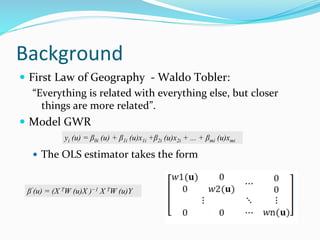
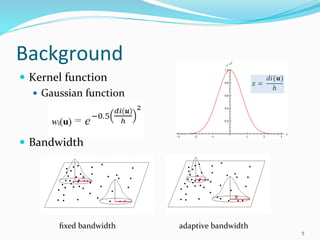
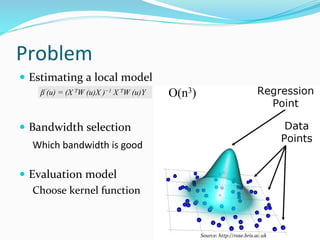
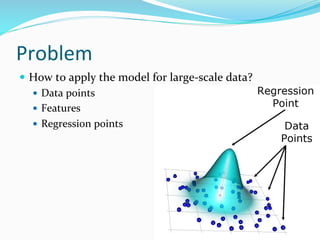
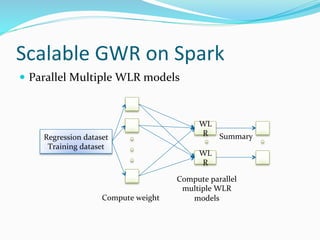
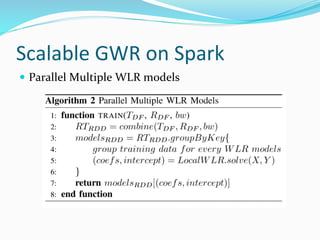
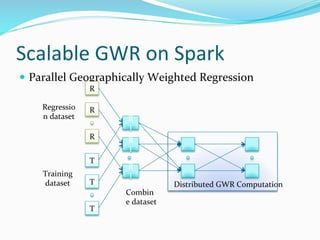
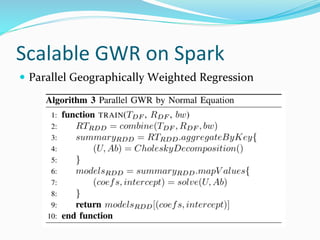
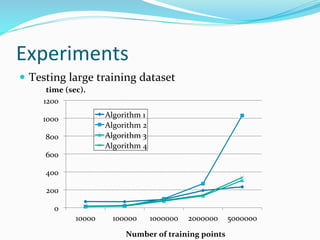
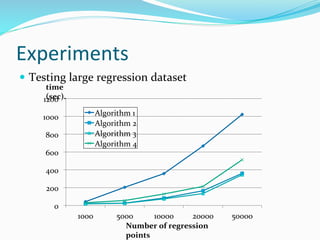
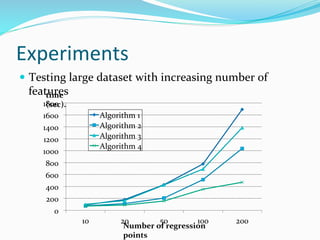
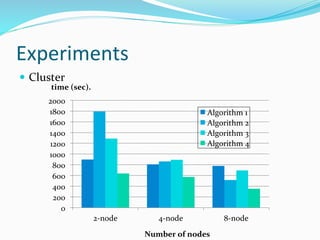
The document discusses the implementation of geographically weighted regression (GWR) using scalable methods on Apache Spark to handle large-scale spatial data. It presents an overview of GWR, challenges in bandwidth selection, and three approaches for its scaling, along with performance evaluation through experiments on a cloud cluster. The findings highlight the effectiveness of using Spark for distributed GWR, with implications for future enhancements and open-source development.