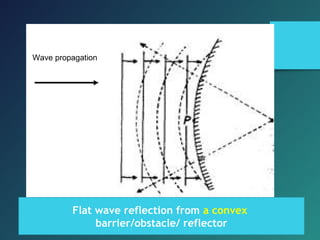
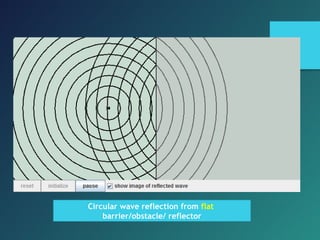
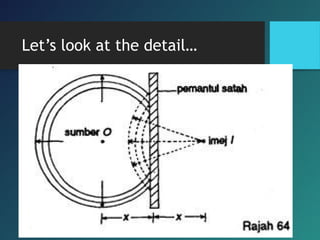
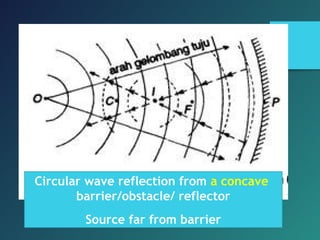
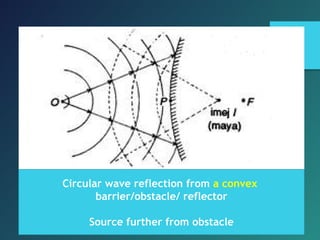
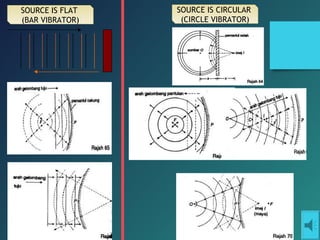
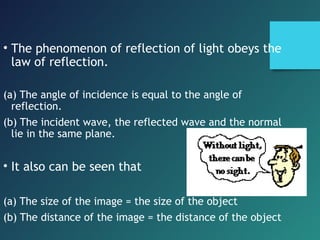
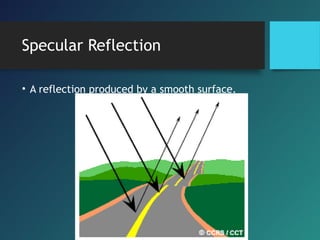
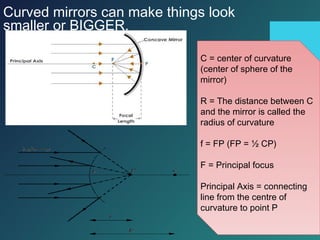
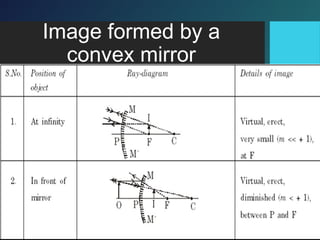
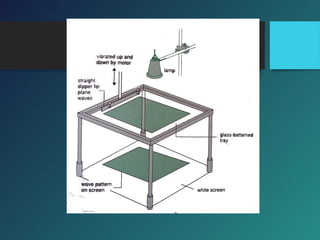
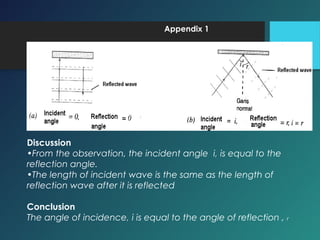
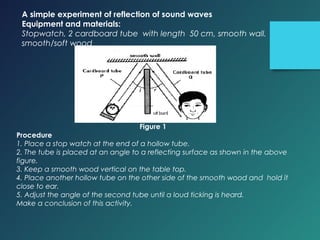
Here are the key points of comparison between incident and reflected waves:
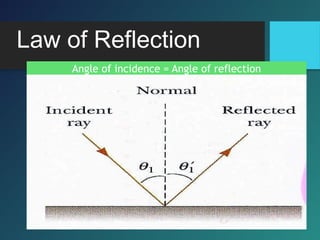
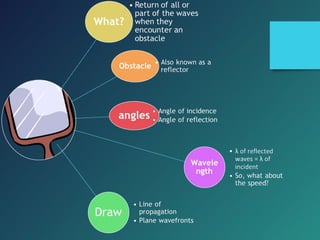
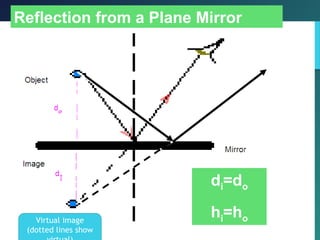
i. Angle of incidence (i) = Angle of reflection (r)
ii. Wavelength (λ), frequency (f) and speed (v) remain the same.
iii. Direction of propagation - Reflected waves propagate in the opposite direction to the incident waves.
iv. Amplitude may decrease slightly due to absorption at the boundary. Otherwise, the wave remains the same.
v. Phase may be reversed depending on the type of boundary - either in phase or 180° out of phase.
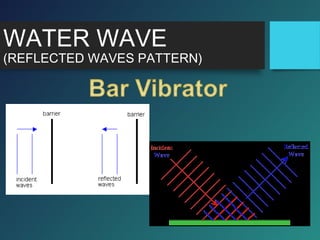
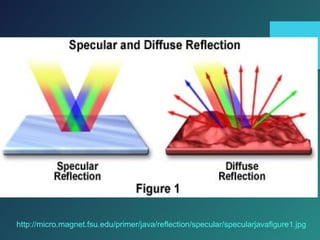
vi. For perfect reflection from a smooth surface, the reflected wavefronts are parallel to the incident wavefronts.