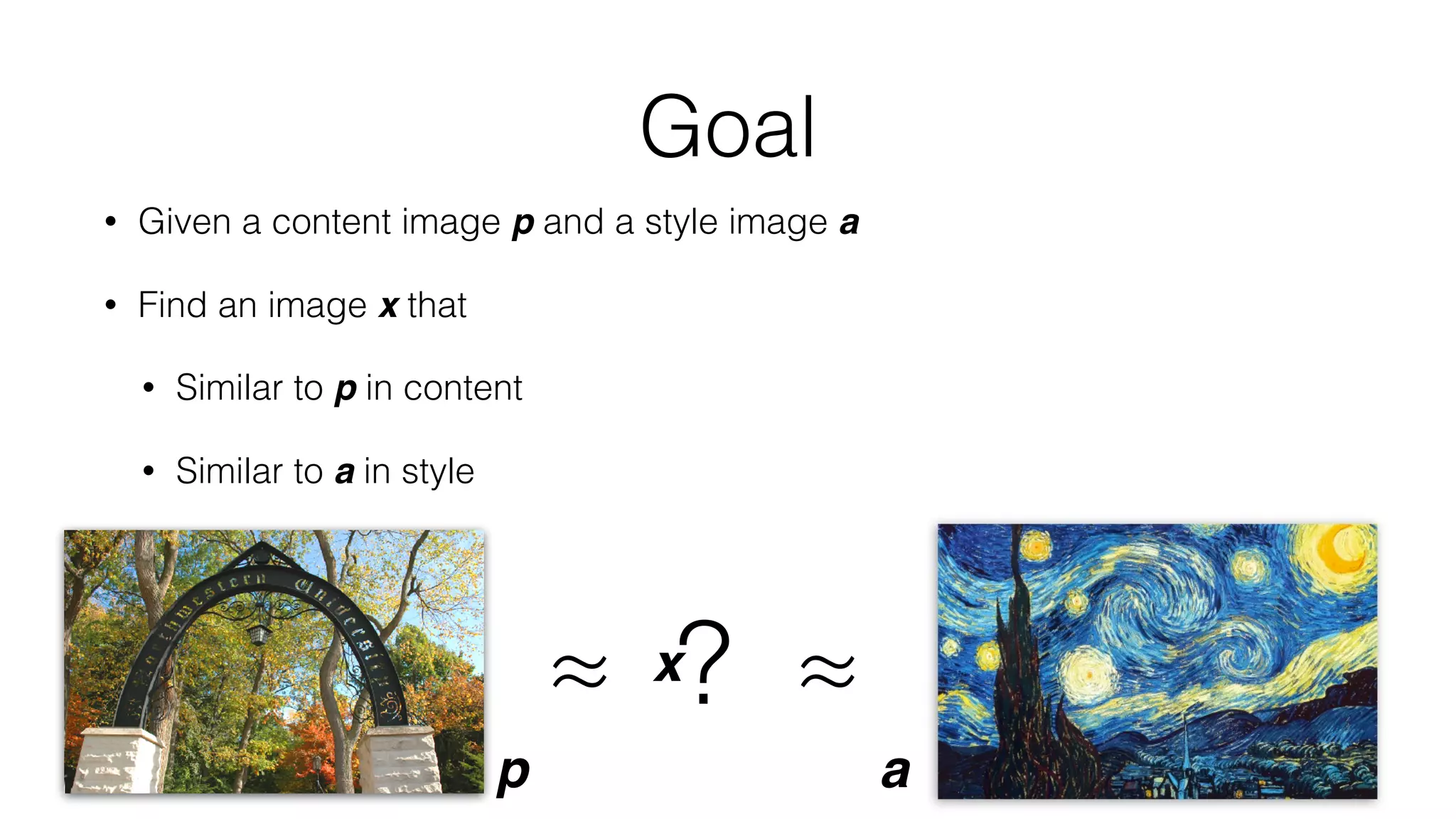
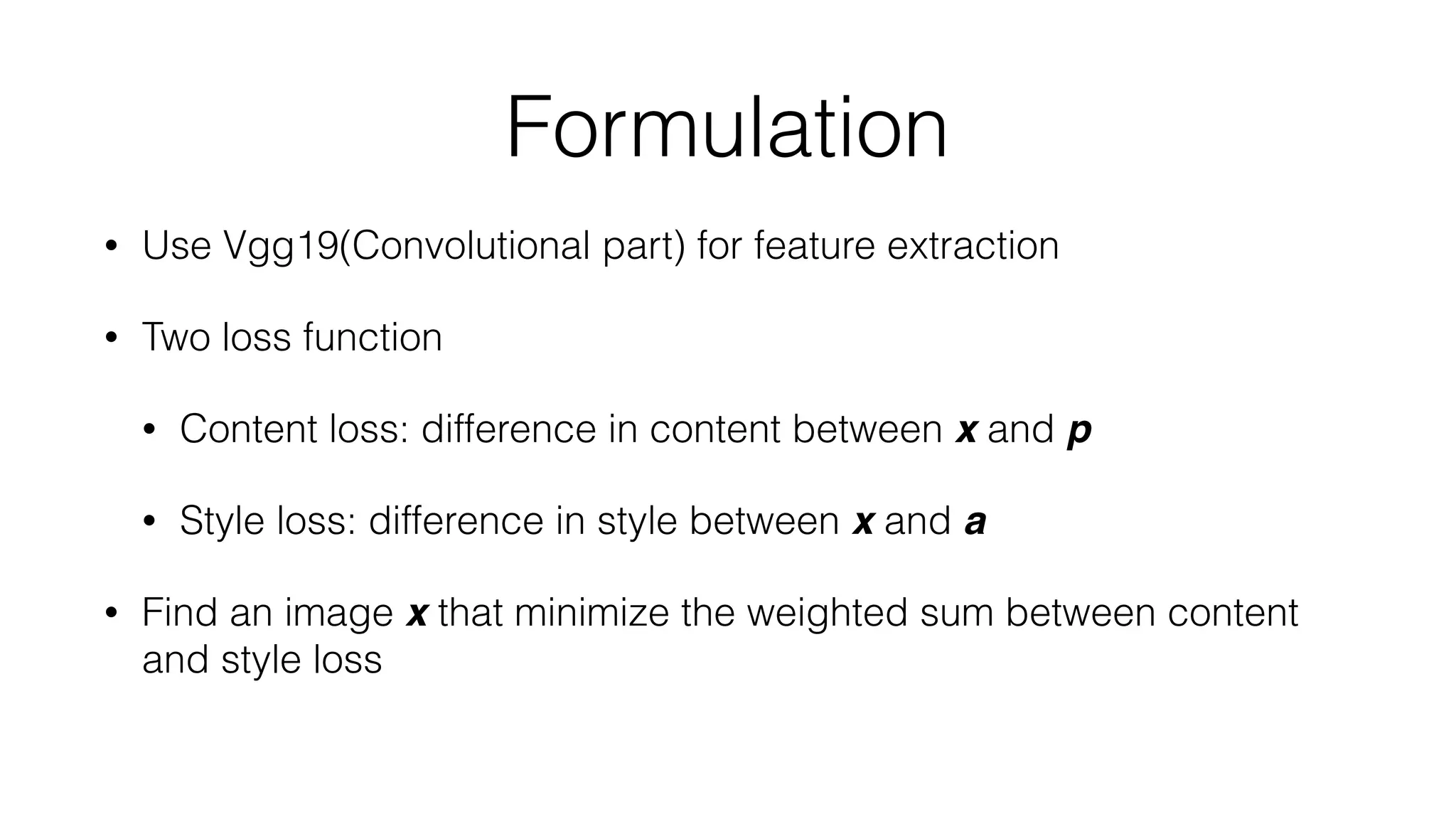
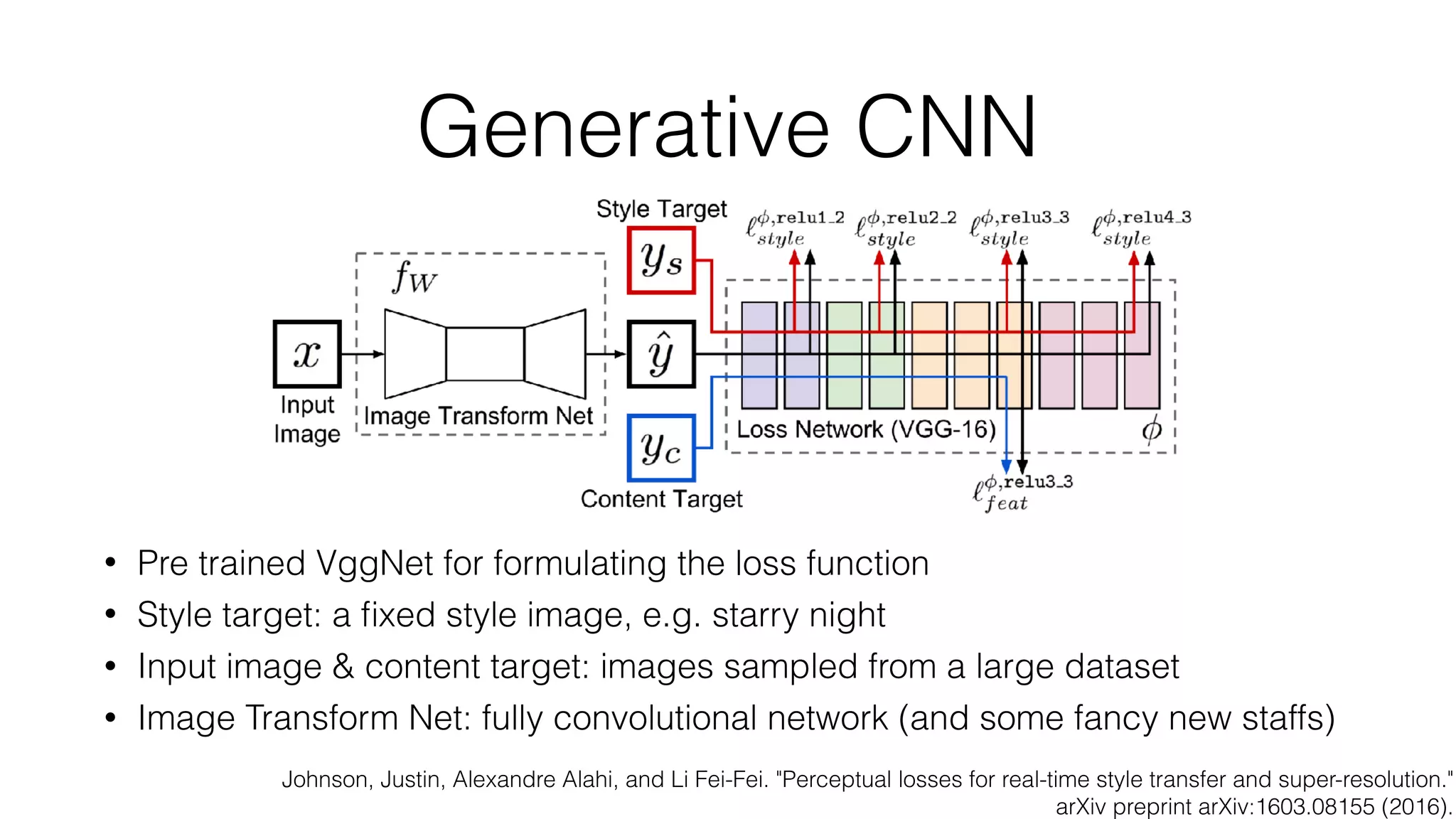
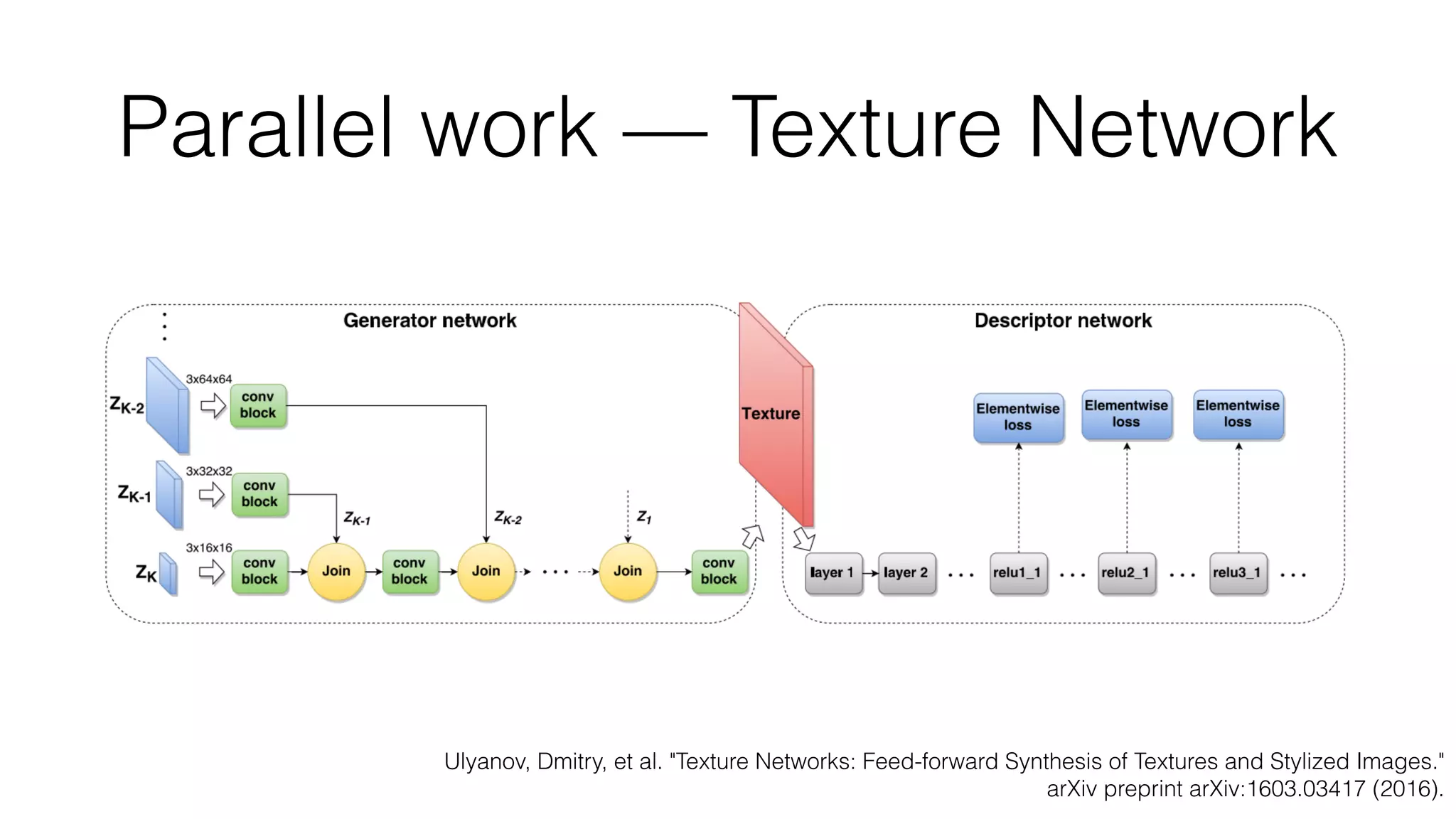
