This document summarizes recent progress in distributed deep learning. It discusses the state of the art in neural networks and deep learning, as well as factors driving advances in deep learning like big data and increased computing power. It then covers approaches for scaling deep learning through model parallelism, data parallelism, and distributed training frameworks. Several deep learning applications developed in Vietnam are presented as examples, including optical character recognition and predictive text. The document concludes with principles for machine learning system design in distributed settings.




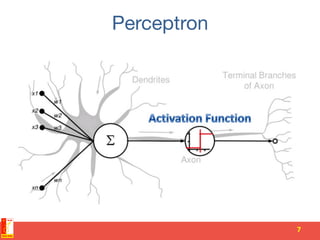
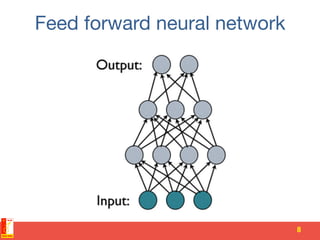

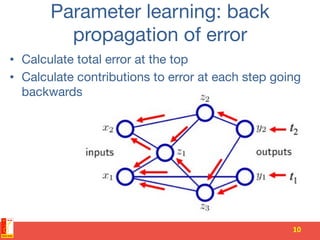
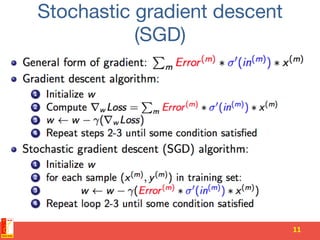







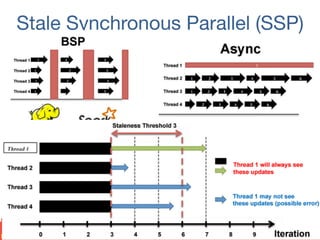
![Model parallelism [cont'd]
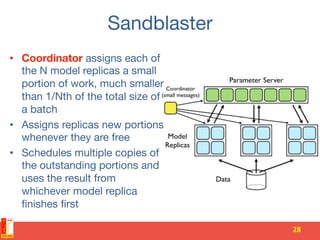
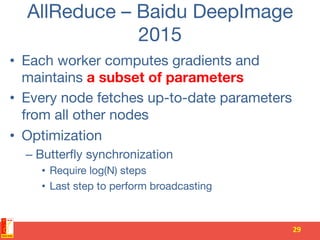
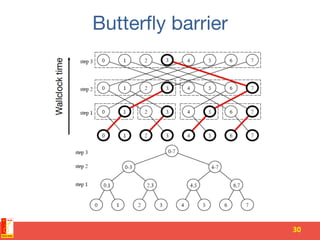
• Message passing during upward and
downward phases
• Distributed computation
• Performance gains are held by
communication costs
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-recentprogressondistributingdeeplearning-160319064857/85/Recent-progress-on-distributing-deep-learning-25-320.jpg)

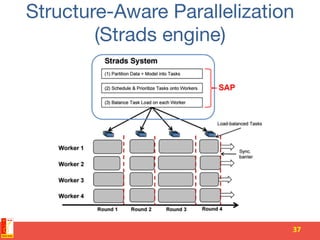
![Parameter server [OSDI 2014]
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-recentprogressondistributingdeeplearning-160319064857/85/Recent-progress-on-distributing-deep-learning-33-320.jpg)
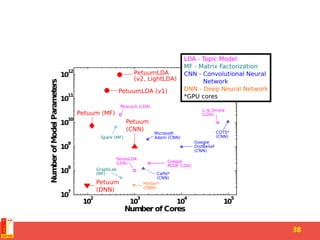
![Apache Singa [2015]
• National University of Singapore
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-recentprogressondistributingdeeplearning-160319064857/85/Recent-progress-on-distributing-deep-learning-34-320.jpg)
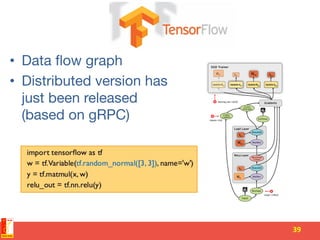
![Petuum CMU [ACML 2015]
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-recentprogressondistributingdeeplearning-160319064857/85/Recent-progress-on-distributing-deep-learning-35-320.jpg)