Recombinant DNA technology has led to many advancements in medicine and biotechnology. Key developments include:
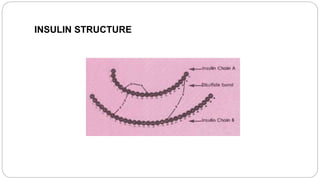
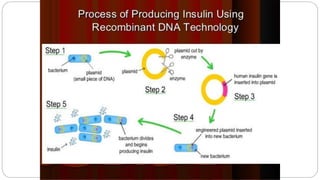
1. The production of human insulin through recombinant DNA techniques, approved for use in 1982. This provided an effective treatment for diabetes and was the first commercial product of rDNA technology.
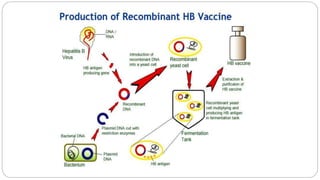
2. Vaccines produced using recombinant DNA techniques, such as vaccines for hepatitis B. This involves inserting the gene for the hepatitis B surface antigen protein into yeast which then produces the protein for the vaccine.
3. Production of other proteins through recombinant DNA like cytokines and interferons, which help modulate the immune system and can be used as treatments for various conditions. Overall, recombinant DNA technology has generated many commercially useful proteins and