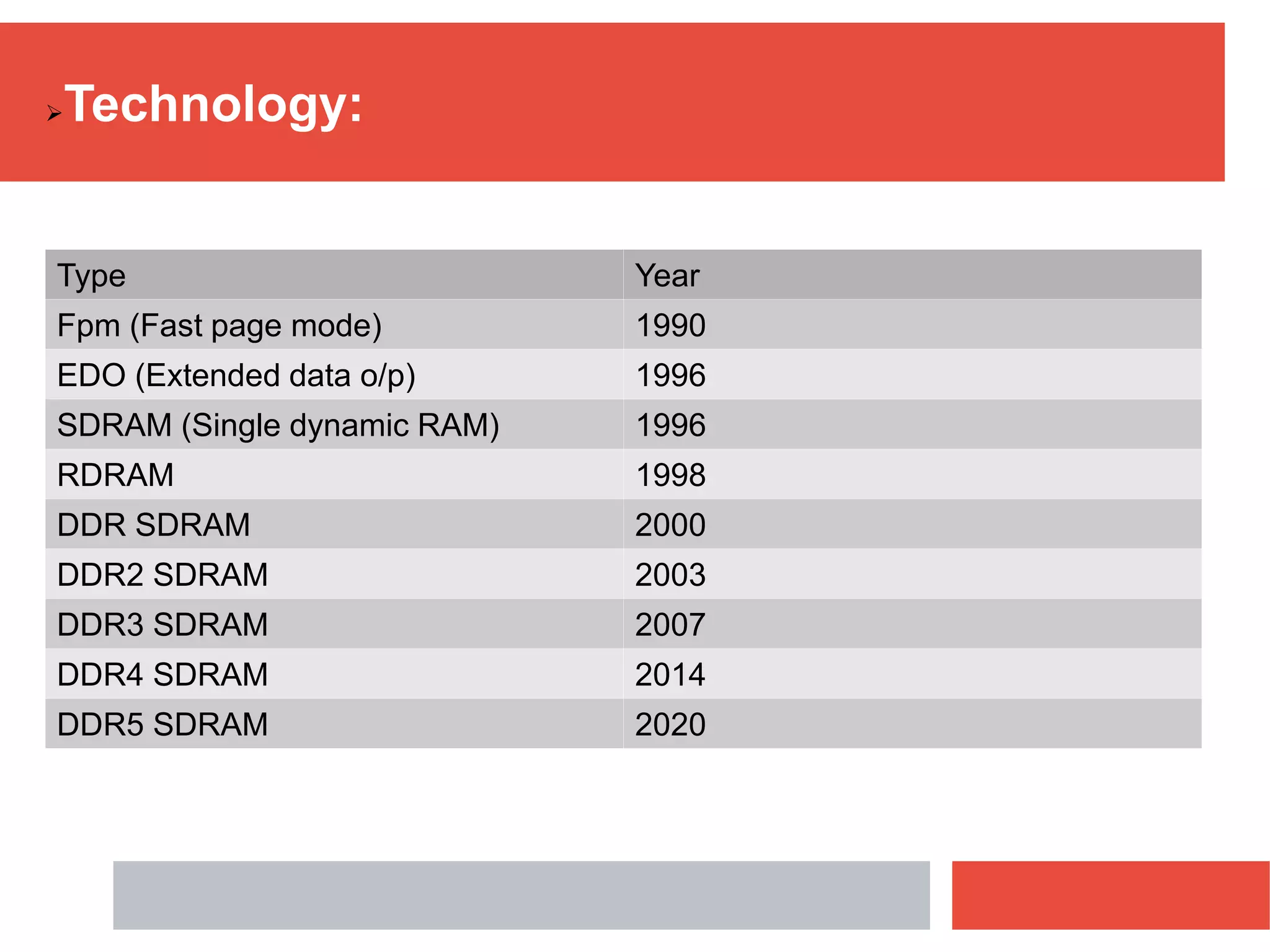
