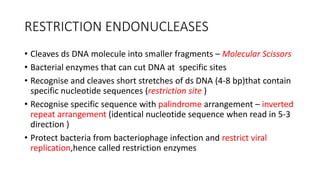
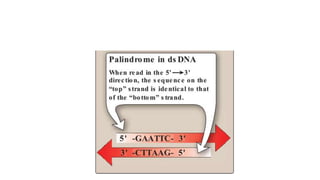
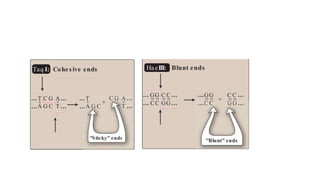
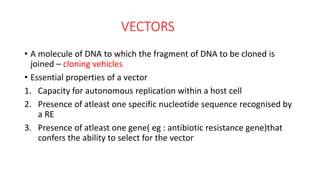
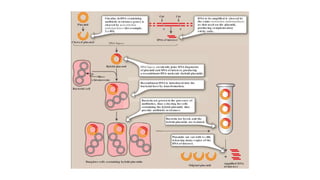
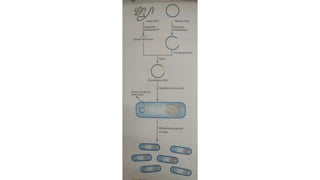
Recombinant DNA technology uses restriction enzymes and DNA ligases to cut and join DNA molecules from different sources, generating recombinant DNA. This DNA can be inserted into vectors like plasmids or viruses and introduced into host cells like bacteria or yeast for replication. The replicated DNA can then be used to produce large quantities of proteins with applications including producing therapeutic agents, vaccines, diagnosing diseases, and gene therapy.