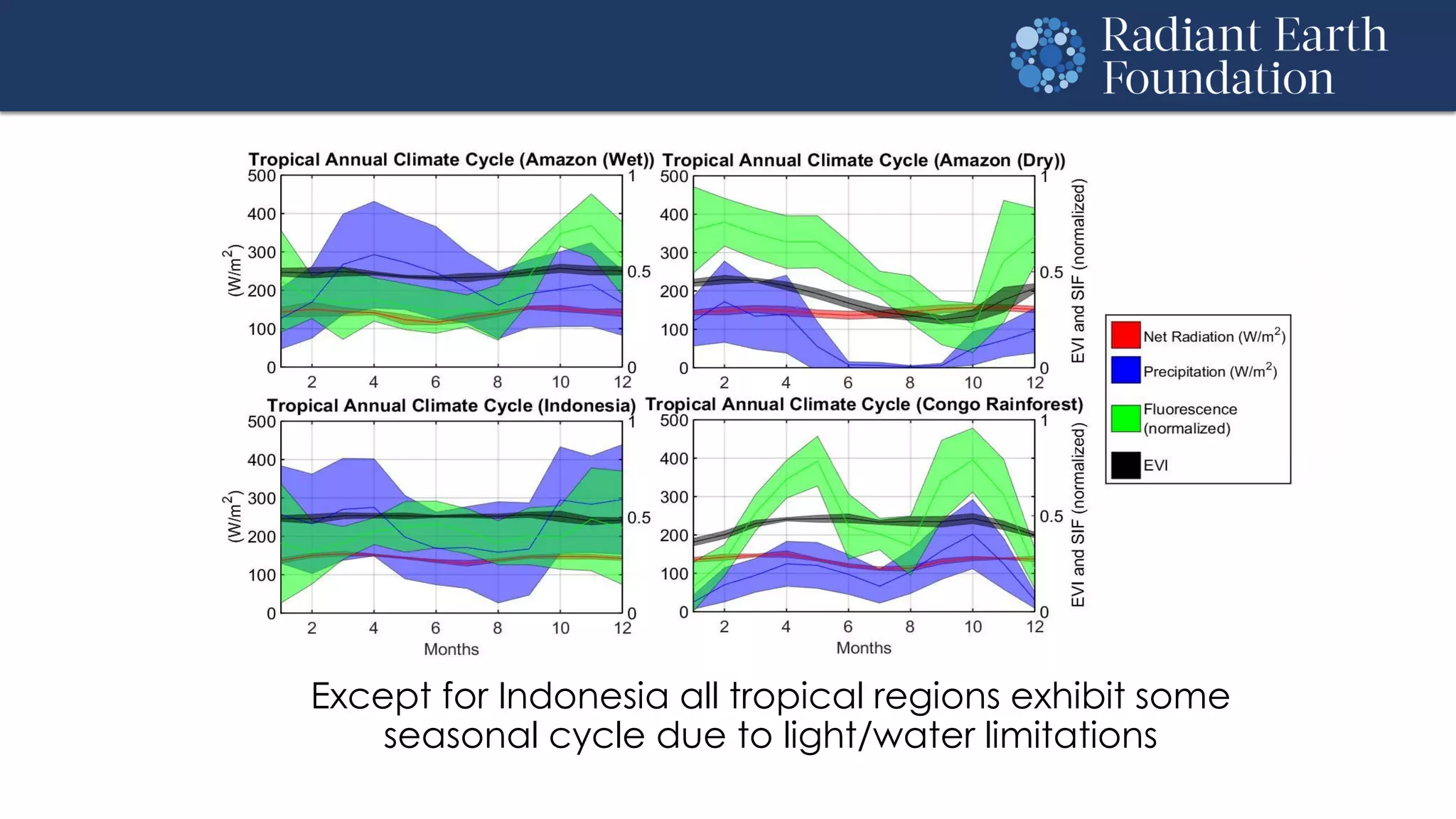
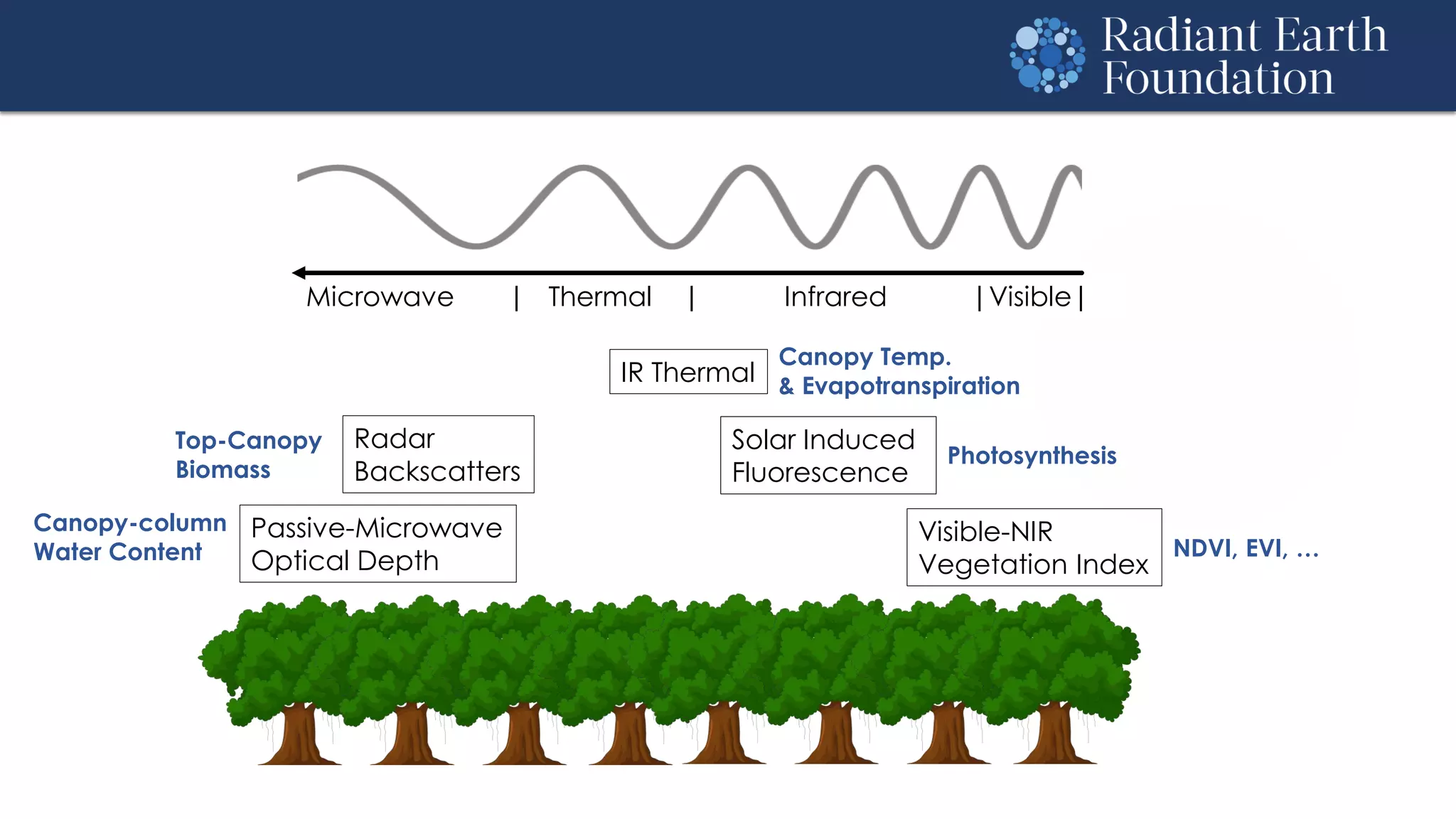
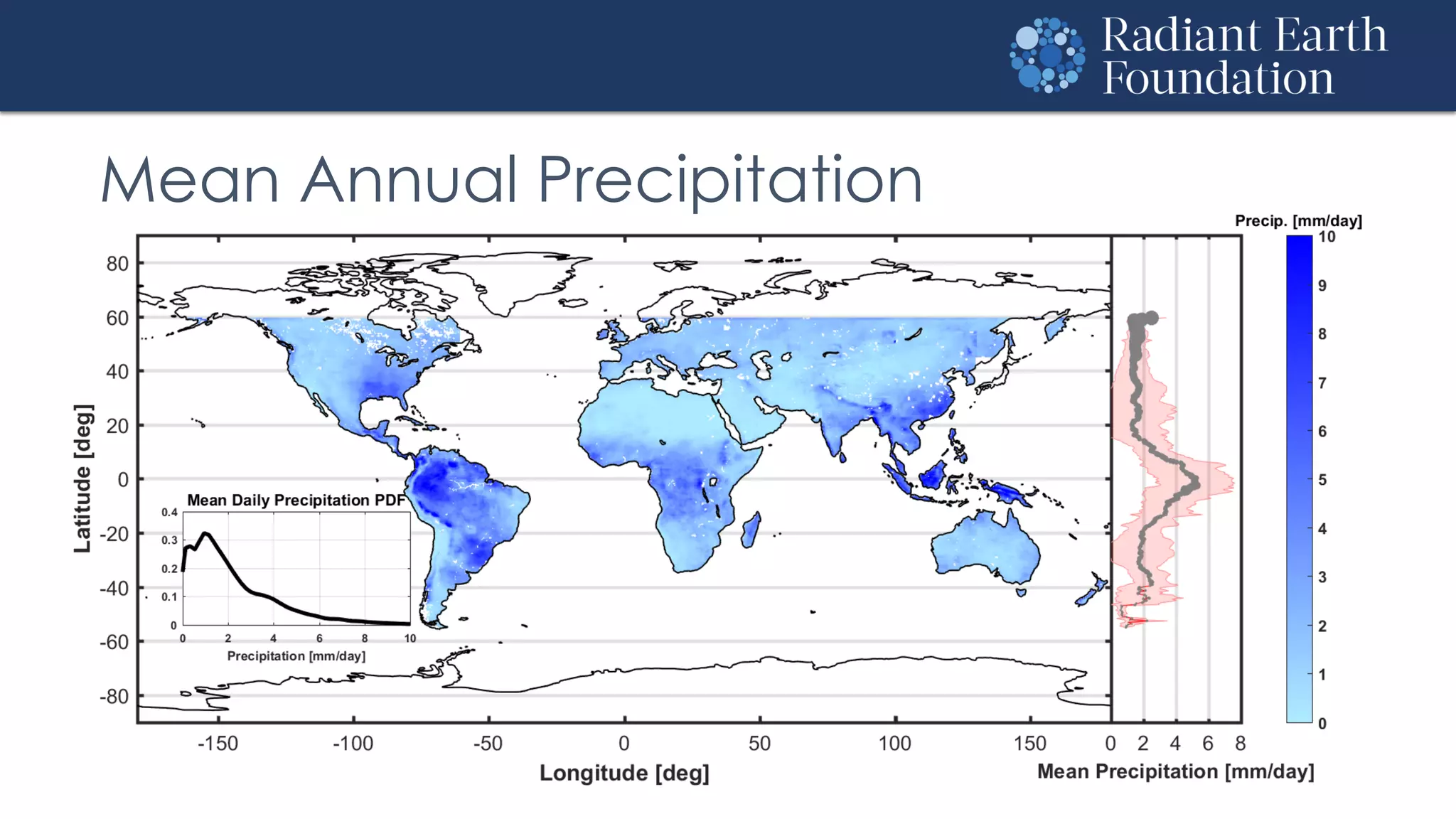
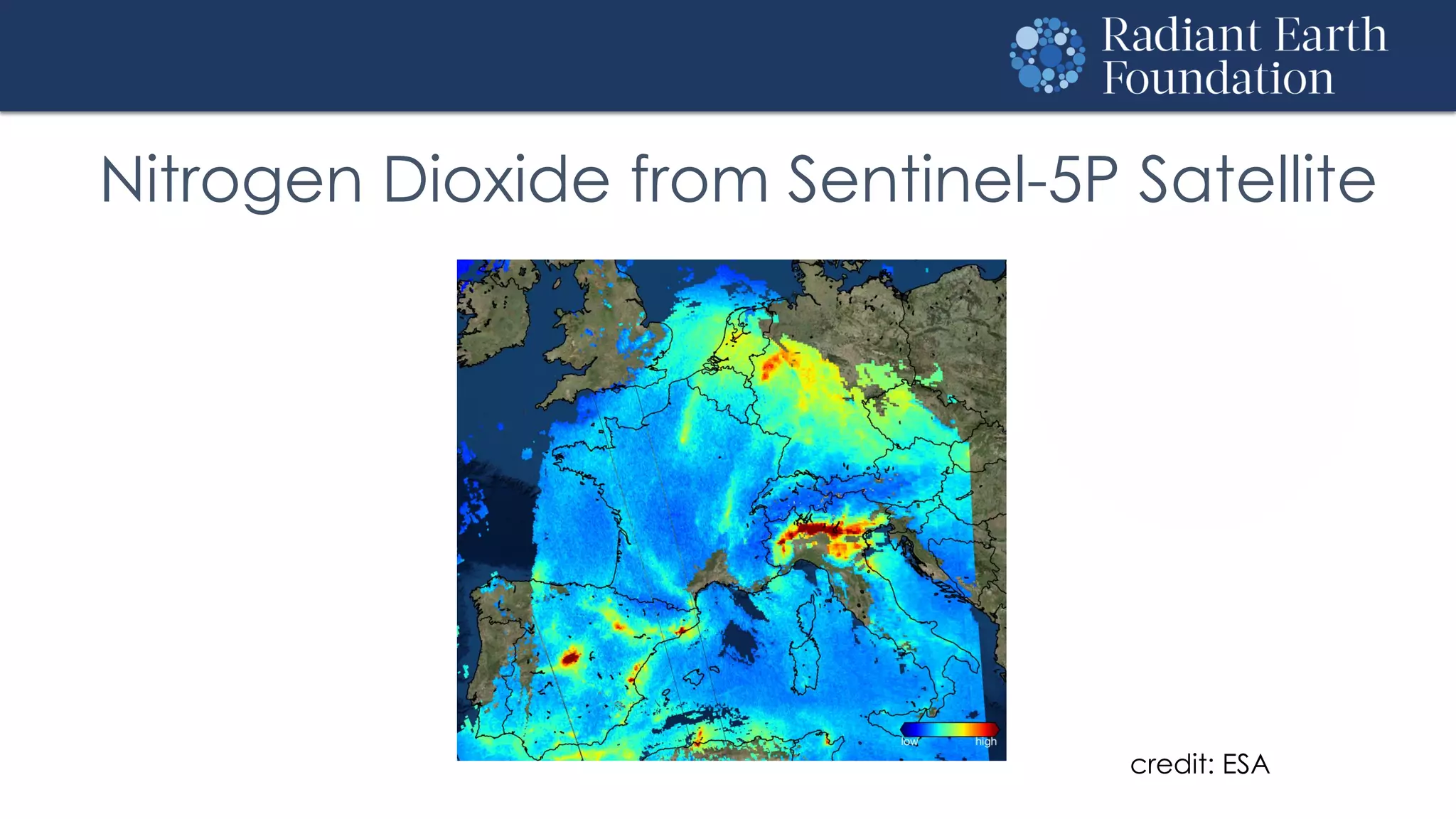
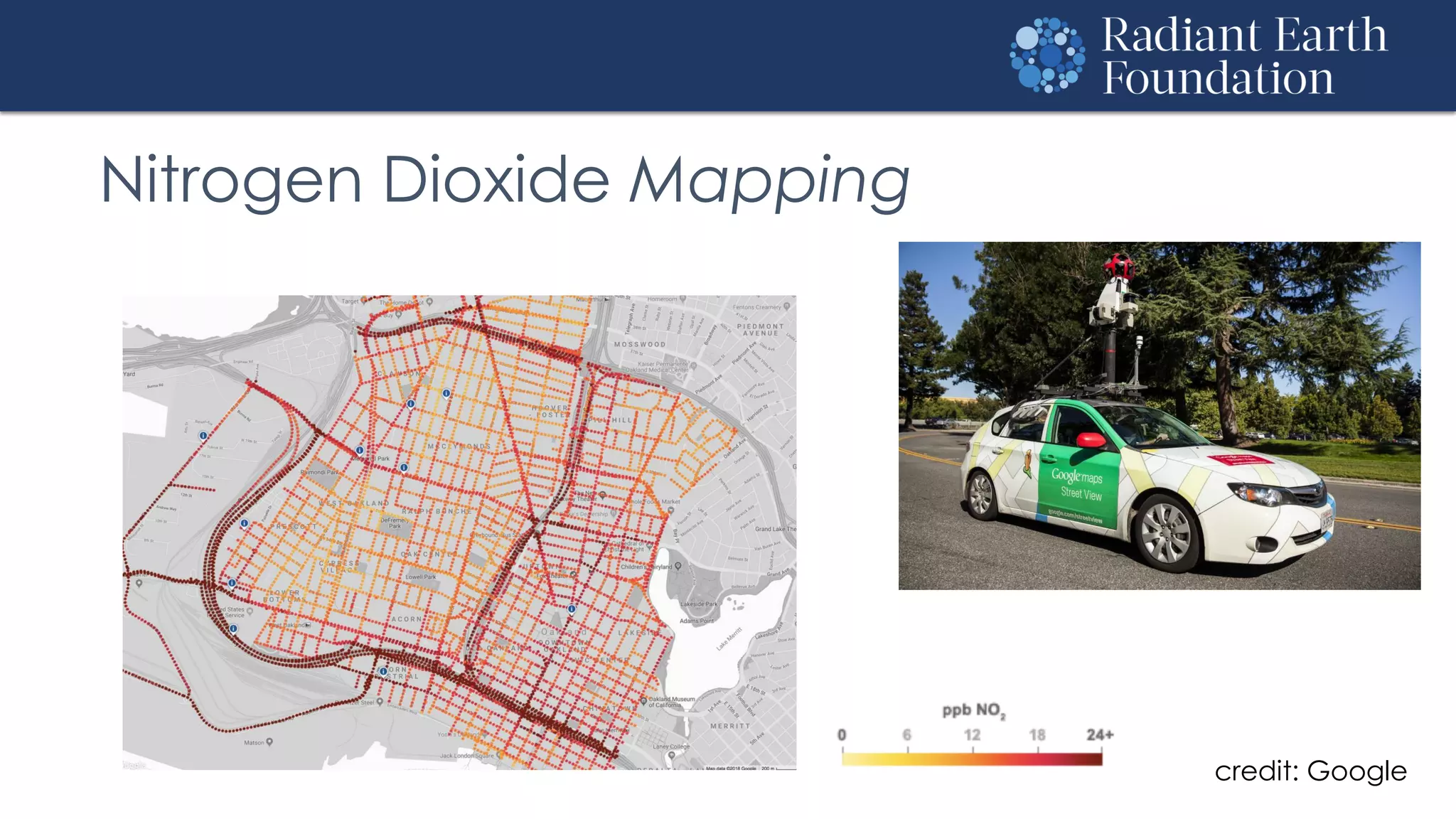