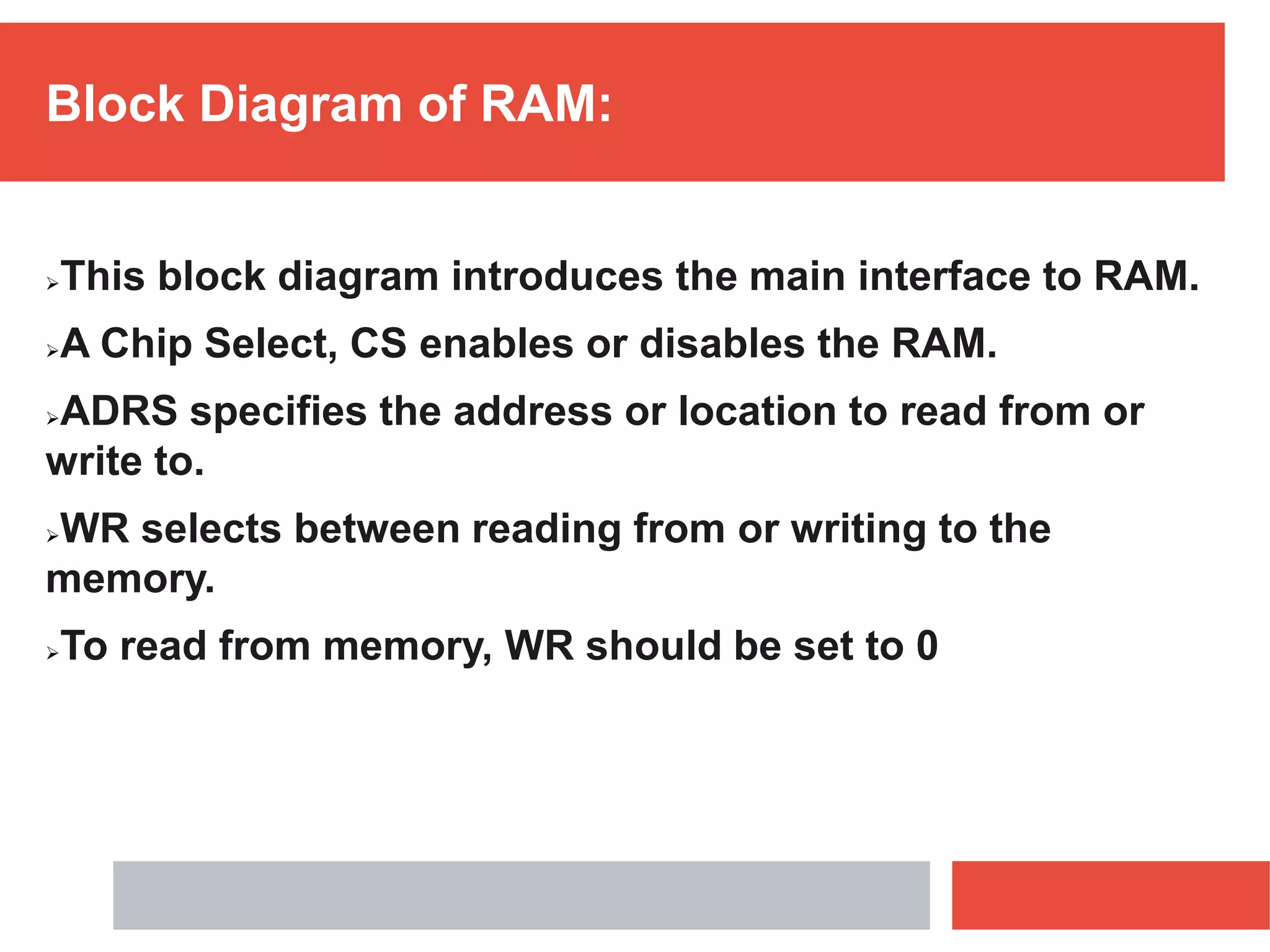
