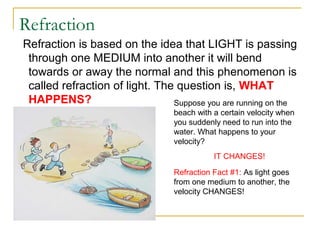
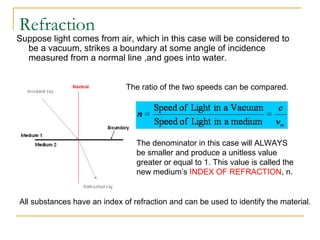
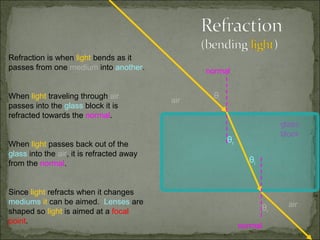
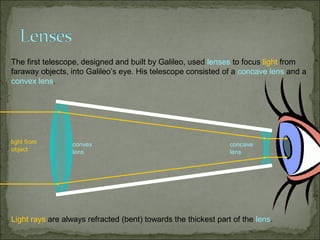
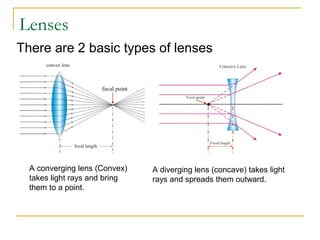
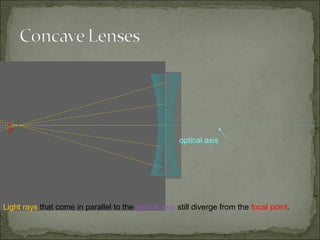
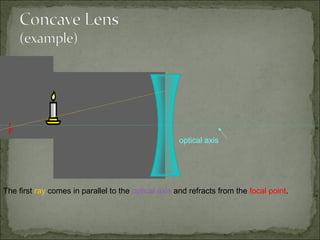
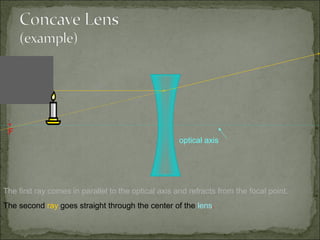
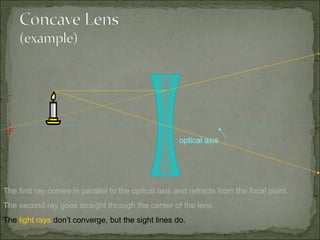
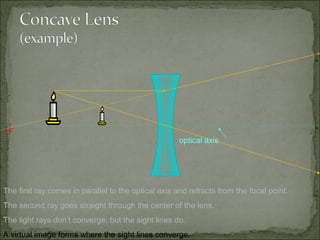
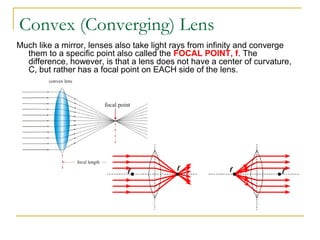
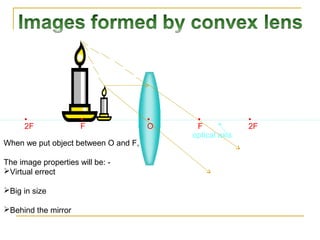
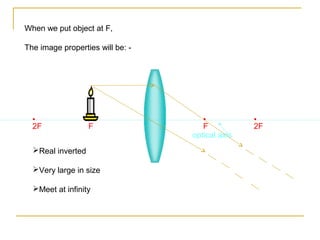
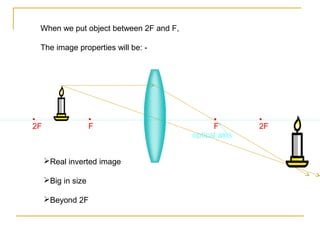
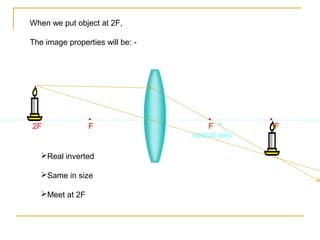
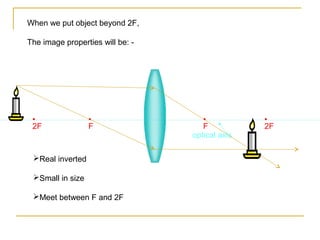
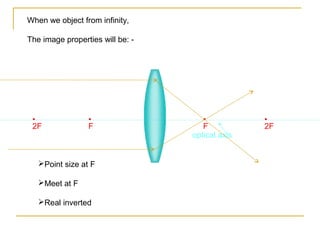
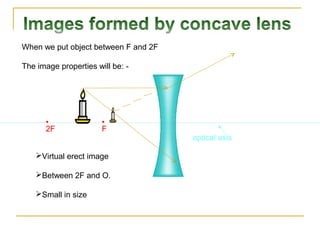
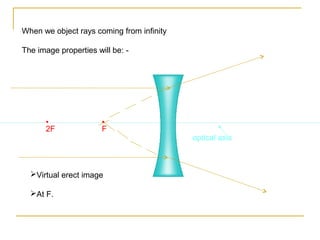
This document discusses refraction and lenses. It begins by explaining that refraction occurs when light passes from one medium to another, causing its velocity and path to change. It then discusses how lenses work, noting that there are two basic types: convex and concave lenses. Convex lenses converge light rays to a focal point, while concave lenses diverge light rays. The document provides examples of how light rays behave when passing through lenses and the characteristics of images formed, such as location, size, and orientation. It concludes by introducing the lens formula, which relates the focal length, object distance, and image distance.