This document provides an overview of objectives and instructions for creating and modifying formulas in Microsoft Excel 2007. It covers topics such as:
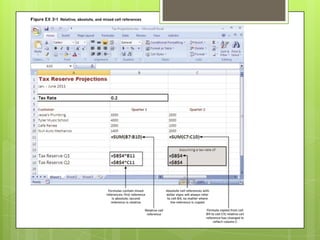
- Referencing data in formulas using relative, absolute, and mixed cell references, and troubleshooting formulas.
- Summarizing data using formulas, subtotals, and conditional formulas.
- Looking up data and using conditional logic in formulas.
- Formatting or modifying text in formulas.
- Displaying and printing formulas.
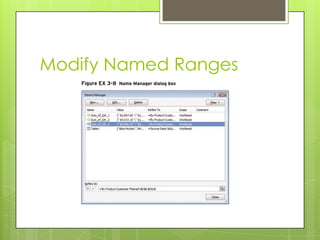
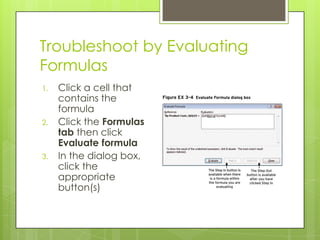
The document provides step-by-step instructions for tasks like naming cell ranges, inserting named ranges in formulas, and troubleshooting formulas using the trace precedents and dependents buttons, error checking, and evaluating formulas.










![Using References to Data in
Other Worksheets
If necessary, open the workbook containing
the data
In the current workbook:
1. Click the cell that will contain the formula and
type =
2. Click the workbook, or worksheet, containing
the value you want to include and click the
cell
3. Type an operand (such as + or -) to continue
the formula and select other cells as necessary
4. Press [Enter]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/referencedatainformulas-111219095643-phpapp01/85/Reference-Data-in-Formulas-14-320.jpg)