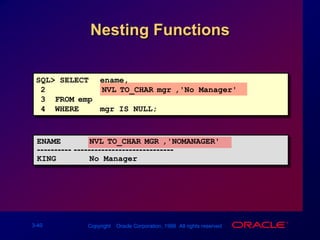
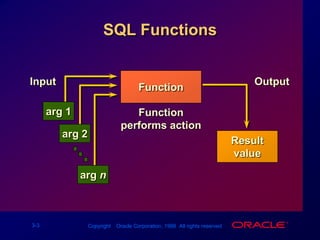
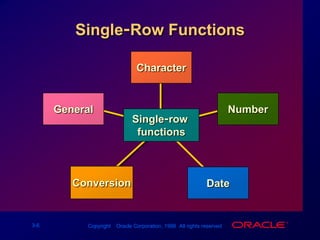
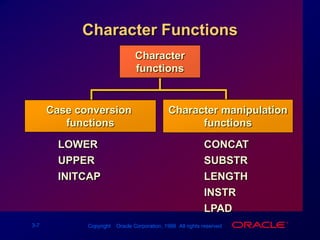
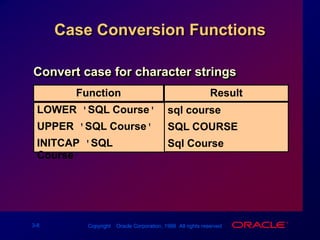
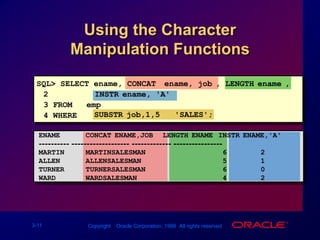
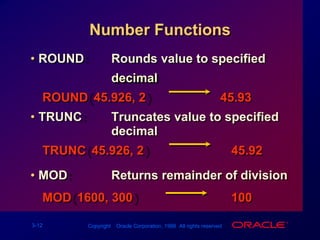
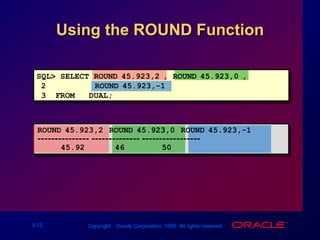
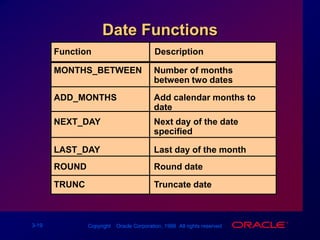
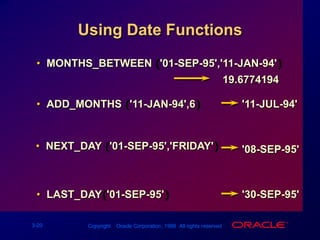
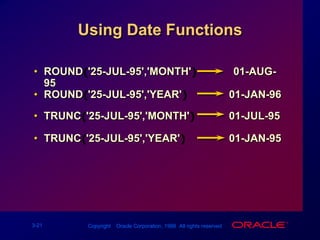
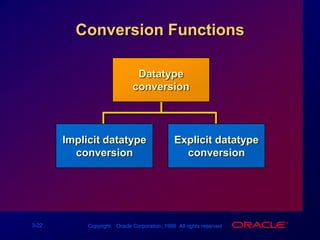
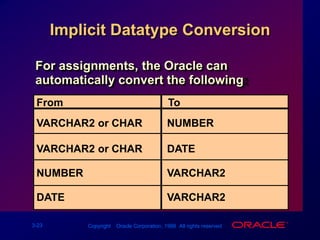
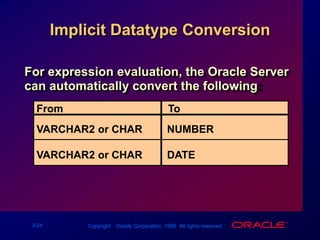
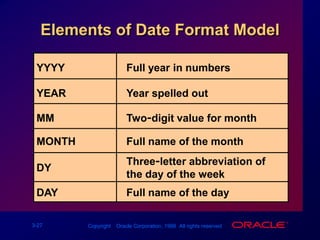
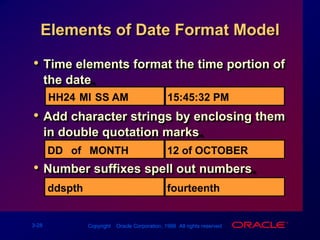
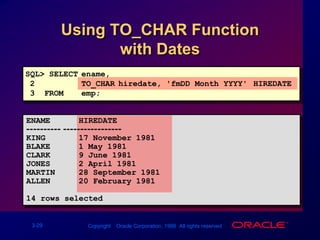
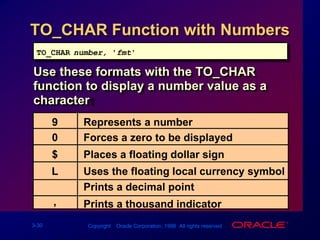
Single-row functions can manipulate data items, accept arguments and return one value, and act on each row returned. There are various types of single-row functions including character, number, date, and conversion functions. Character functions manipulate character strings, number functions perform calculations, and date functions modify date formats. Functions allow data to be formatted, calculated, and converted as needed for different queries and outputs.

