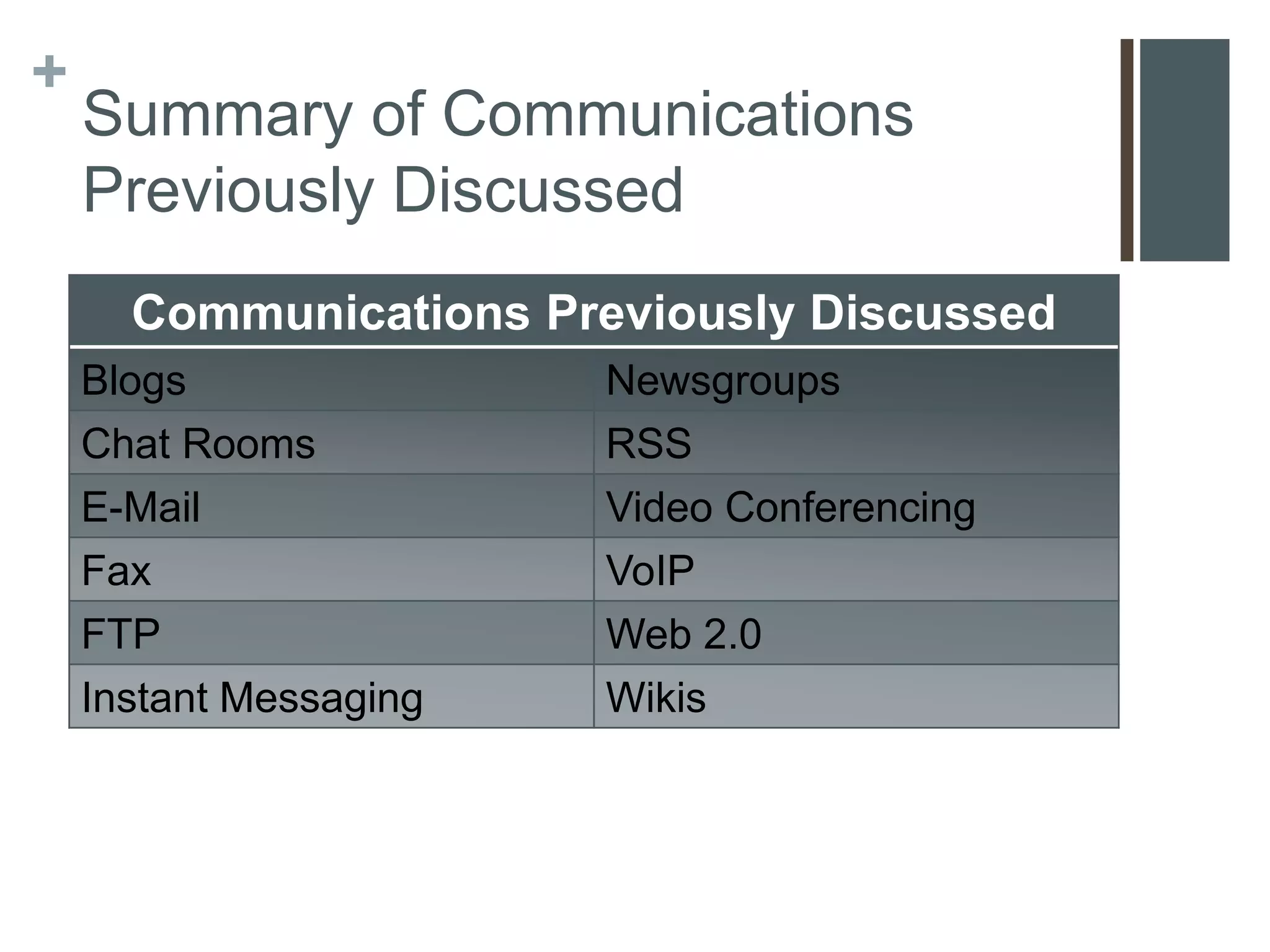
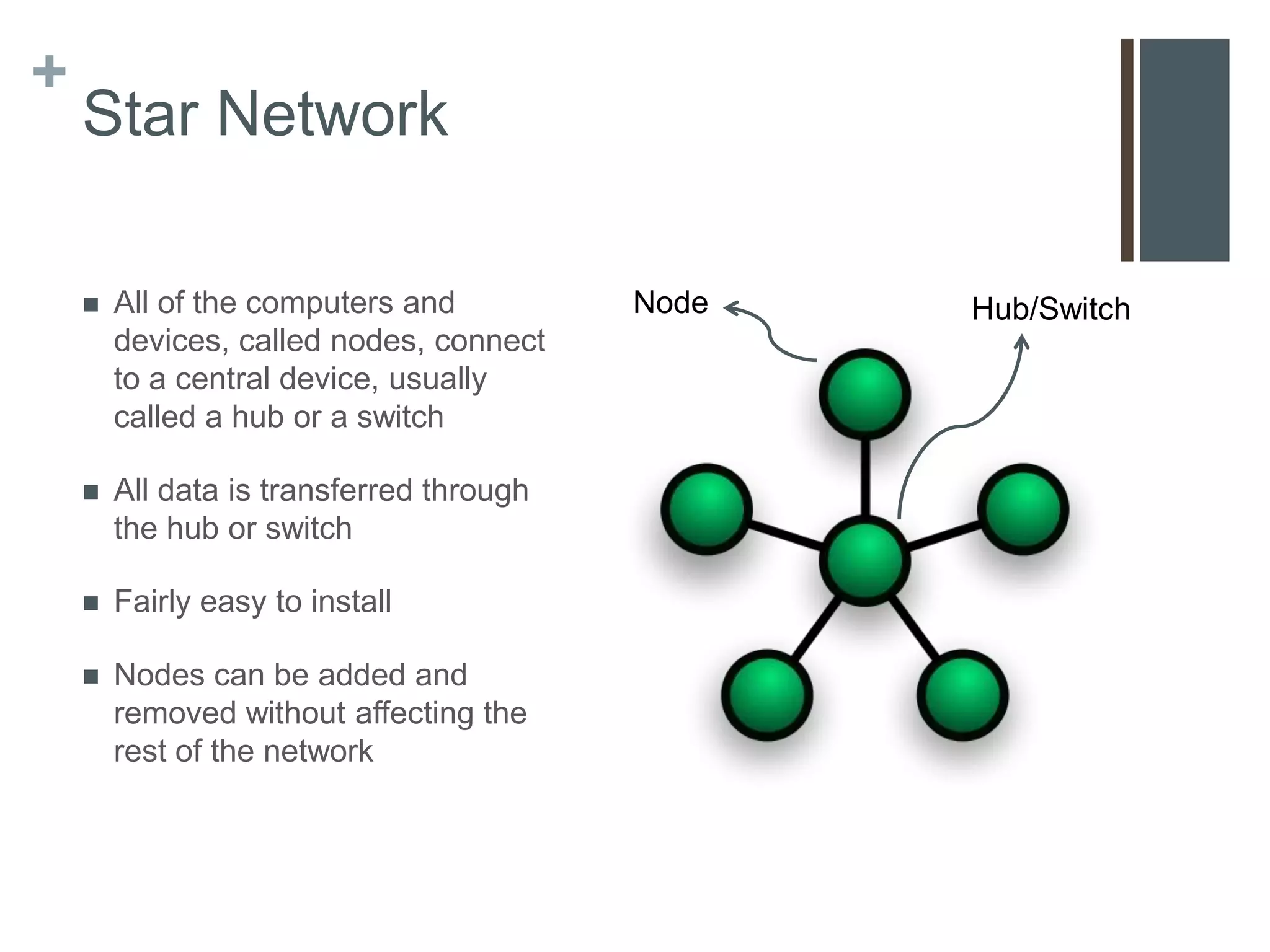
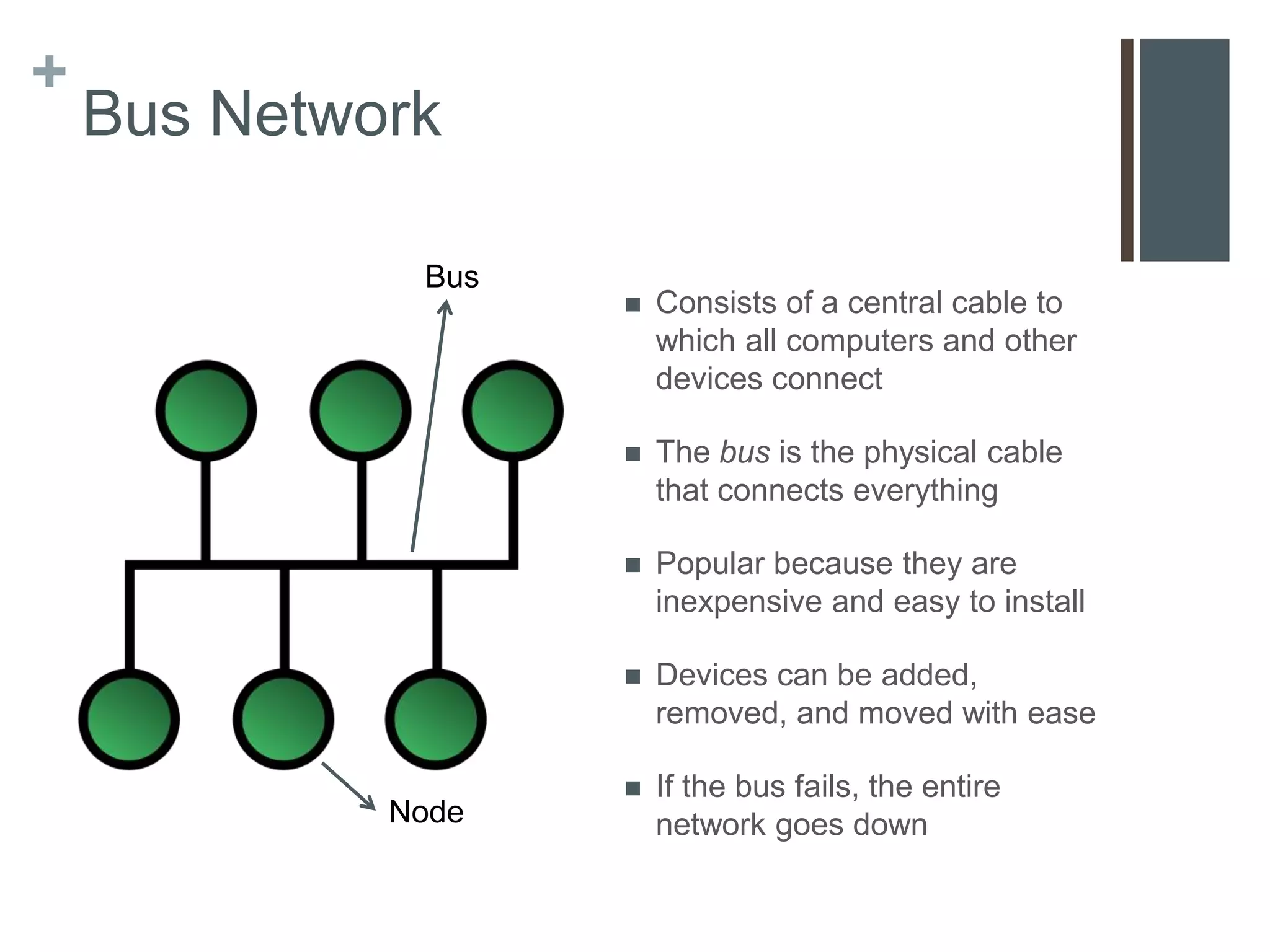
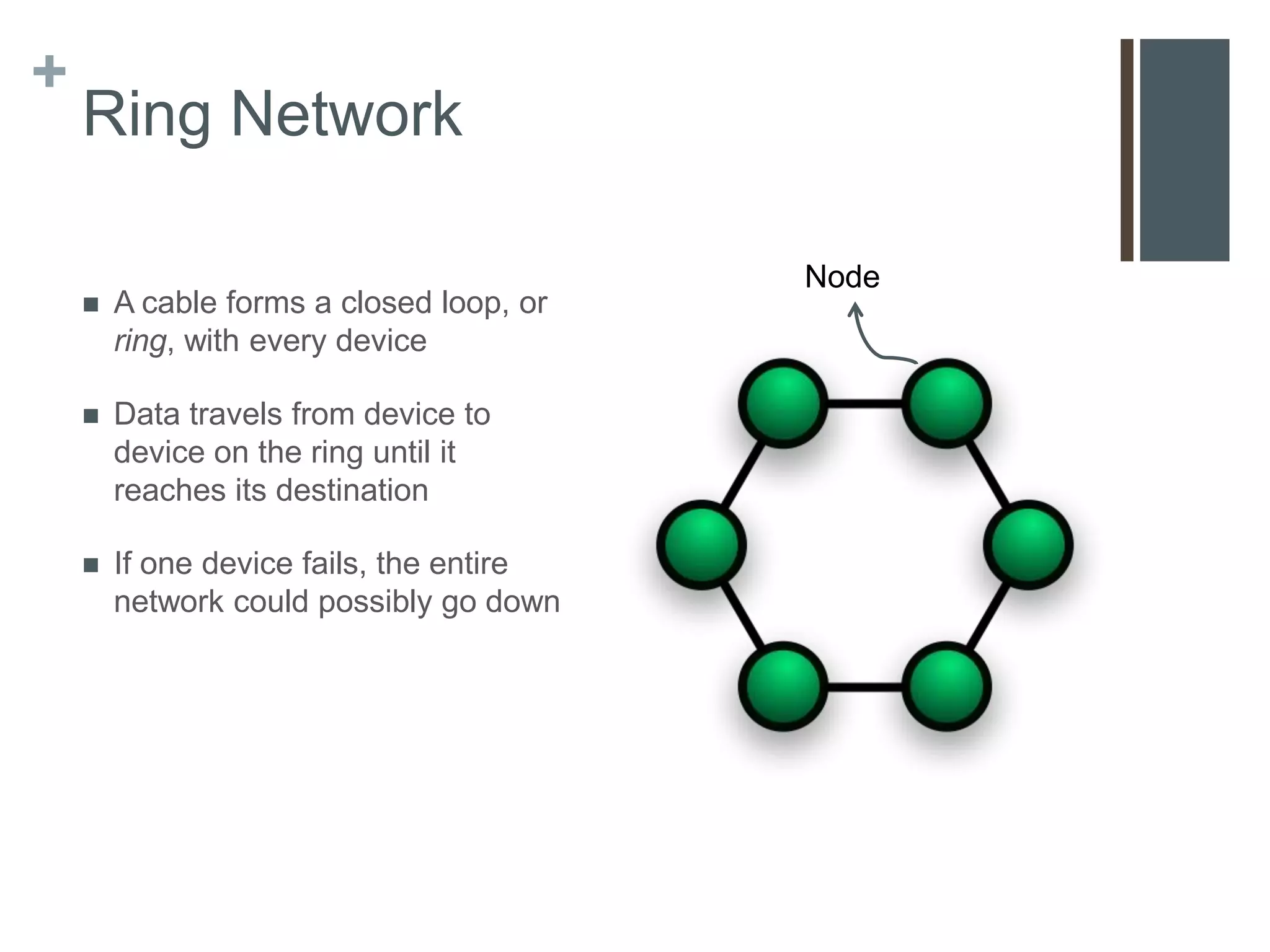
This document provides an overview of communications and networks. It discusses the components required for successful communications including sending and receiving devices. It describes different types of networks including LANs (local area networks), MANs (metropolitan area networks), and WANs (wide area networks). It also differentiates between client/server and peer-to-peer network architectures. The document aims to help readers understand computer communications and networking concepts.