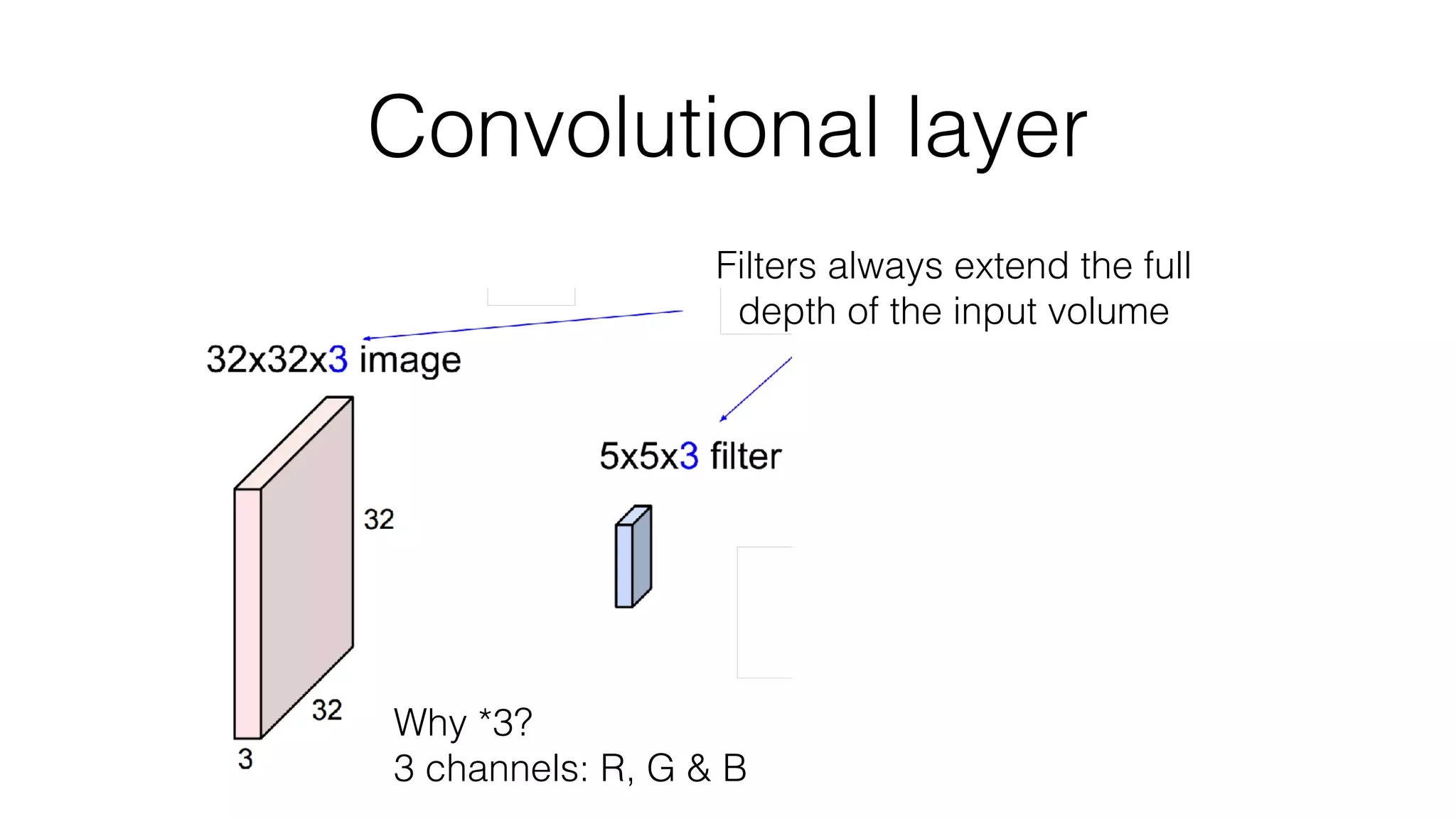
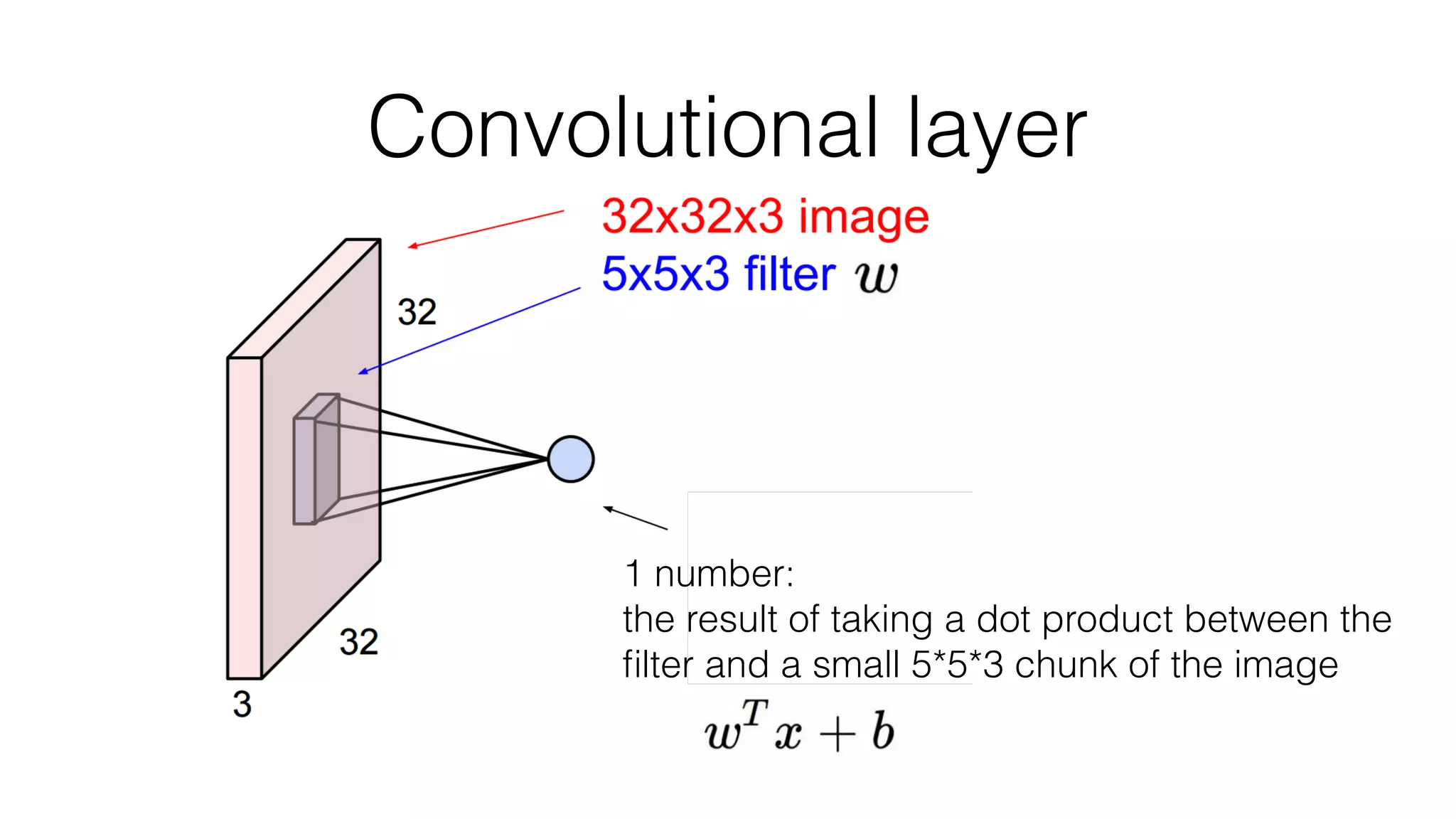
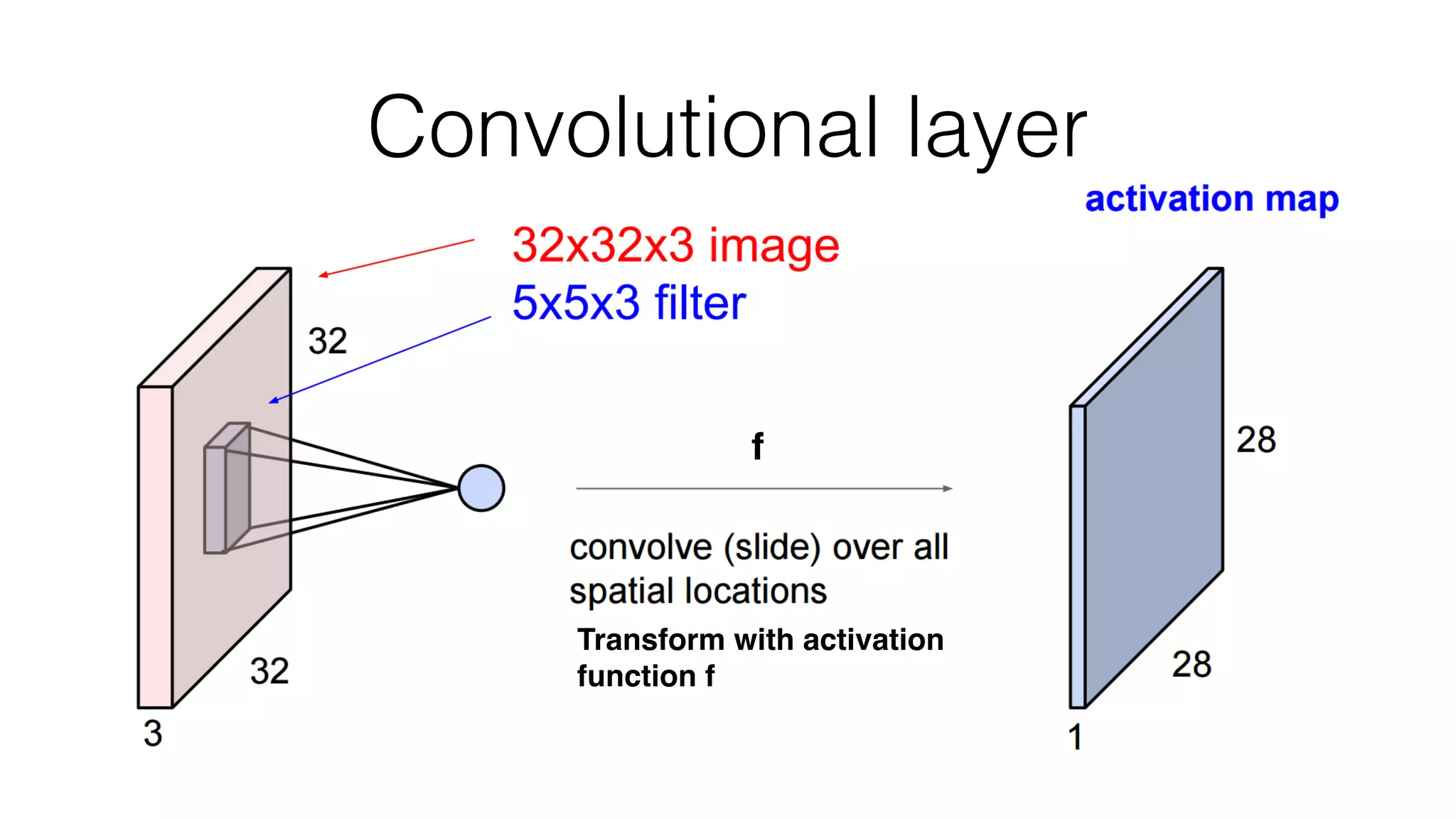
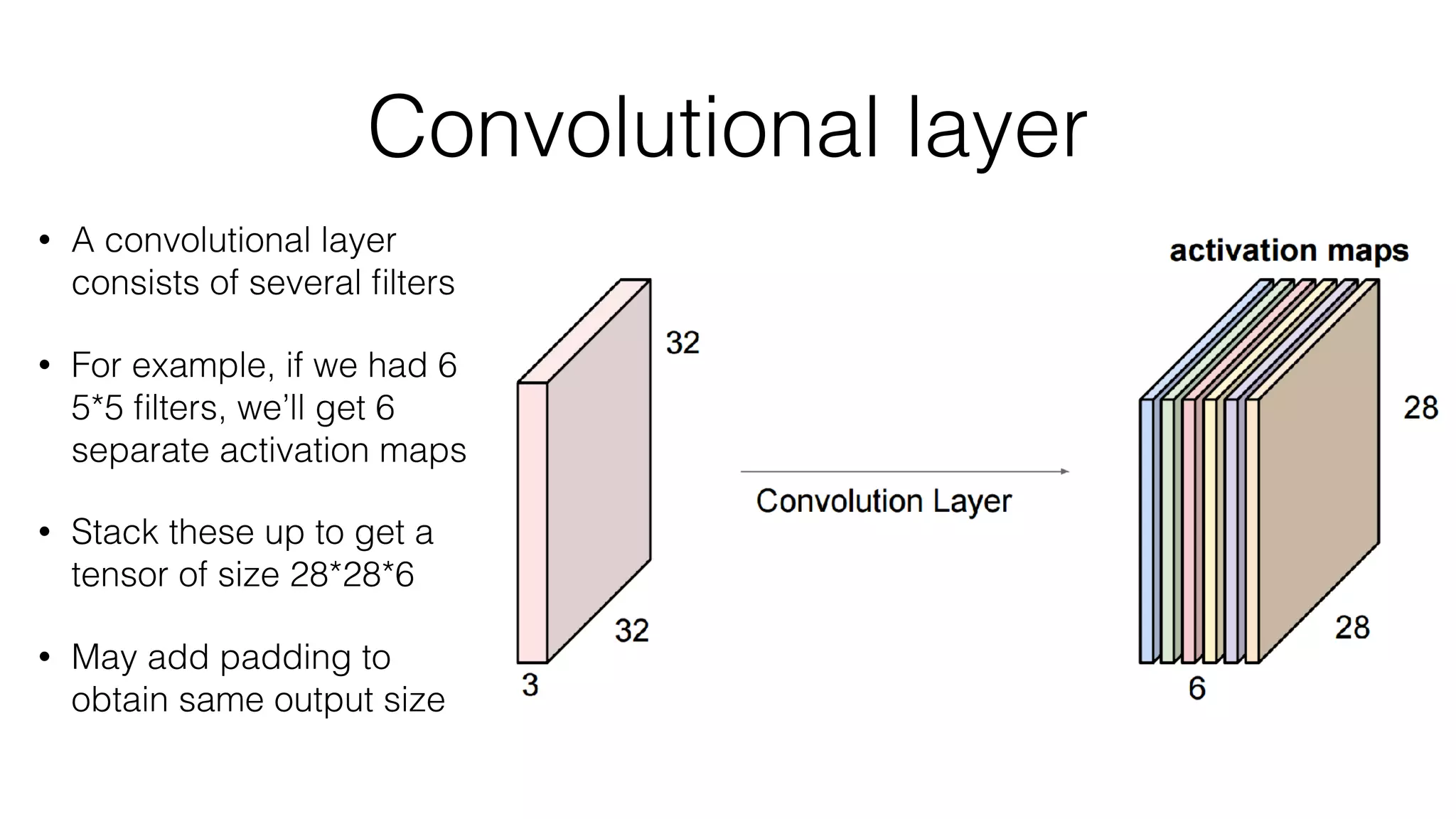
Prisma uses deep learning techniques like neural style transfer to transform photos into artworks. Neural style transfer uses convolutional neural networks to extract features from content and style images, then finds an image that minimizes differences in these features. Early work used iterative optimization, but real-time style transfer trains a generative CNN on a dataset to synthesize stylized images with one forward pass. Prisma's offline mode likely uses a similar generative approach to enable fast stylization on mobile.