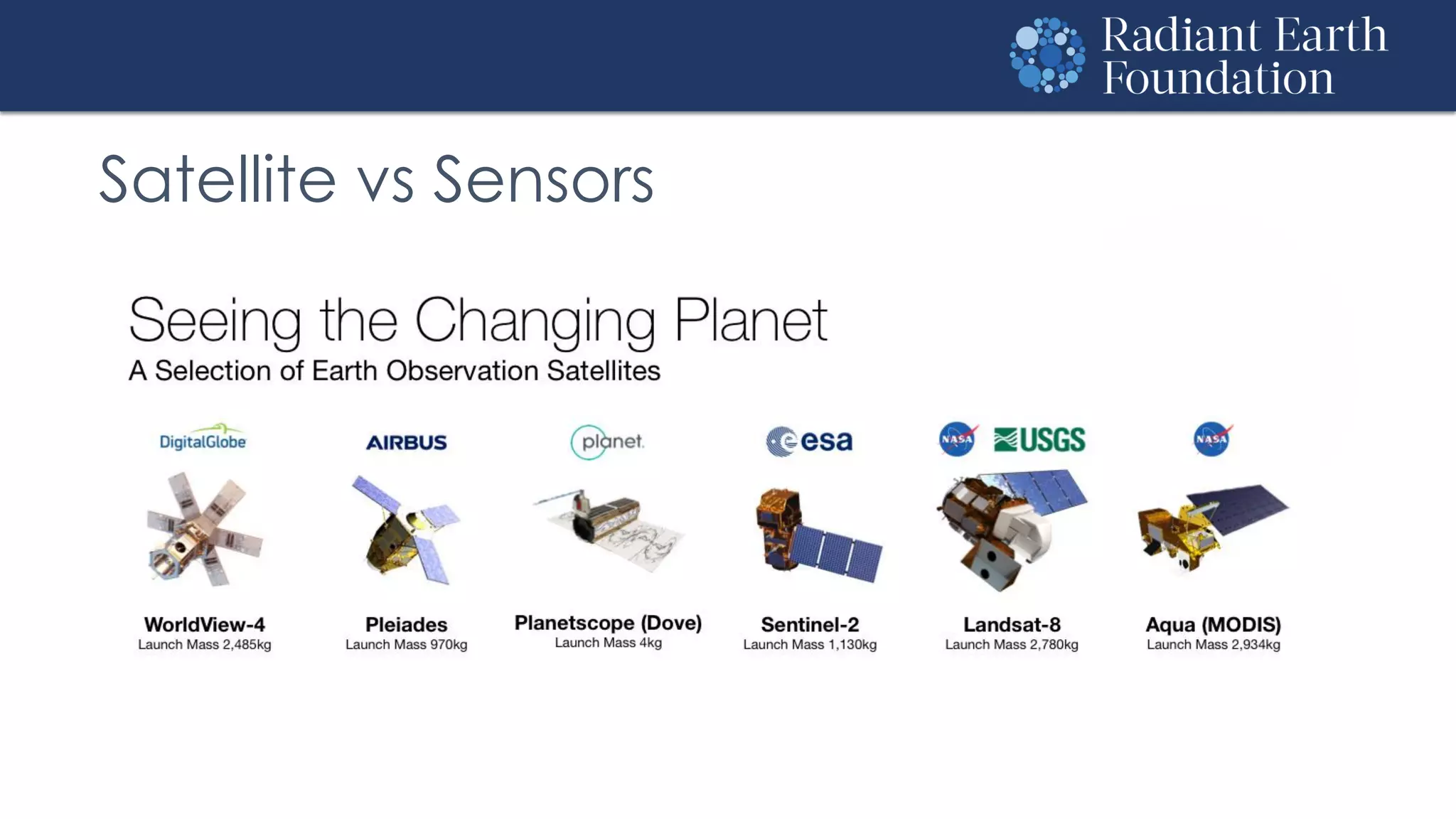
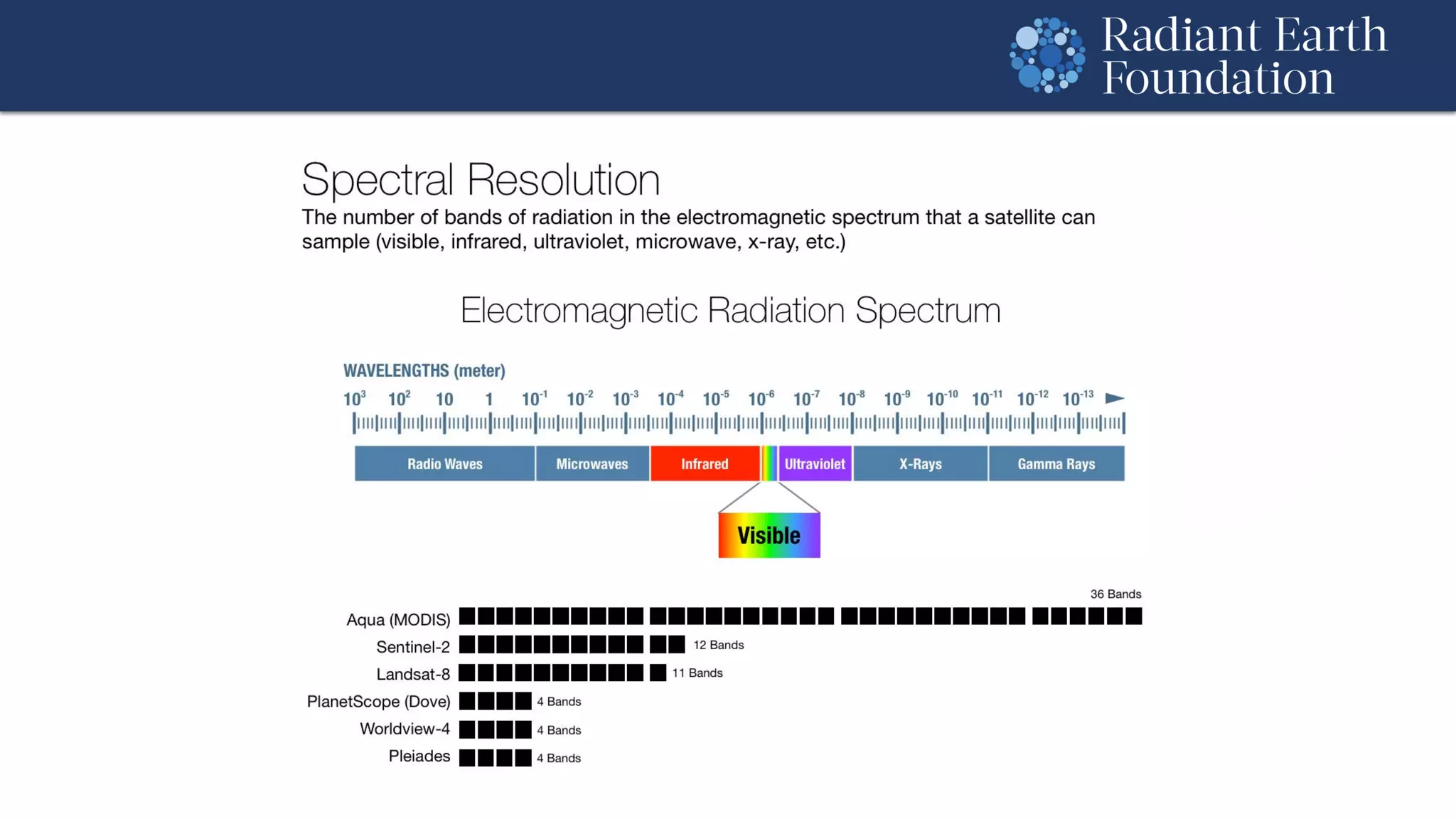
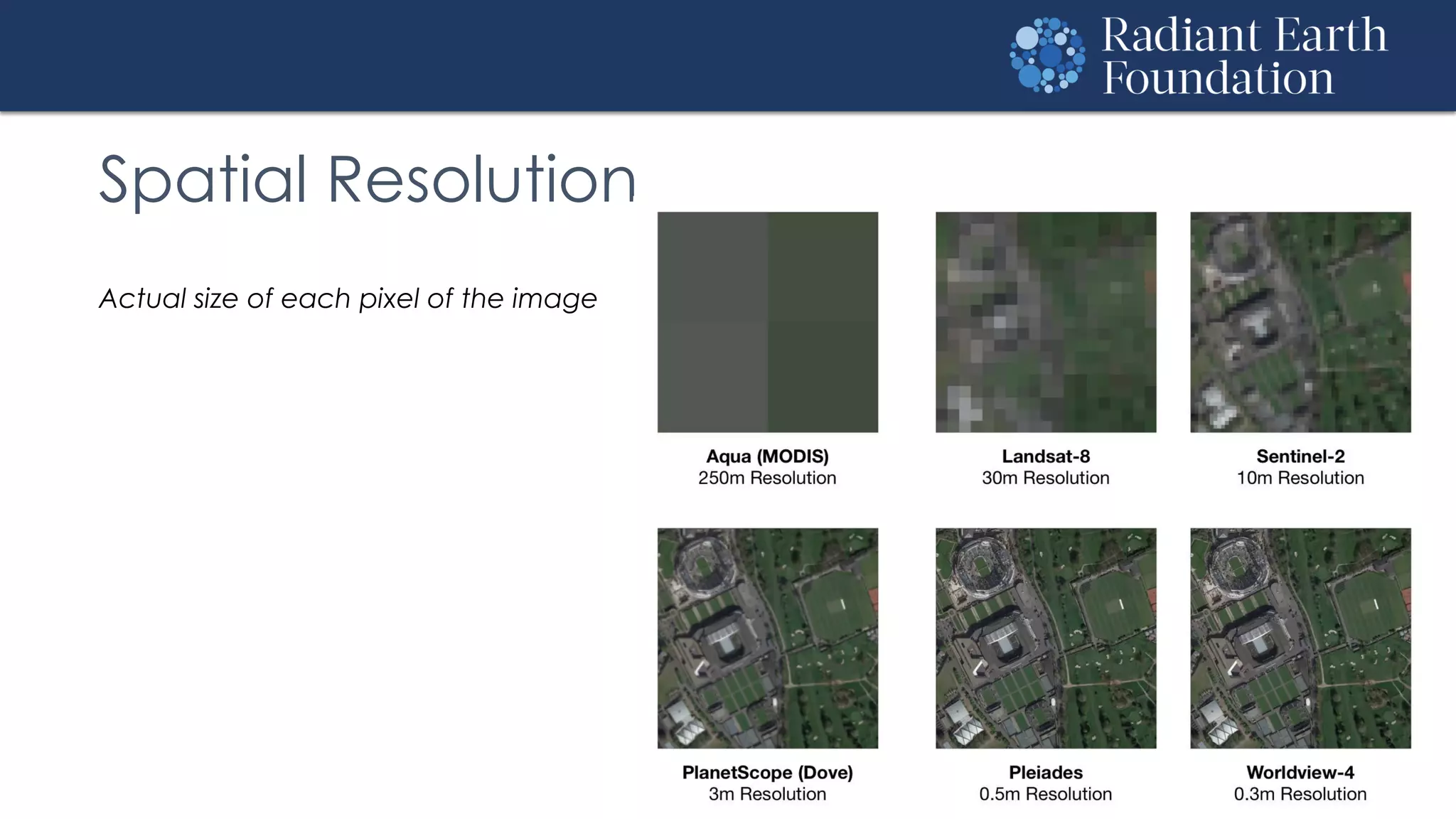
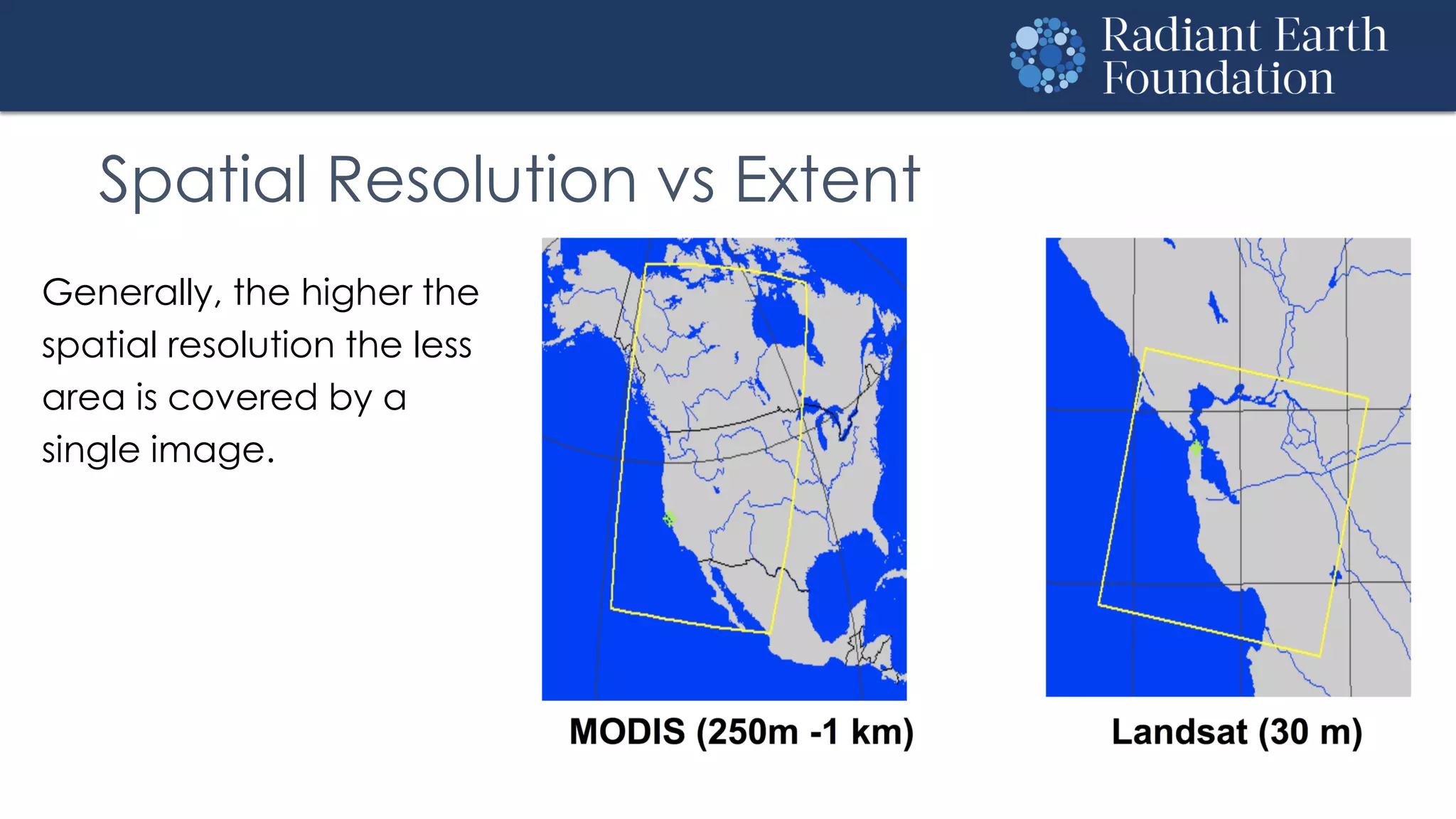
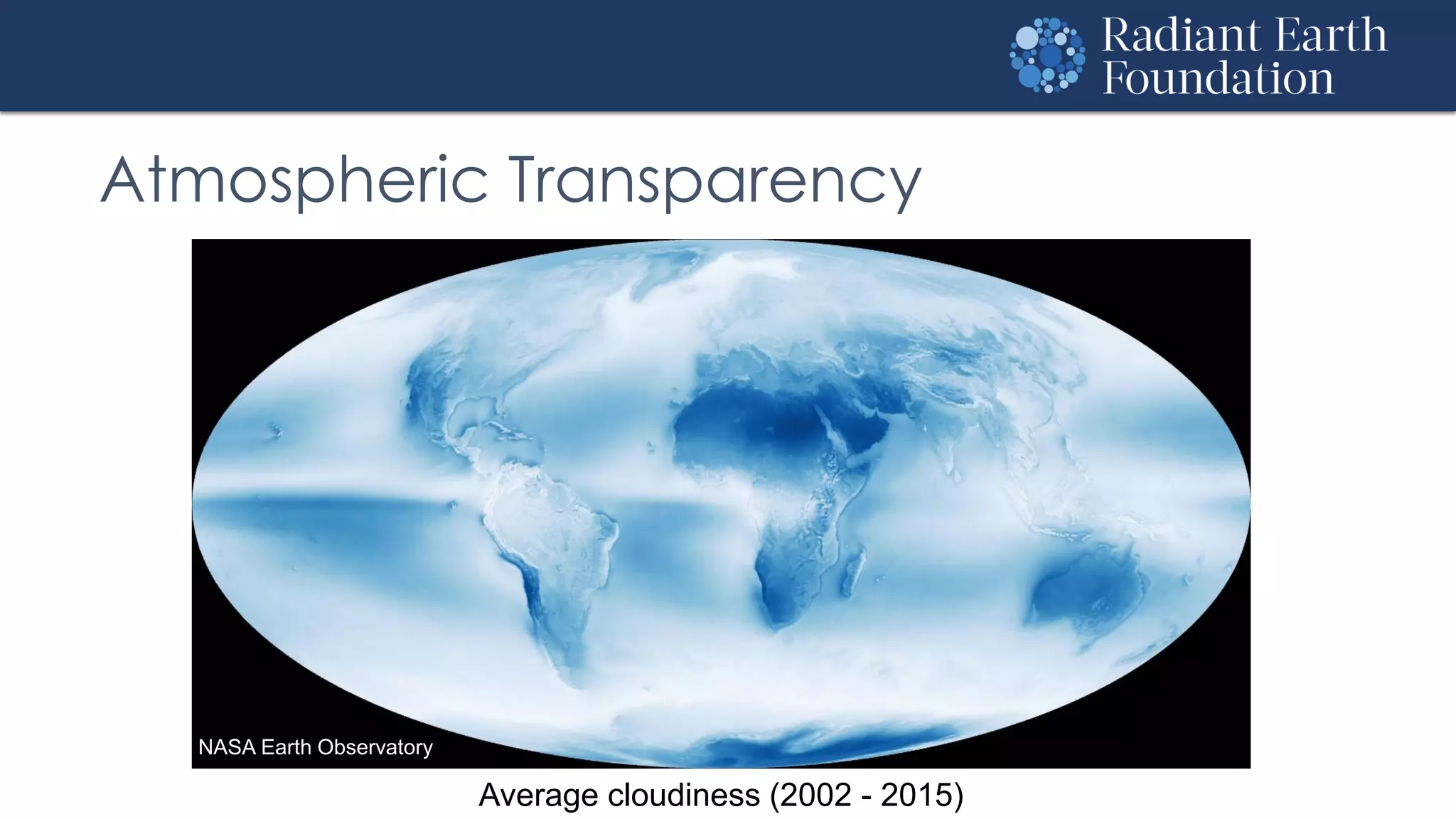