![Single-Row FunctionsManipulate data itemsAccept arguments and return one valueAct on each row returnedReturn one result per rowMay modify the datatypeCan be nestedfunction_name (column|expression, [arg1, arg2,...])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les03singlerowfunction-090827015016-phpapp02/85/Les03-Single-Row-Function-5-320.jpg)




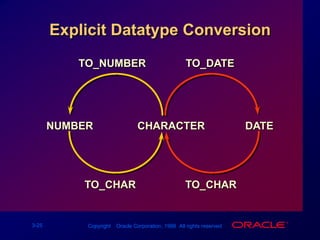
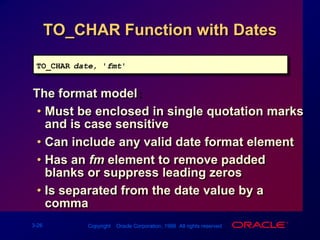
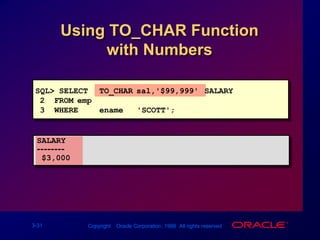

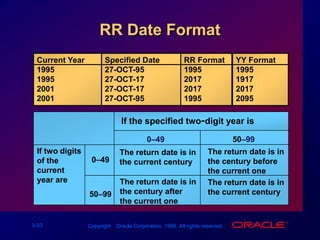

![TO_NUMBER and TO_DATE Functions Convert a character string to a number format using the TO_NUMBER functionTO_NUMBER(char[, 'fmt'])Convert a character string to a date format using the TO_DATE functionTO_DATE(char[, 'fmt'])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les03singlerowfunction-090827015016-phpapp02/85/Les03-Single-Row-Function-35-320.jpg)
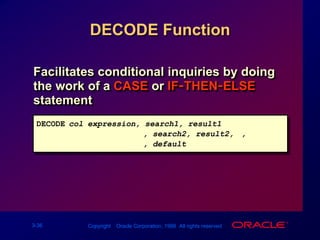
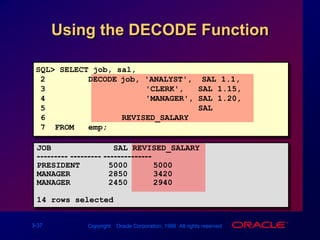

![DECODE FunctionFacilitates conditional inquiries by doing the work of a CASE or IF-THEN-ELSE statementDECODE(col/expression, search1, result1[, search2, result2,...,][, default])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les03singlerowfunction-090827015016-phpapp02/85/Les03-Single-Row-Function-39-320.jpg)