![Typical architecture
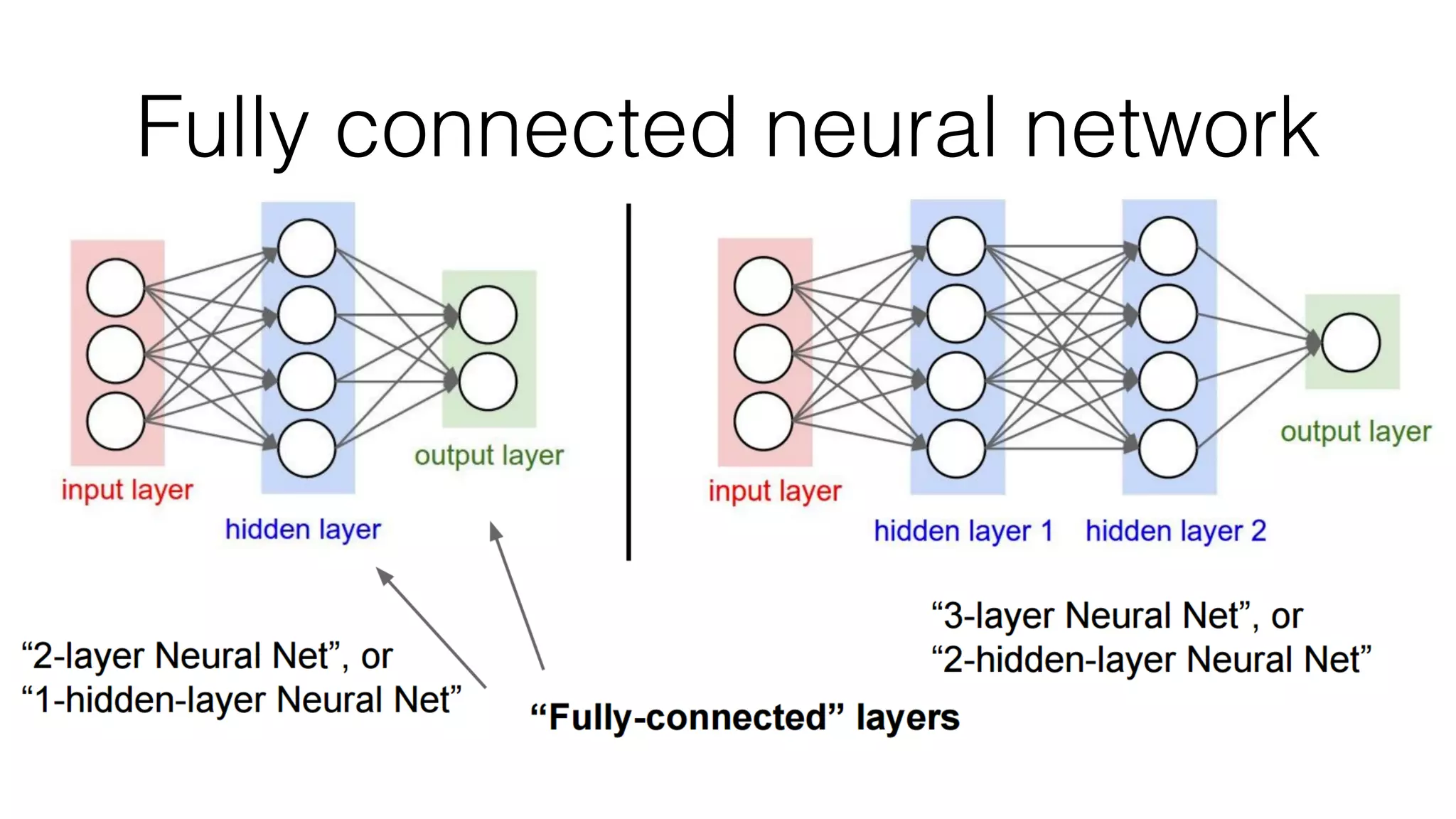
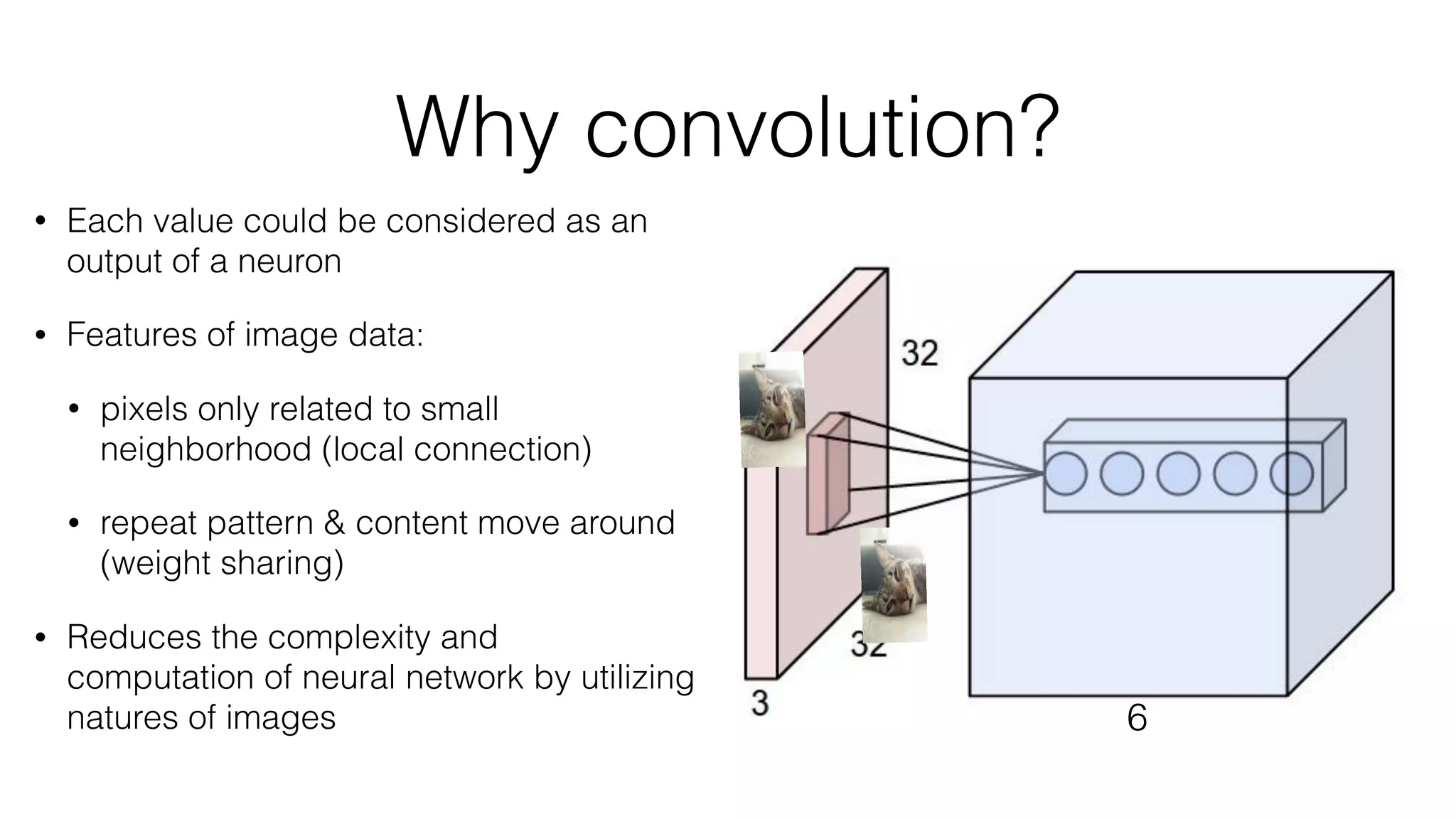
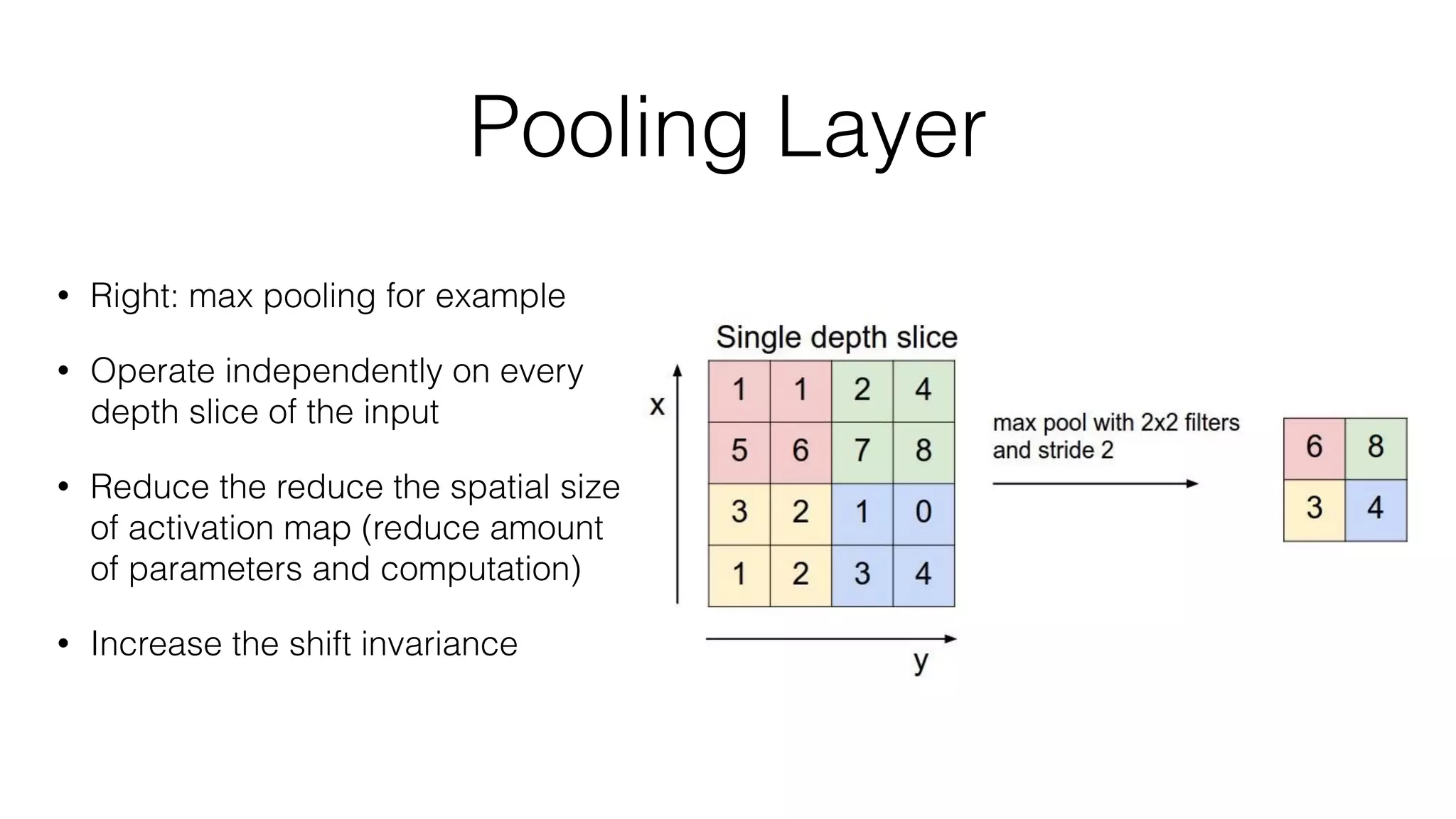