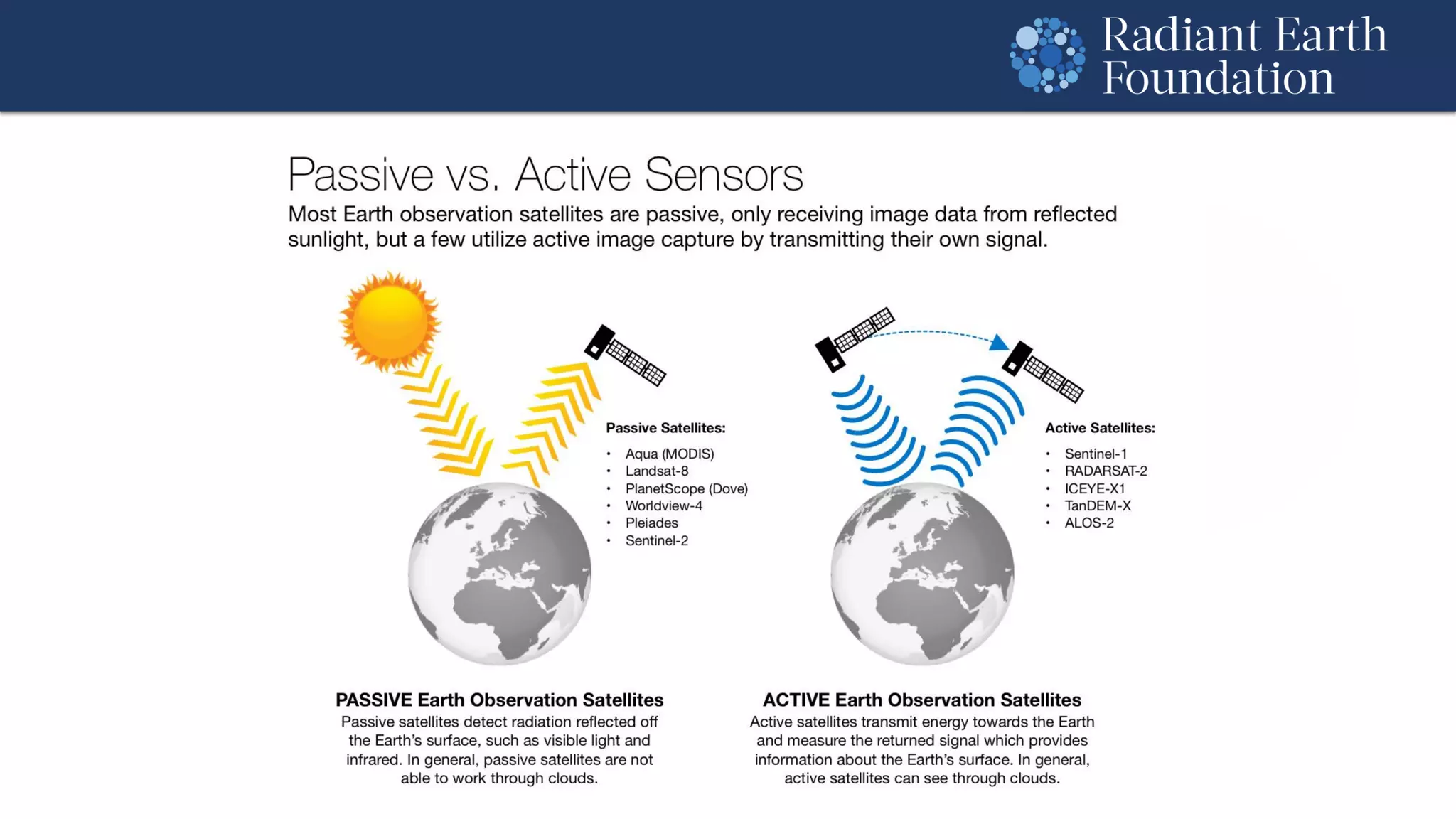
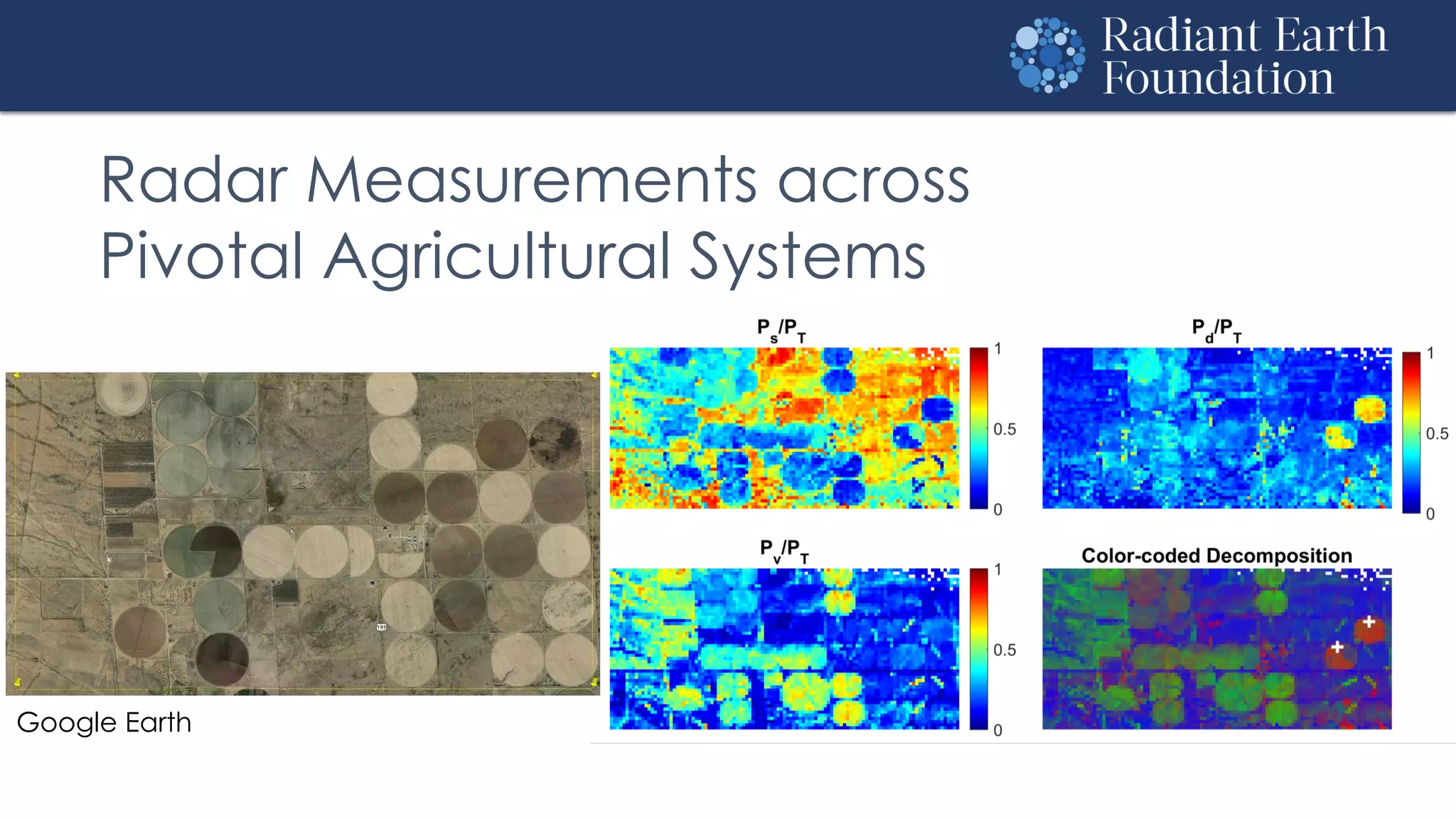
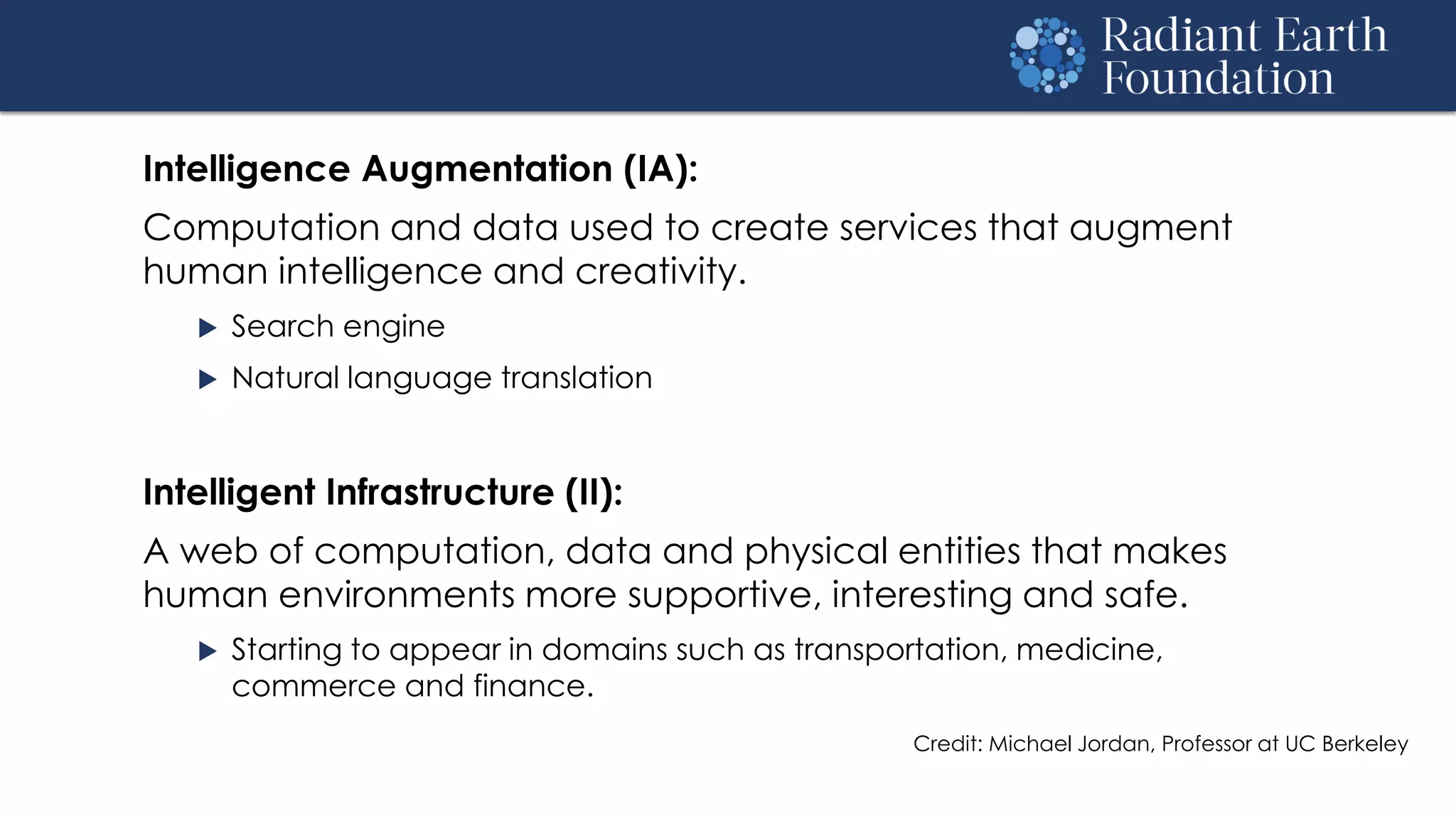
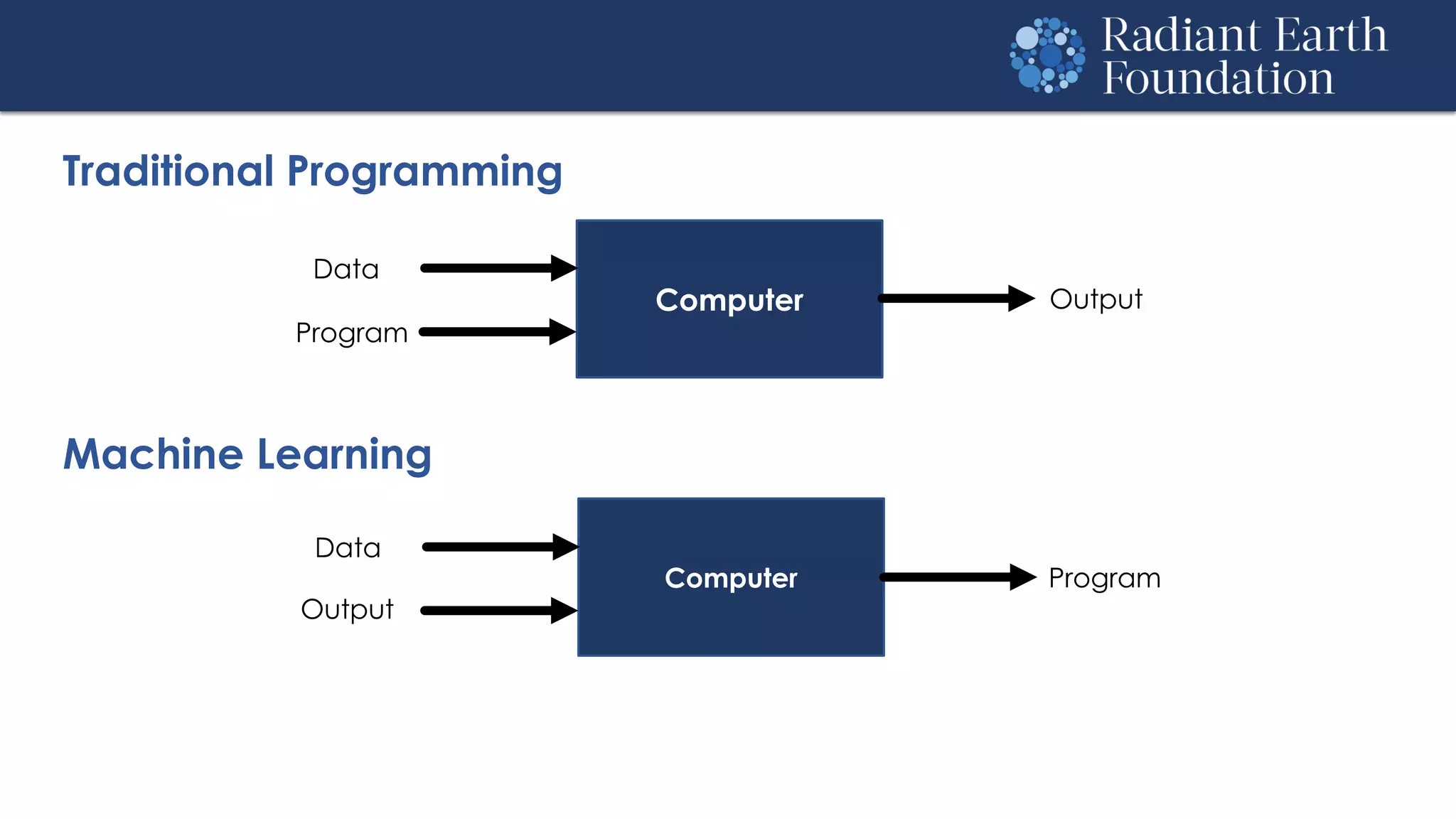
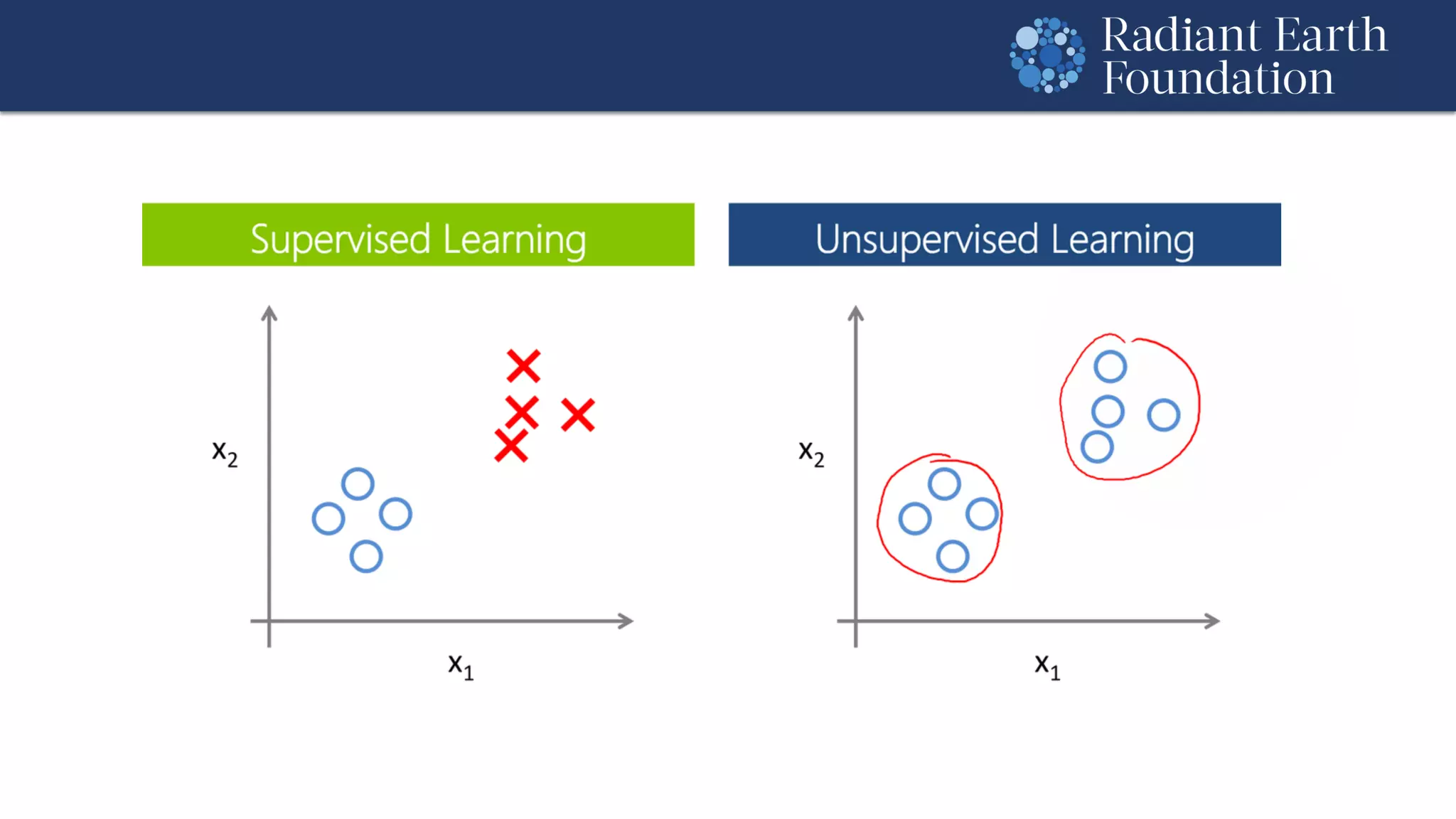
