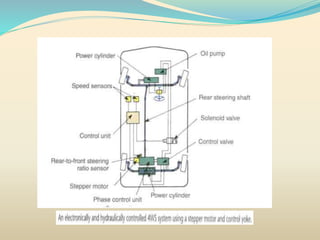
The document discusses steering systems in vehicles, focusing on the types, particularly four-wheel steering (4WS), which enhances maneuverability and vehicle stability. 4WS allows for tighter turning radii at low speeds and increased stability at high speeds, boasting a significant reduction in turning radius compared to traditional two-wheel steering. The conclusion highlights the potential for widespread adoption of 4WS, which, despite high initial costs, promises improved efficiency and functionality in vehicle handling.