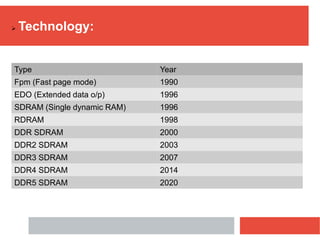
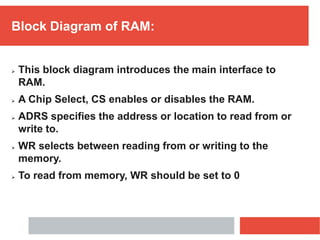
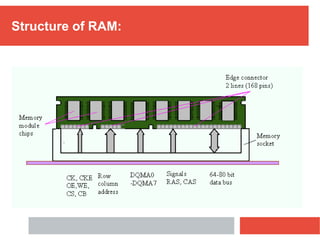
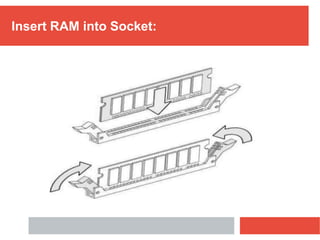
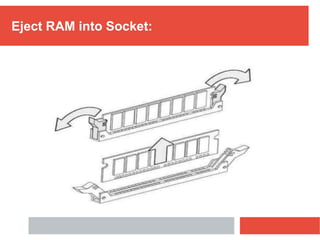
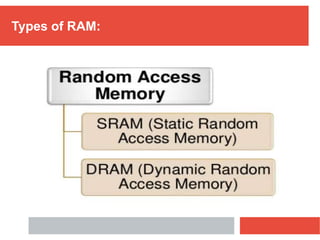
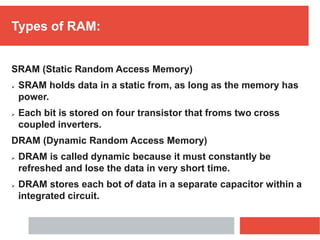
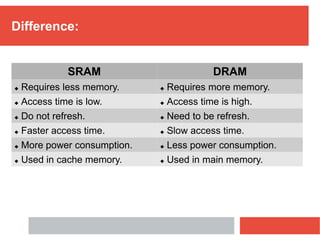
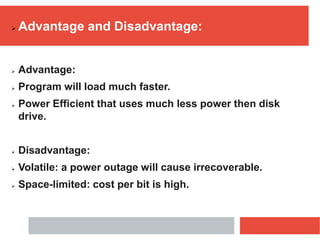
RAM is a type of volatile computer memory that can be accessed randomly. It is faster than other types of memory like SSD/HDD, so programs load faster from RAM. RAM was invented in 1968 and its technology has improved over time from FPM to DDR5 RAM. There are two main types - SRAM which holds data statically but uses more power, and DRAM which must be refreshed but uses less power. The capacity of RAM in computers has increased significantly over time from 256 MB to 8 GB currently. RAM provides faster loading of programs but has the disadvantage of being volatile and space-limited.