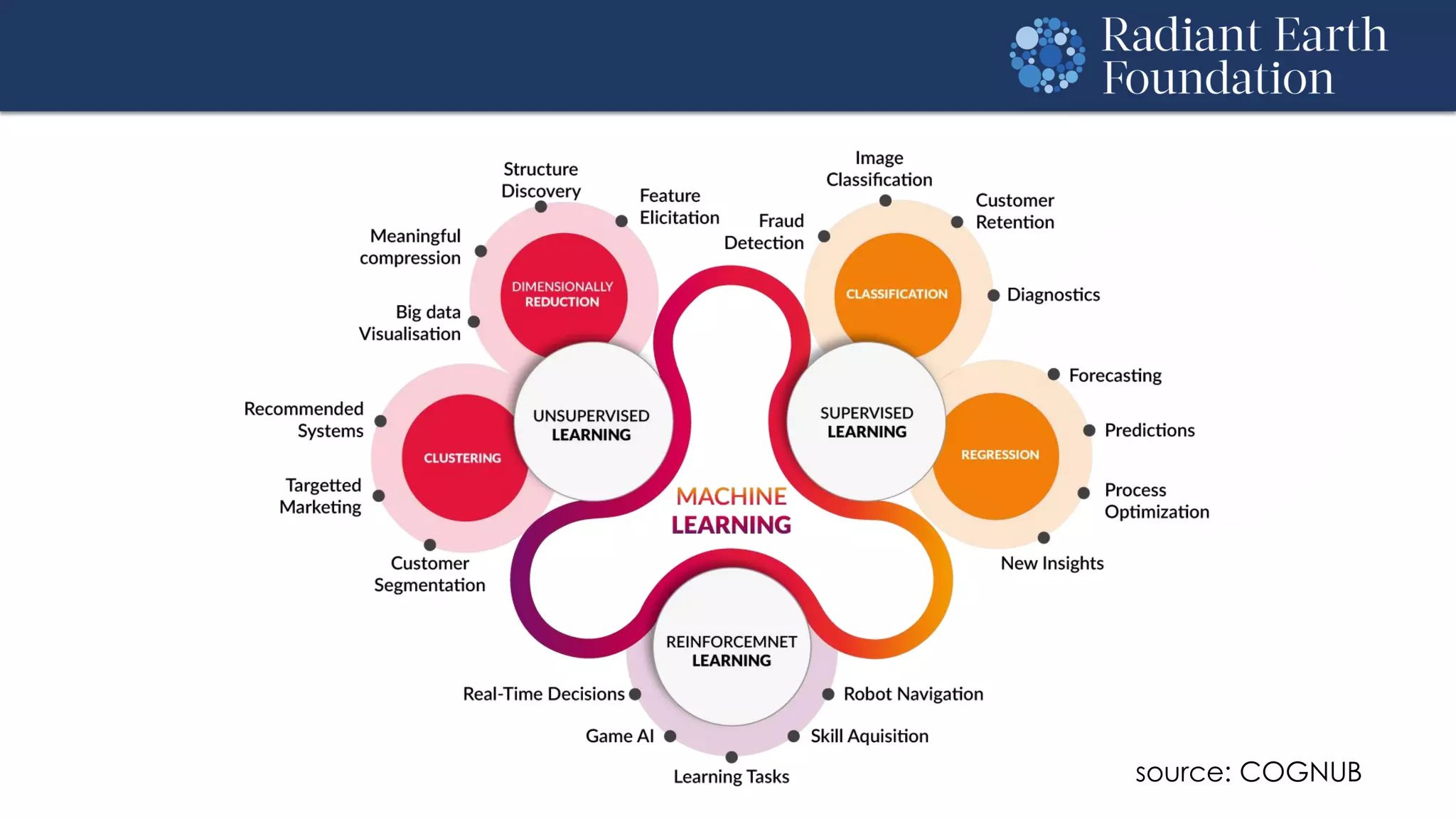
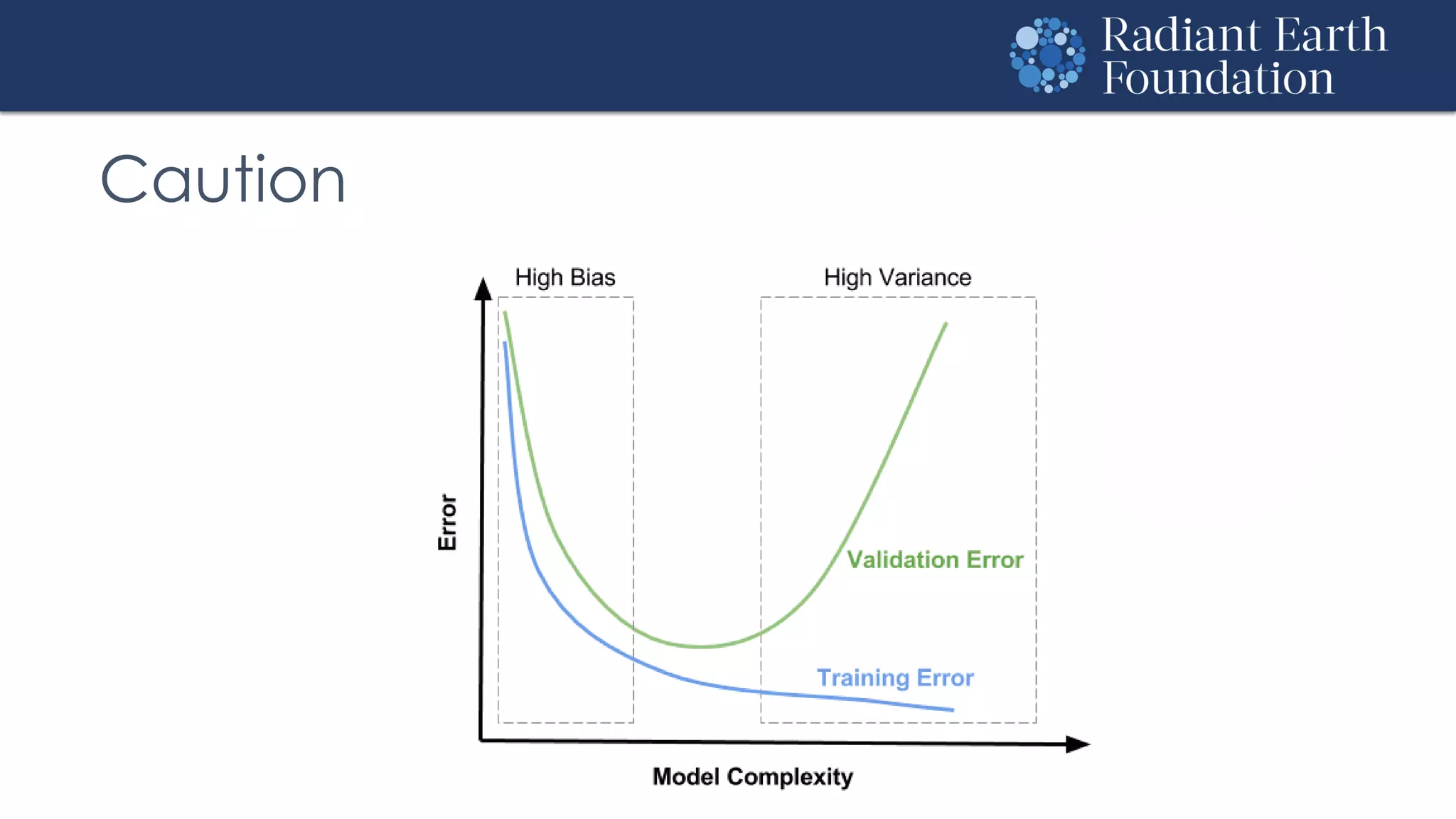
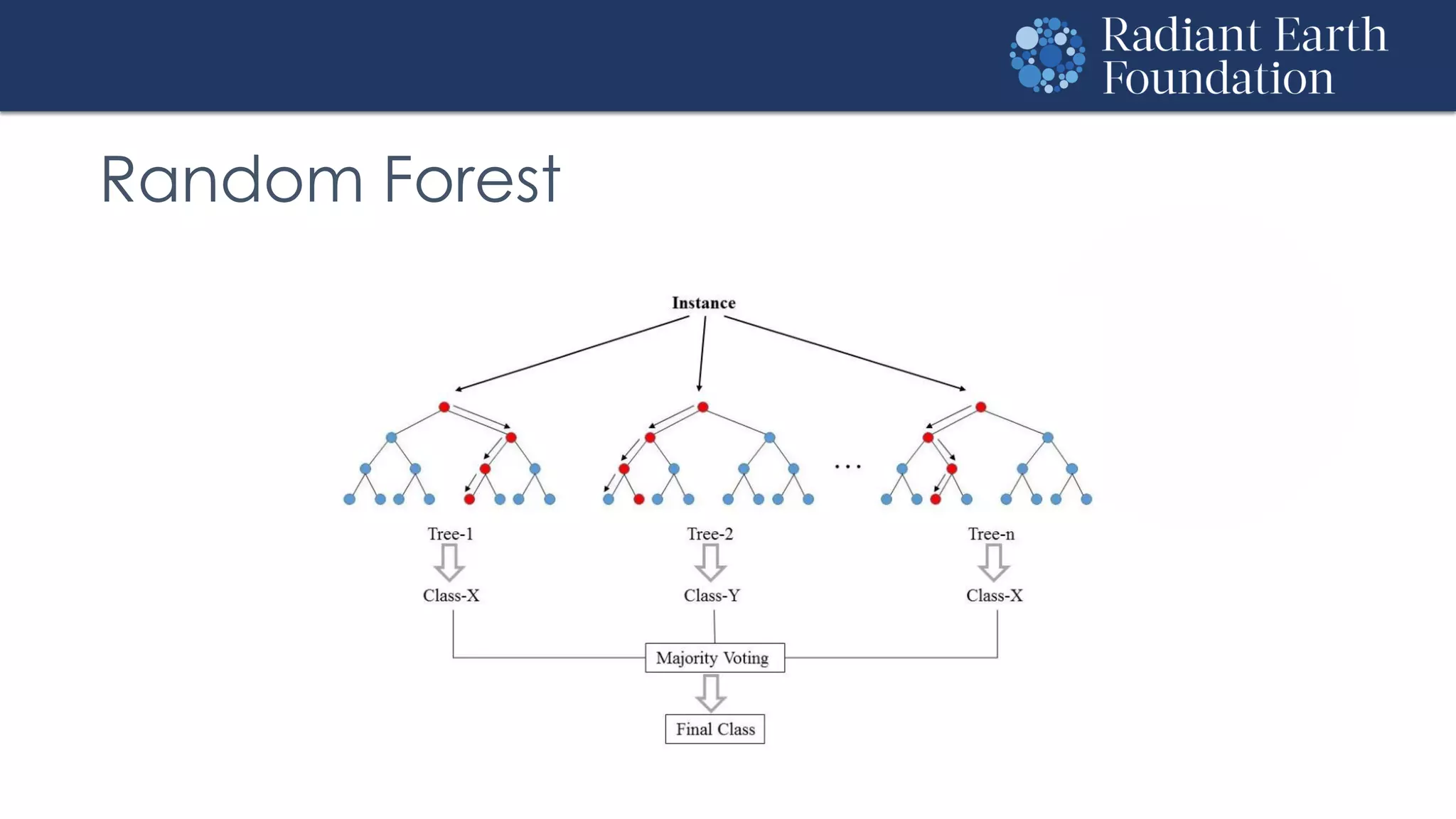
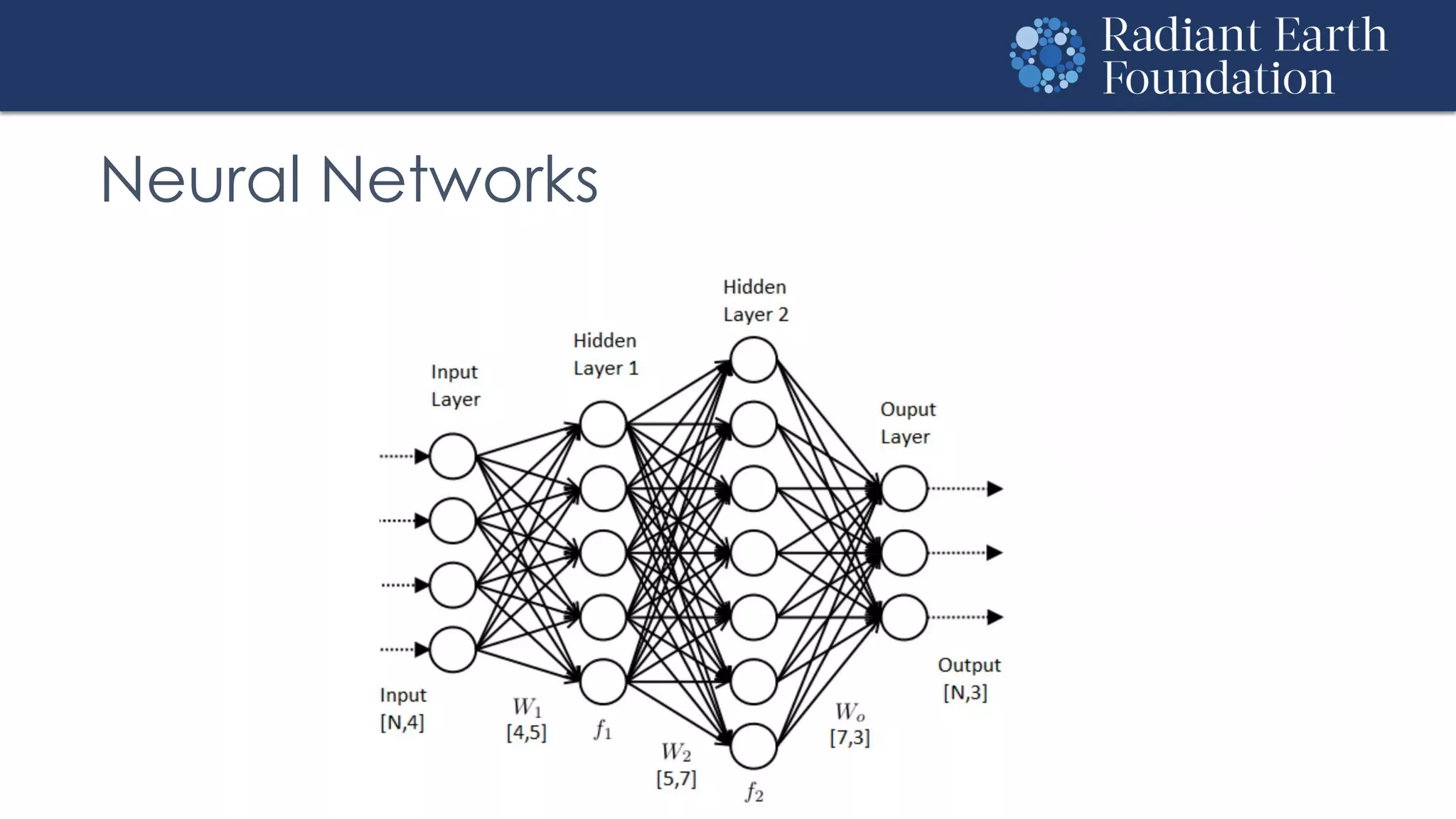
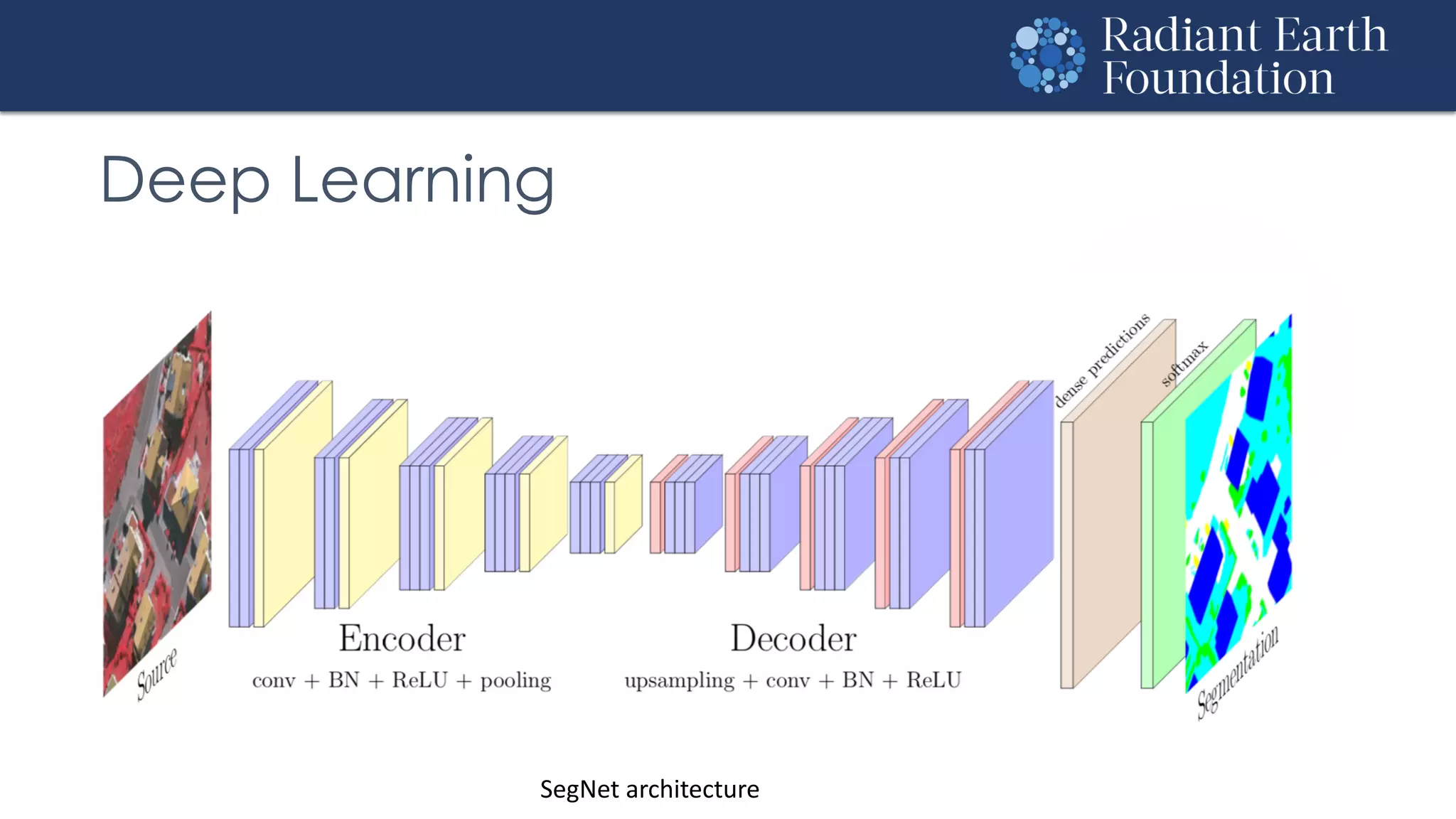
