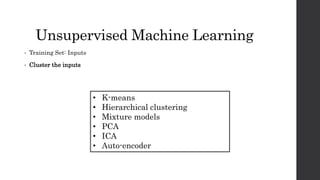
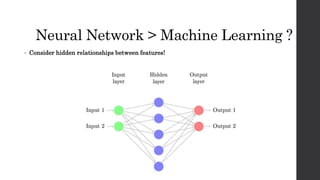
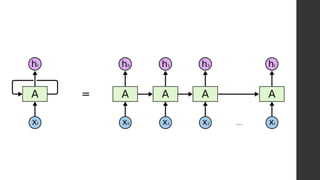
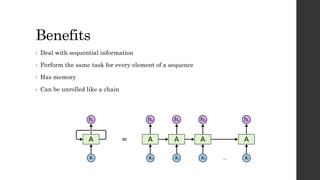
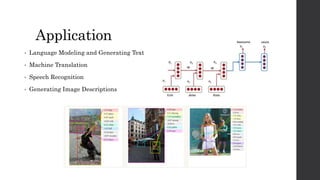
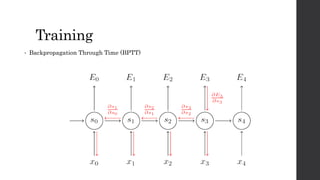
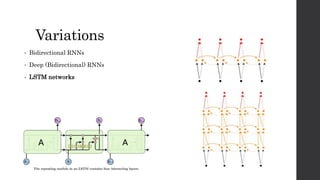
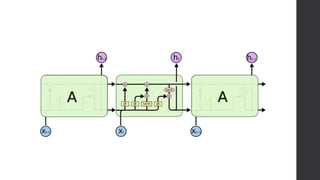
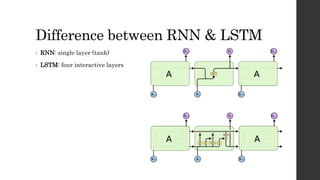
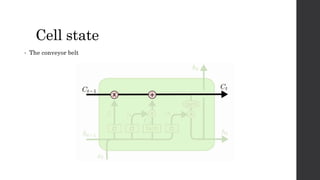
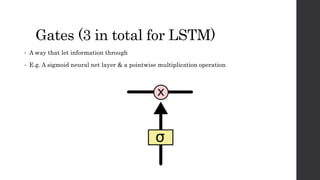
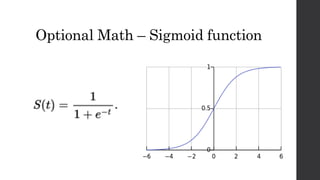
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks can process sequential data like text and time series data. RNNs have memory and can perform the same task for every element in a sequence, but struggle with long-term dependencies. LSTMs address this issue using memory cells and gates that allow them to learn long-term dependencies. LSTMs have four interacting layers - a forget gate, input gate, cell state, and output gate that allow them to store and access information over long periods of time. RNNs and LSTMs are applied to tasks like language modeling, machine translation, speech recognition, and image caption generation.








![Step 1: Forget Gate Layer
• Decide what info to throw away
• Look at h[t-1] and x[t] and output a number 0~1 to decide how much cell state to keep C[t-1]
• E.g. When see a new subject, we want to forget the gender of the old subject](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jpmrnnlstmsmalltalk-171208093736/85/RNN-LSTM-Neural-Network-for-Sequential-Data-22-320.jpg)
![Step 2: Input Gate Layer
• Decide what info to add
• A sigmoid: decide which value to update
• A tanh layer: create a new candidate value C~[t]
• E.g. add a new gender of the new subject](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jpmrnnlstmsmalltalk-171208093736/85/RNN-LSTM-Neural-Network-for-Sequential-Data-23-320.jpg)
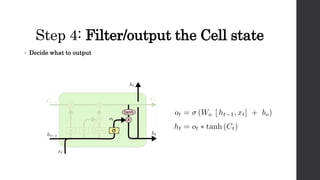
![Step 3: Combine step 1 & 2
• Combine step 1 & 2
• Multiply the old state by f[t]: to forget the things
• Add i[t] * C~[t] : to add new candidate value (scaled)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jpmrnnlstmsmalltalk-171208093736/85/RNN-LSTM-Neural-Network-for-Sequential-Data-24-320.jpg)

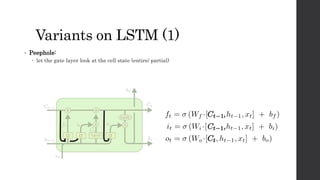
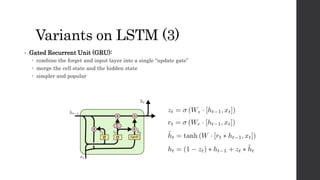
![Variants on LSTM (2)
• Coupled forgot and input gates:
Not deciding separately
f[t] * C[t-1] + (1-f[t]) * C~[t]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jpmrnnlstmsmalltalk-171208093736/85/RNN-LSTM-Neural-Network-for-Sequential-Data-28-320.jpg)




![Great references
• [1] RNN: http://www.wildml.com/2015/09/recurrent-neural-networks-
tutorial-part-1-introduction-to-rnns/?subscribe=success#blog_subscription-2
• [2] LSTM: http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/
• [3] RNN Effectiveness: http://karpathy.github.io/2015/05/21/rnn-
effectiveness/
• [4] Backpropagation: http://cs231n.github.io/optimization-2/#backprop
• [5] ML categories: http://enhancedatascience.com/2017/07/19/machine-
learning-explained-supervised-learning-unsupervised-learning-and-
reinforcement-learning/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jpmrnnlstmsmalltalk-171208093736/85/RNN-LSTM-Neural-Network-for-Sequential-Data-35-320.jpg)