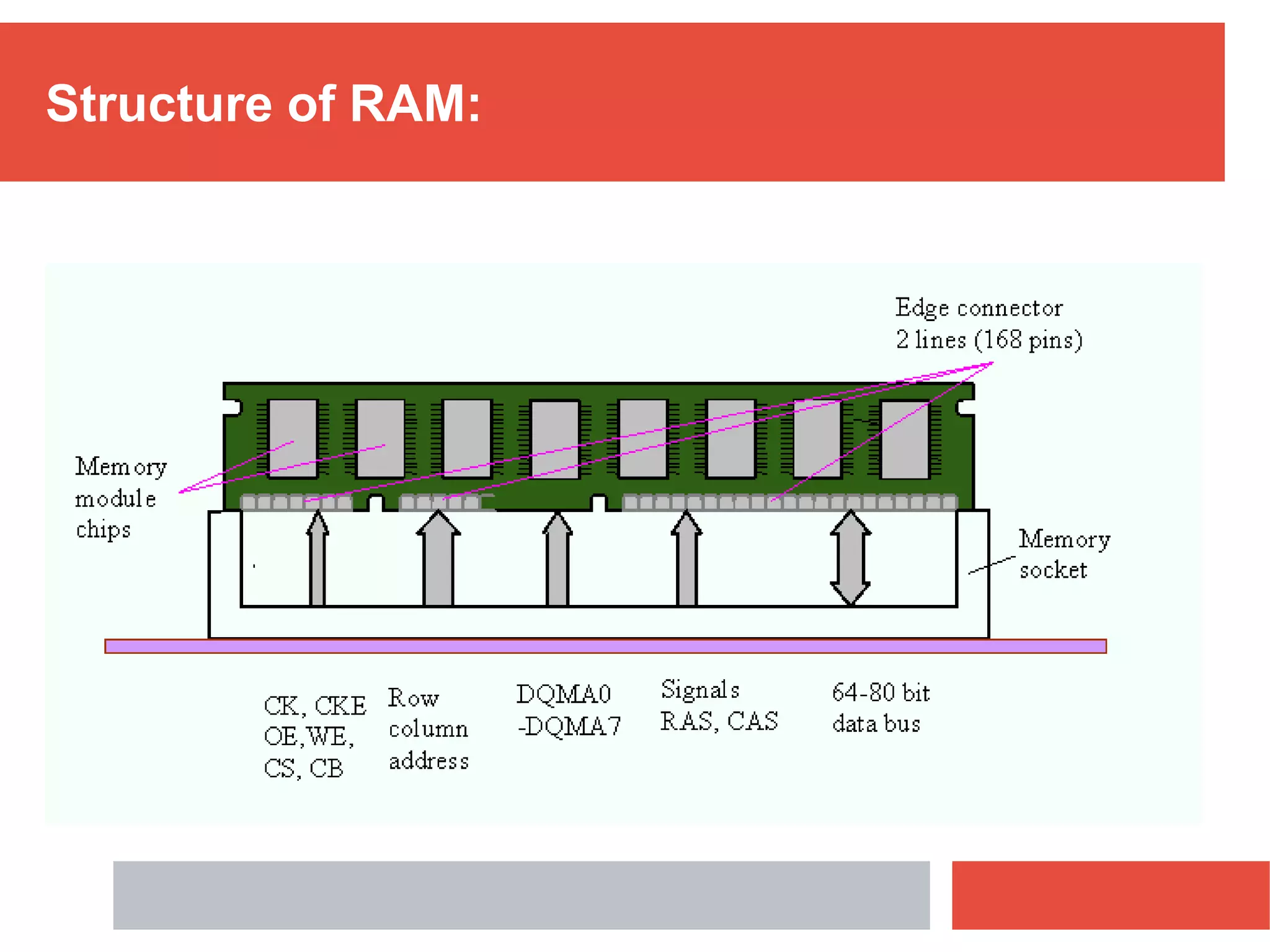