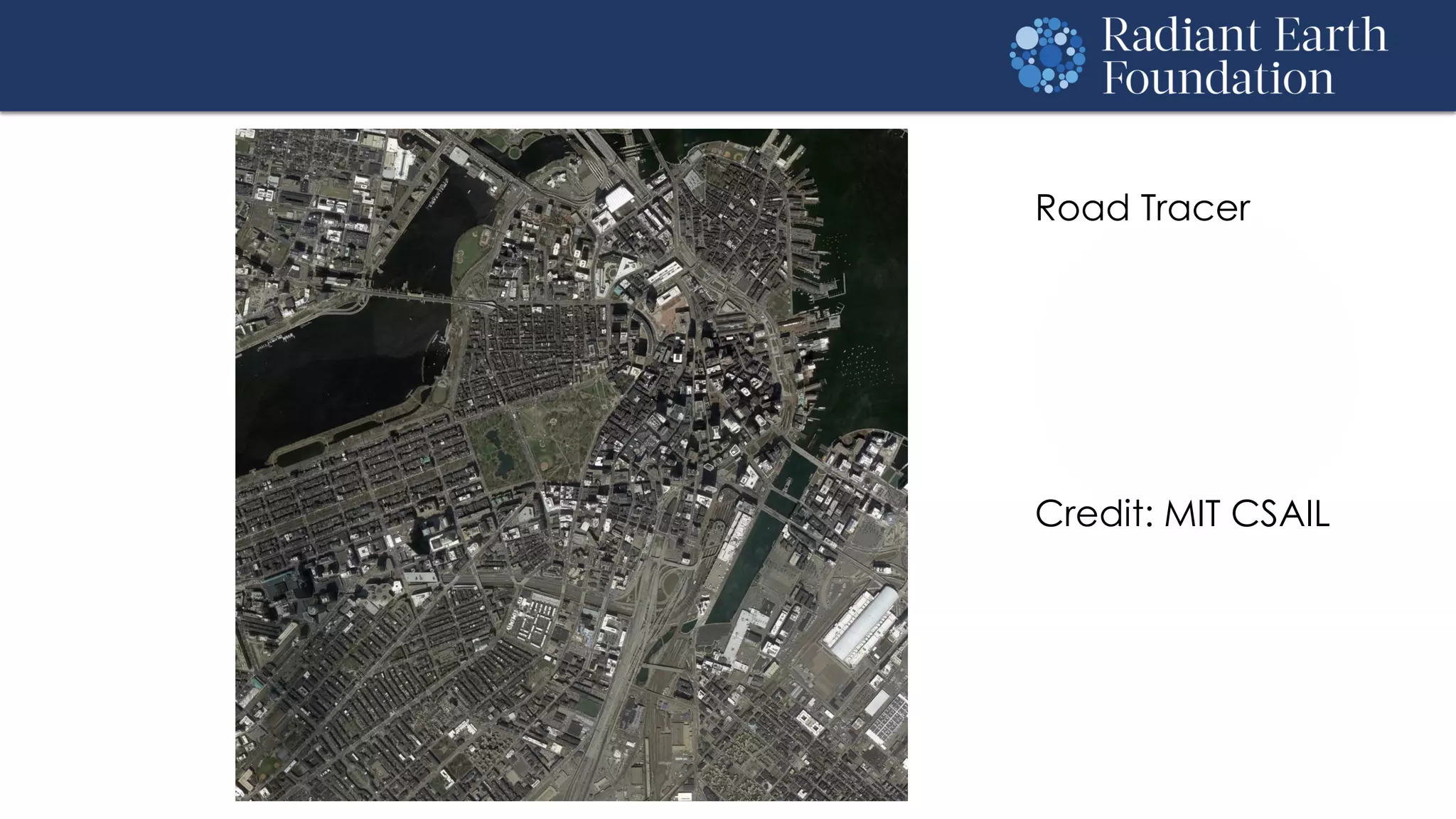
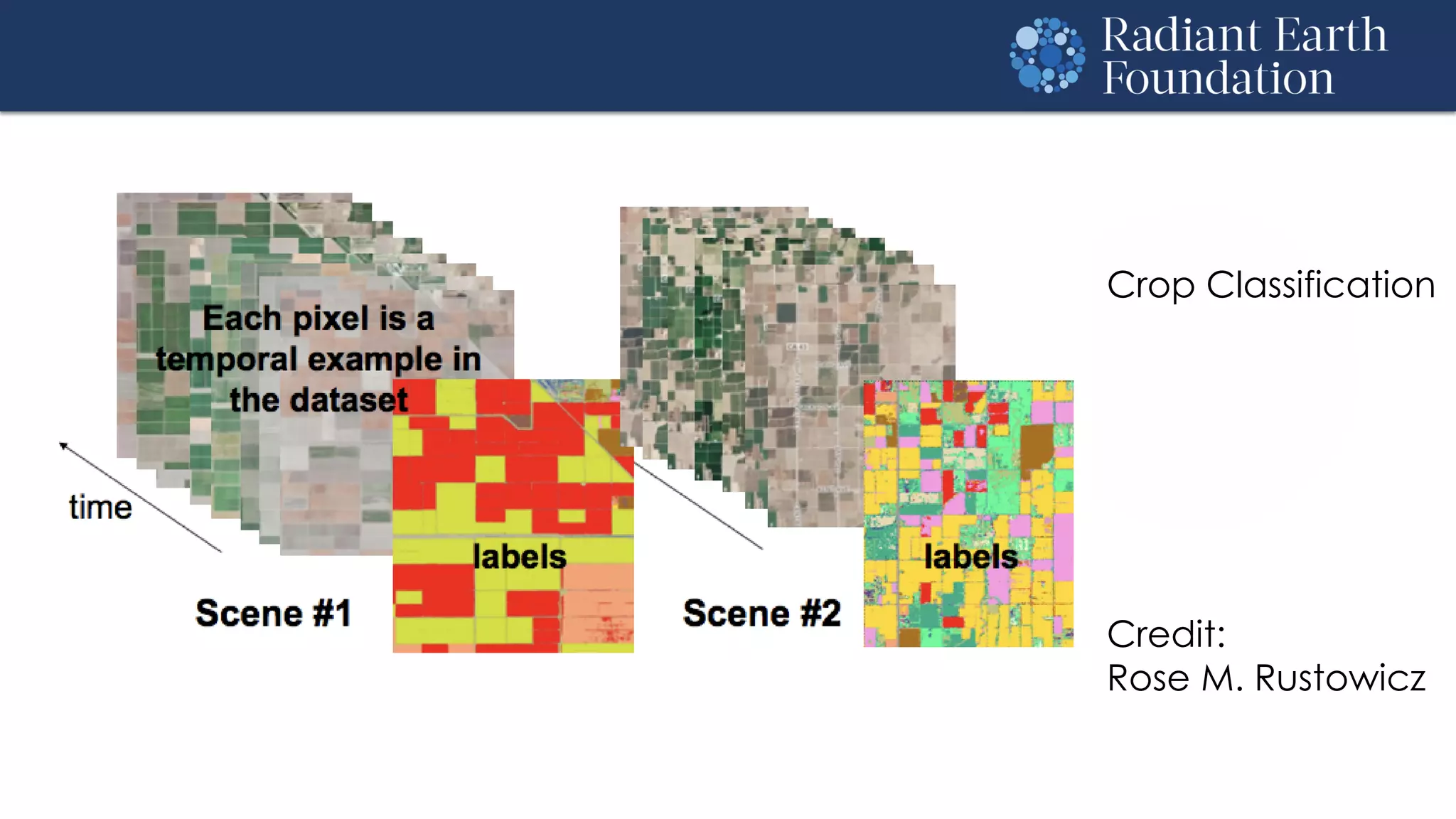
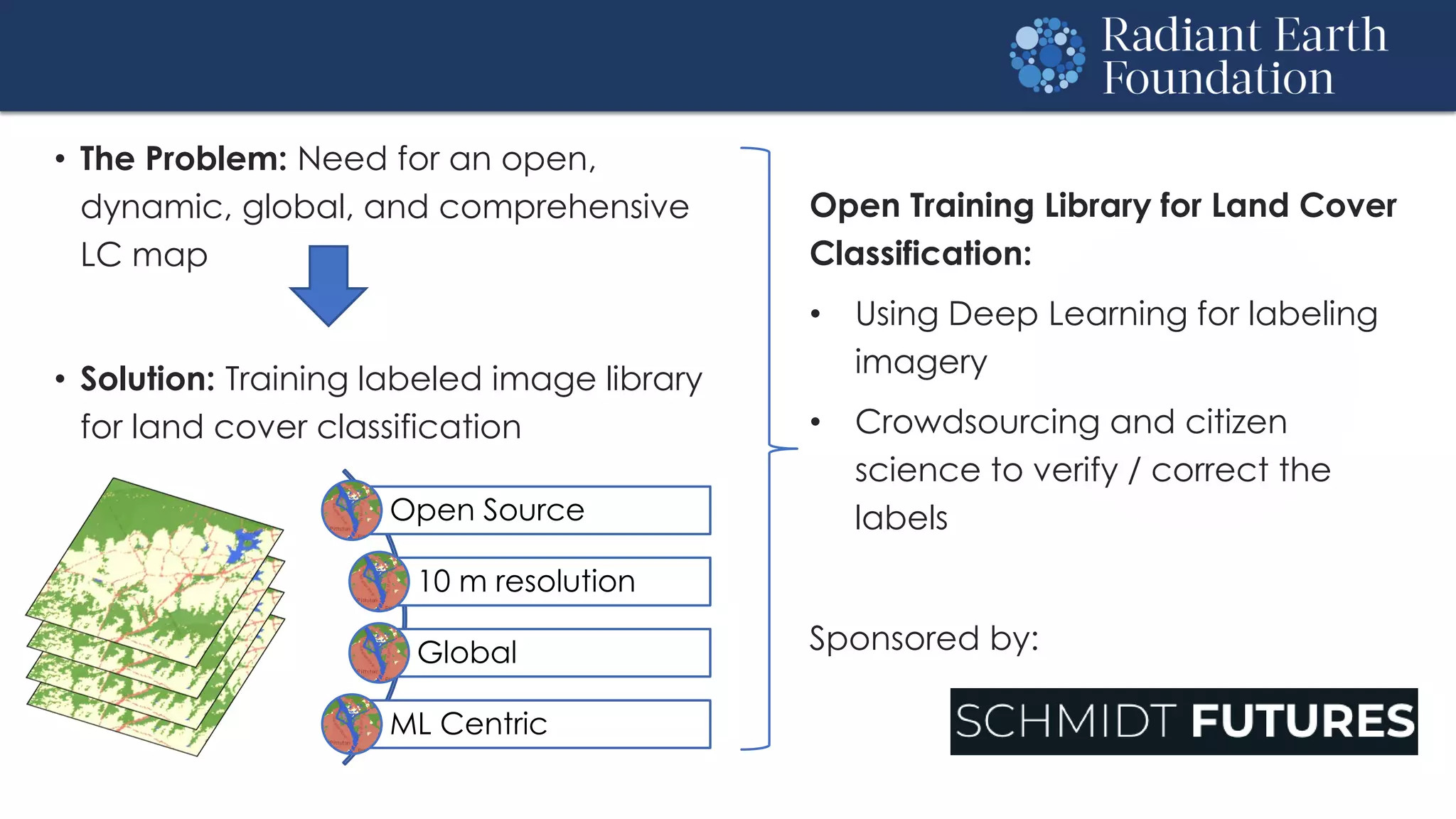
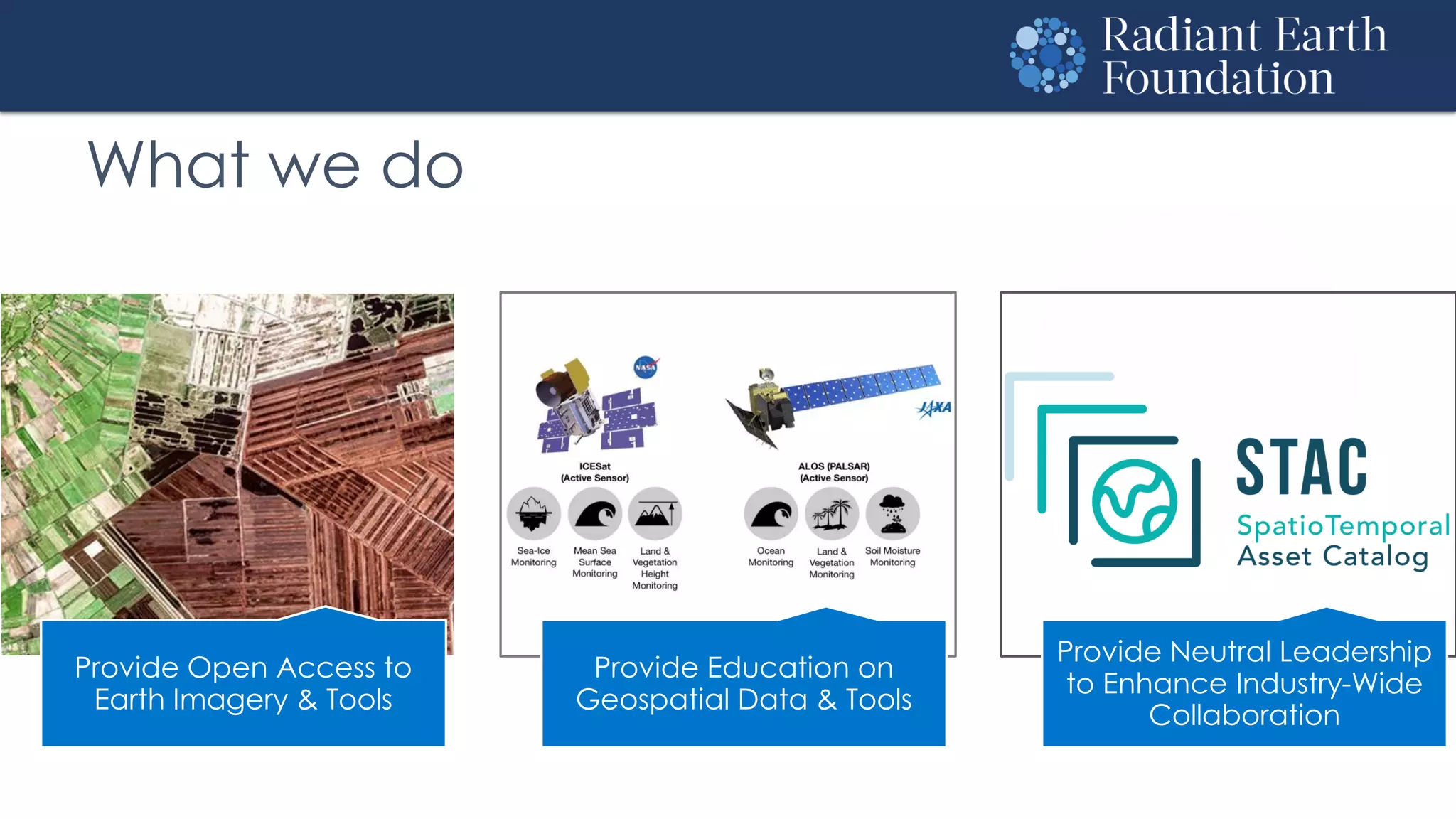
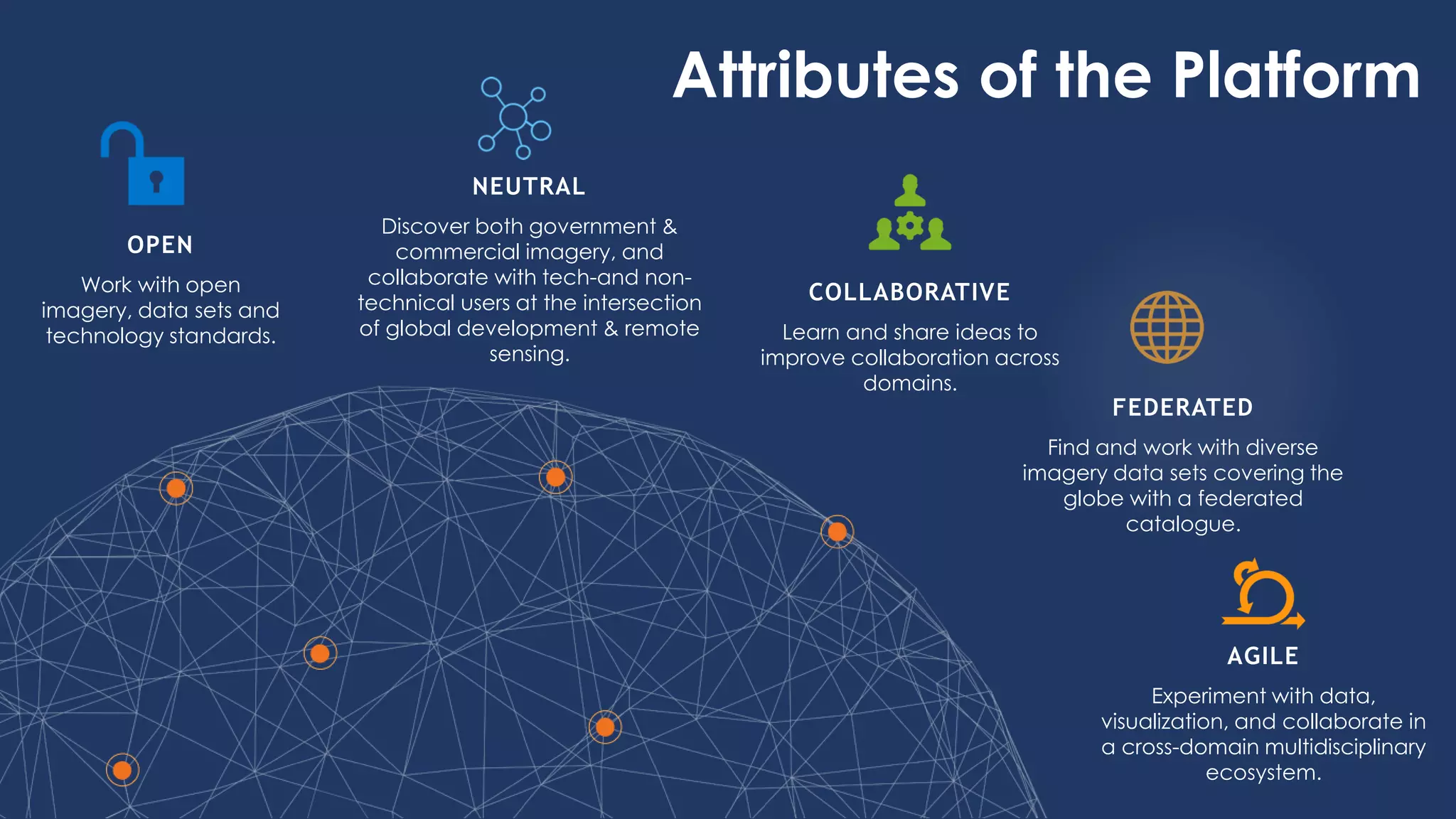
