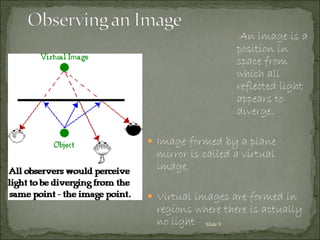
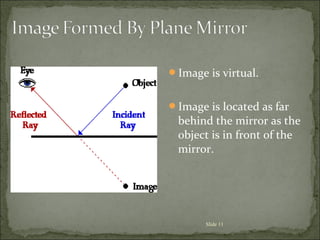
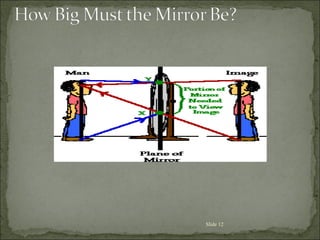
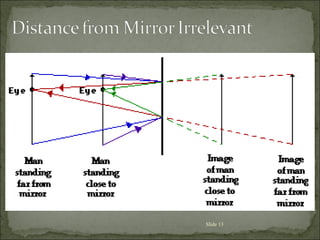
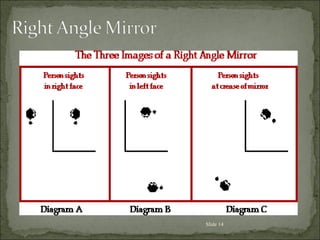
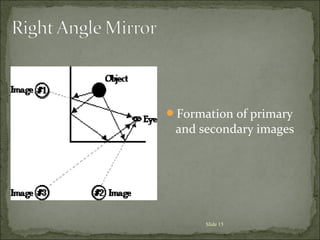
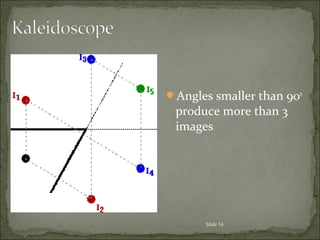
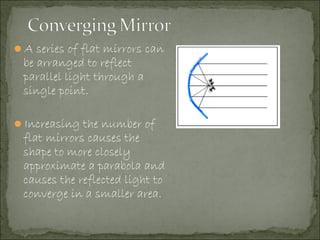
The document discusses key concepts related to reflection of light, including:
1) Luminous objects generate their own light, while illuminated objects reflect light. Reflection occurs when light bounces off a smooth, shiny surface at the same angle as it hits the surface.
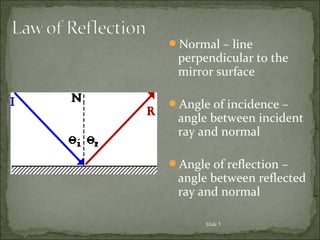
2) The incident ray strikes the mirror, and the reflected ray leaves the mirror and strikes the eye, forming the line of sight from the image to the eye.
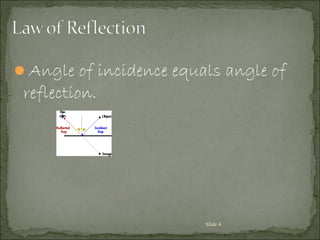
3) The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.