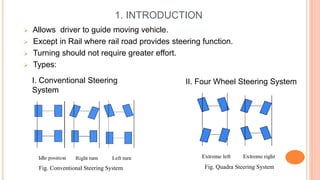
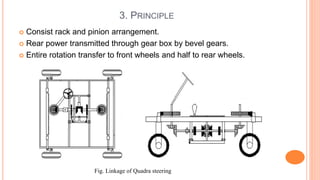
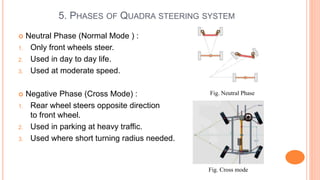
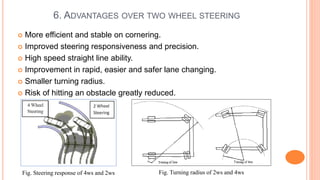
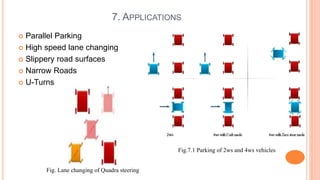
The document discusses four wheel steering systems and their advantages over conventional two wheel steering. It describes the different phases (modes) of a quadra steering system including neutral phase, negative phase, positive phase, and zero steer mode. The four wheel steering system provides improved steering precision and stability during cornering as well as smaller turning radii and safer lane changes compared to two wheel steering. Future advanced four wheel steering systems may be fully electronic and allow for maximum maneuverability.