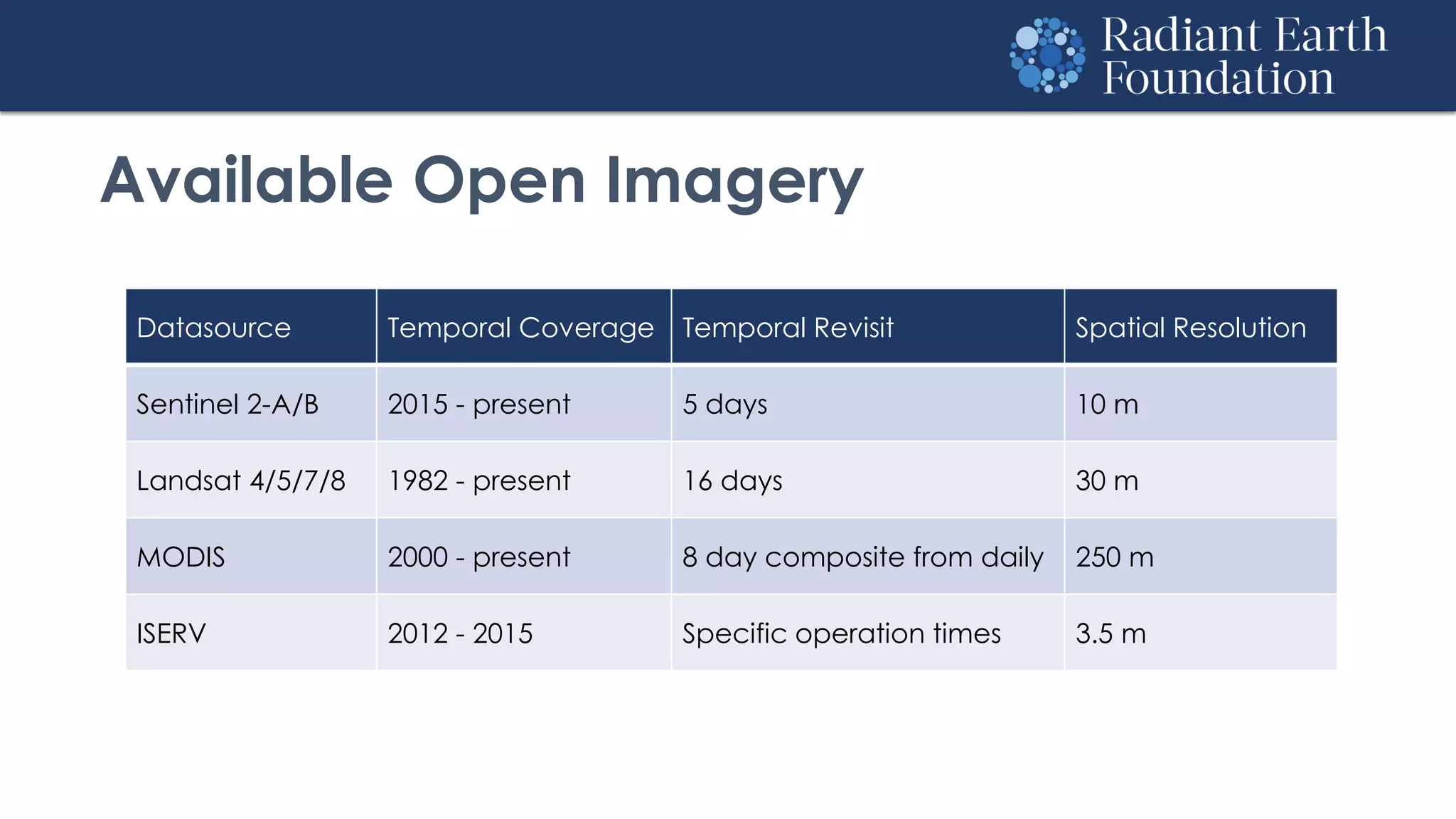
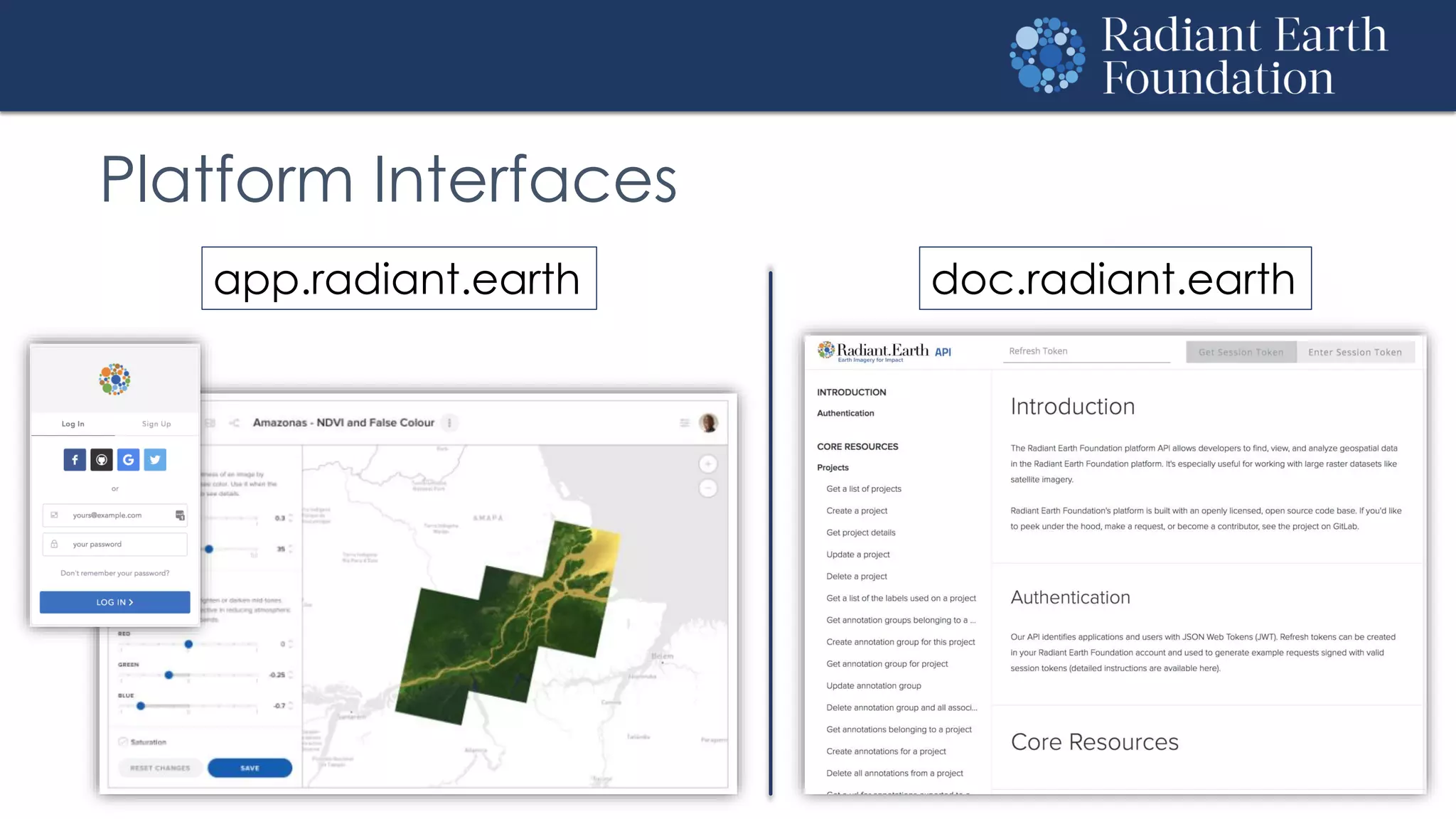
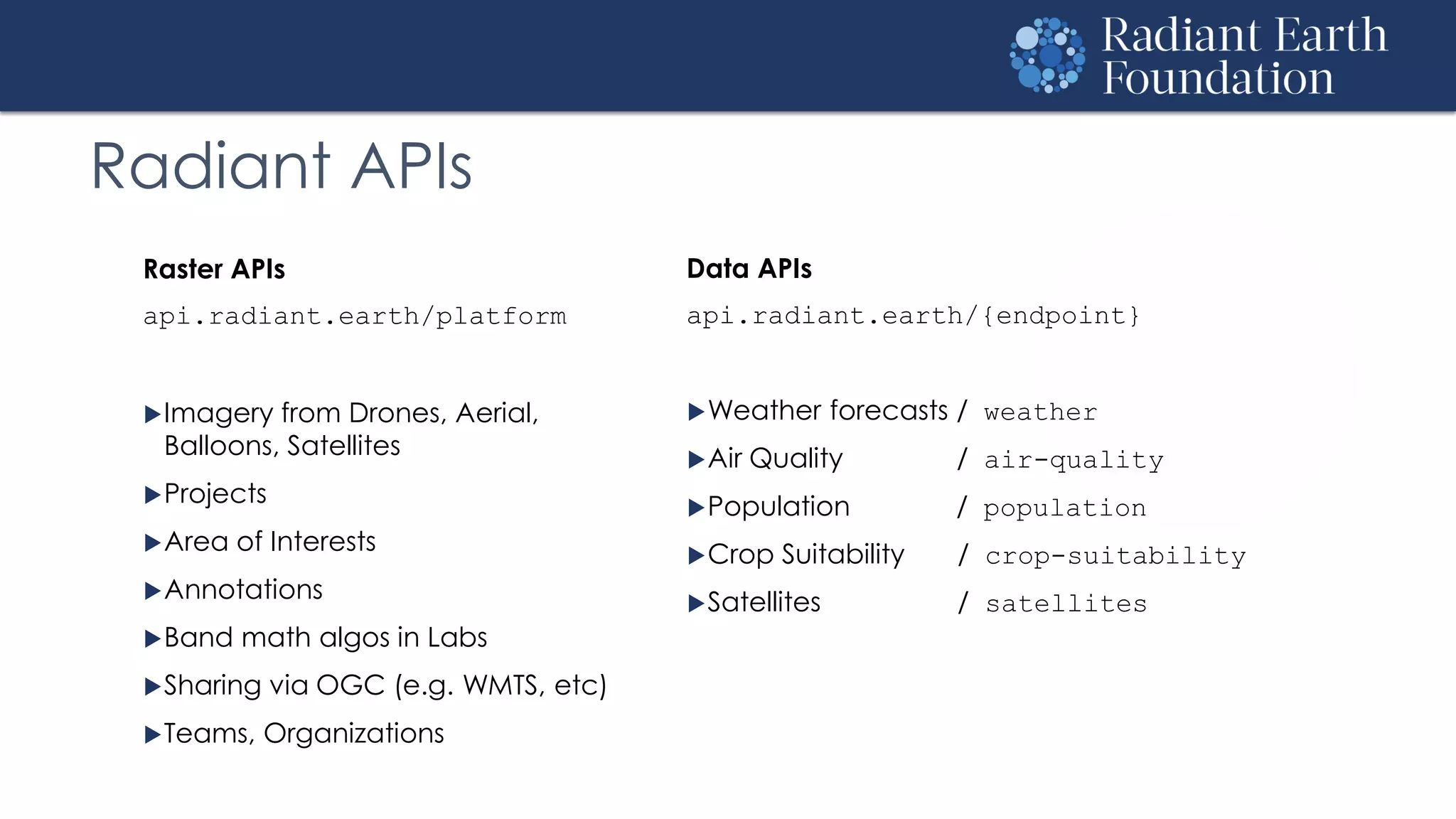
The document introduces remote sensing and machine learning, emphasizing how satellites capture data related to Earth's surface and atmosphere through electromagnetic radiation. It discusses the importance of vegetation indices and spectral signatures, along with the challenges in machine learning training data for land cover classification. The Radiant Earth Foundation aims to provide open access to geospatial data and enhance global collaboration in tackling critical challenges through its platform.