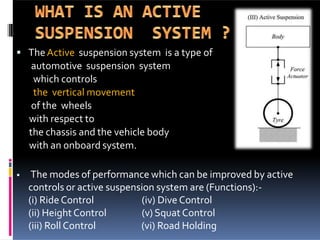
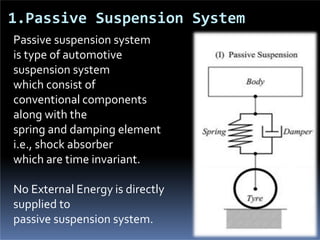
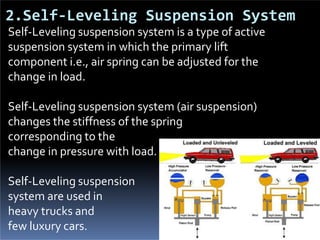
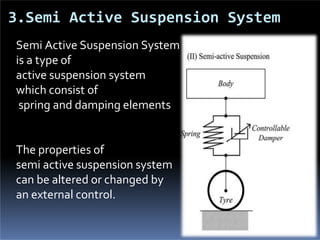
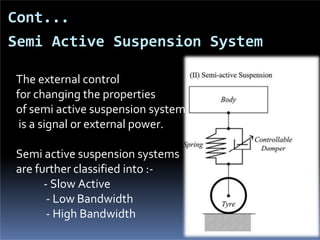
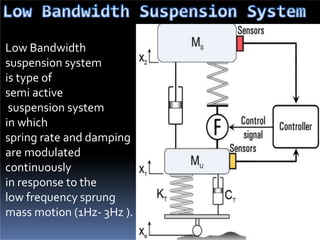
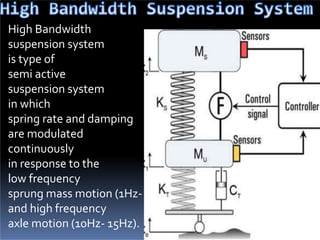
The document discusses various types of automotive suspension systems, focusing on active suspension systems and their advantages over passive systems. It categorizes these systems into passive, self-leveling, semi-active, and full active suspensions, detailing their functions, components, and performance improvements. The active suspension systems offer enhanced ride quality, handling, and safety at the expense of increased complexity and cost.