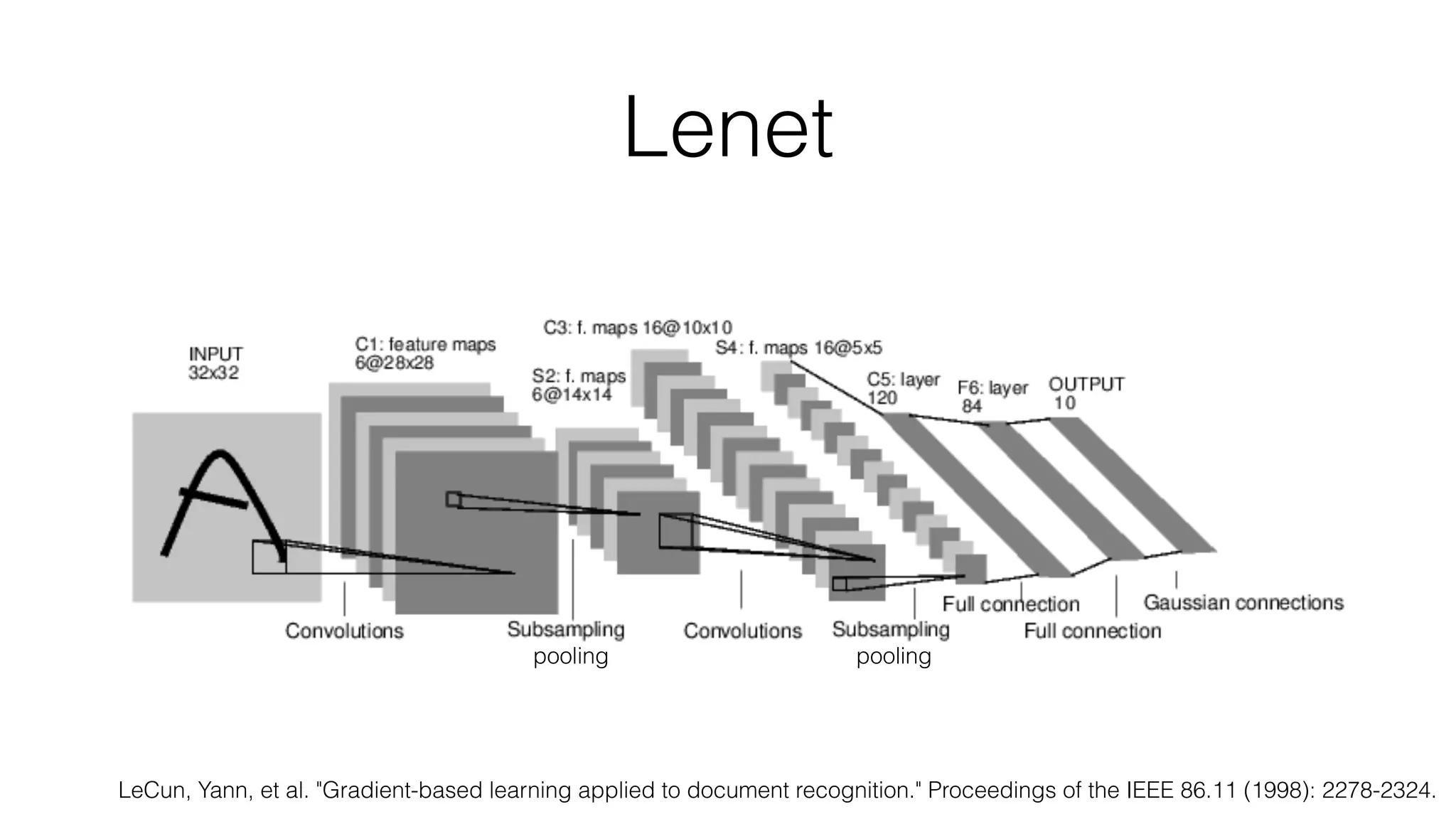
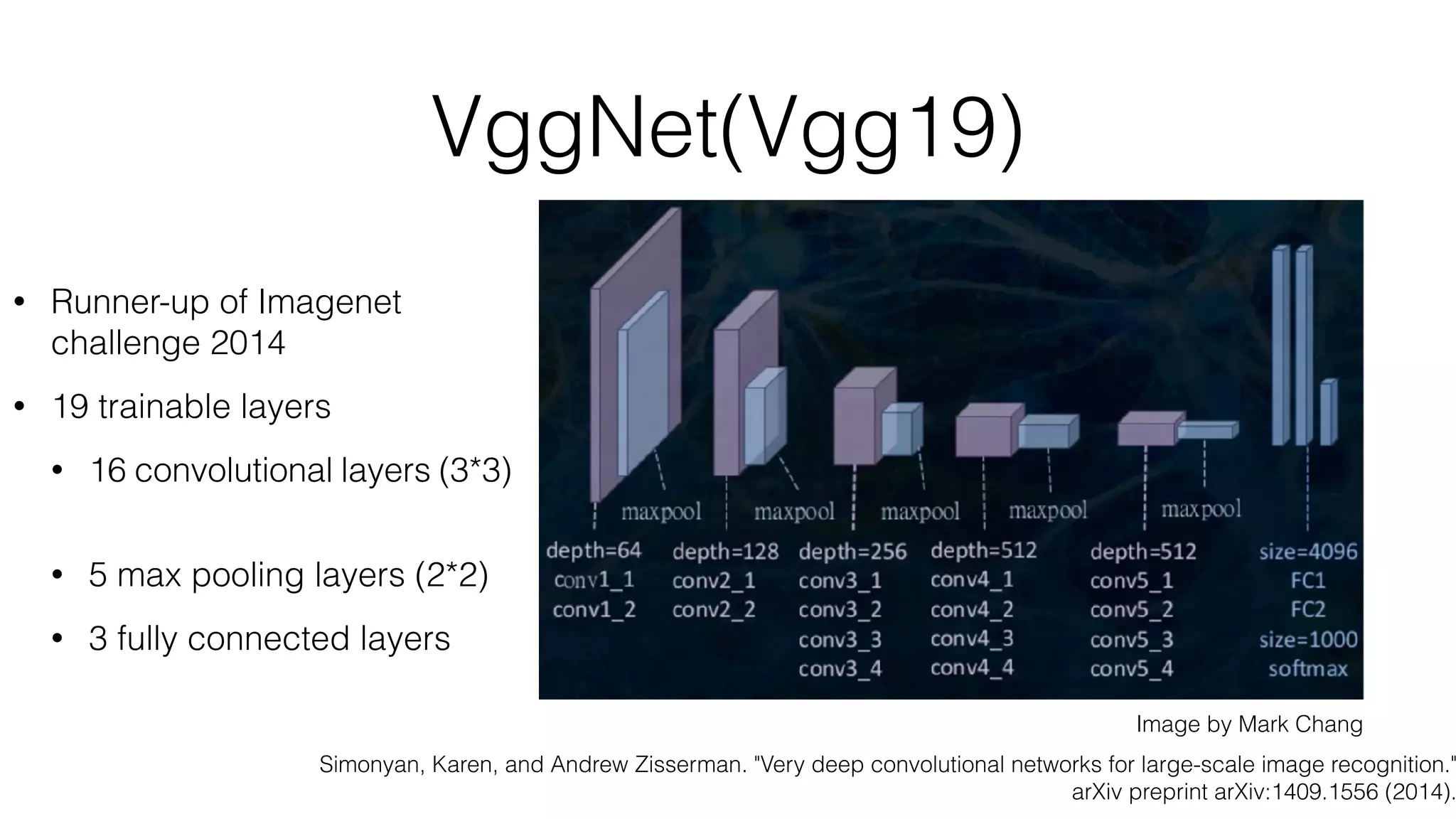
• Convolutional part & Fully connected part
• [(CONV-RELU)*N-POOL?]*M-(FC-RELU)*K,SOFTMAX](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/styletemp-161002182243/75/Deep-Learning-behind-Prisma-20-2048.jpg)