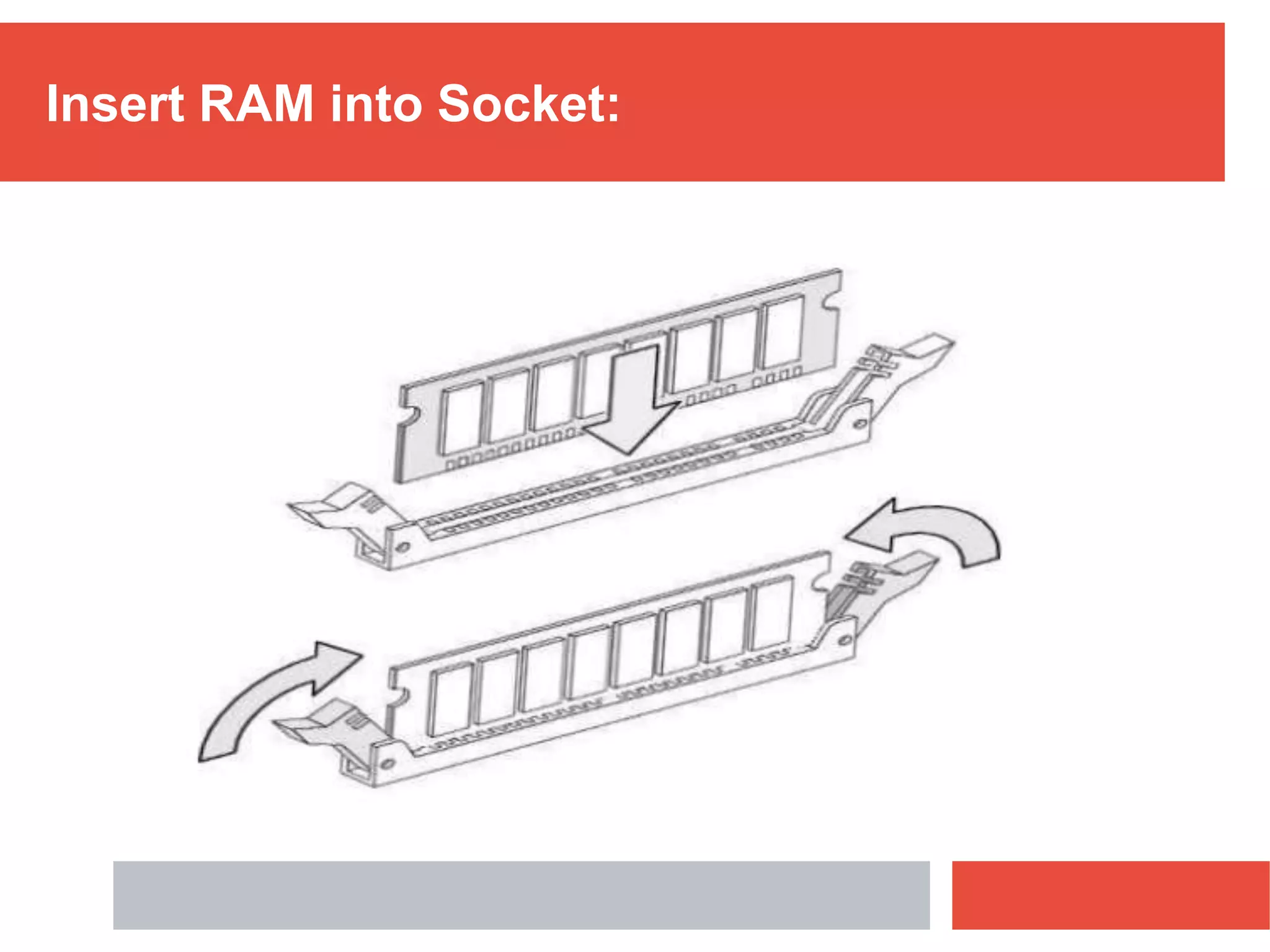
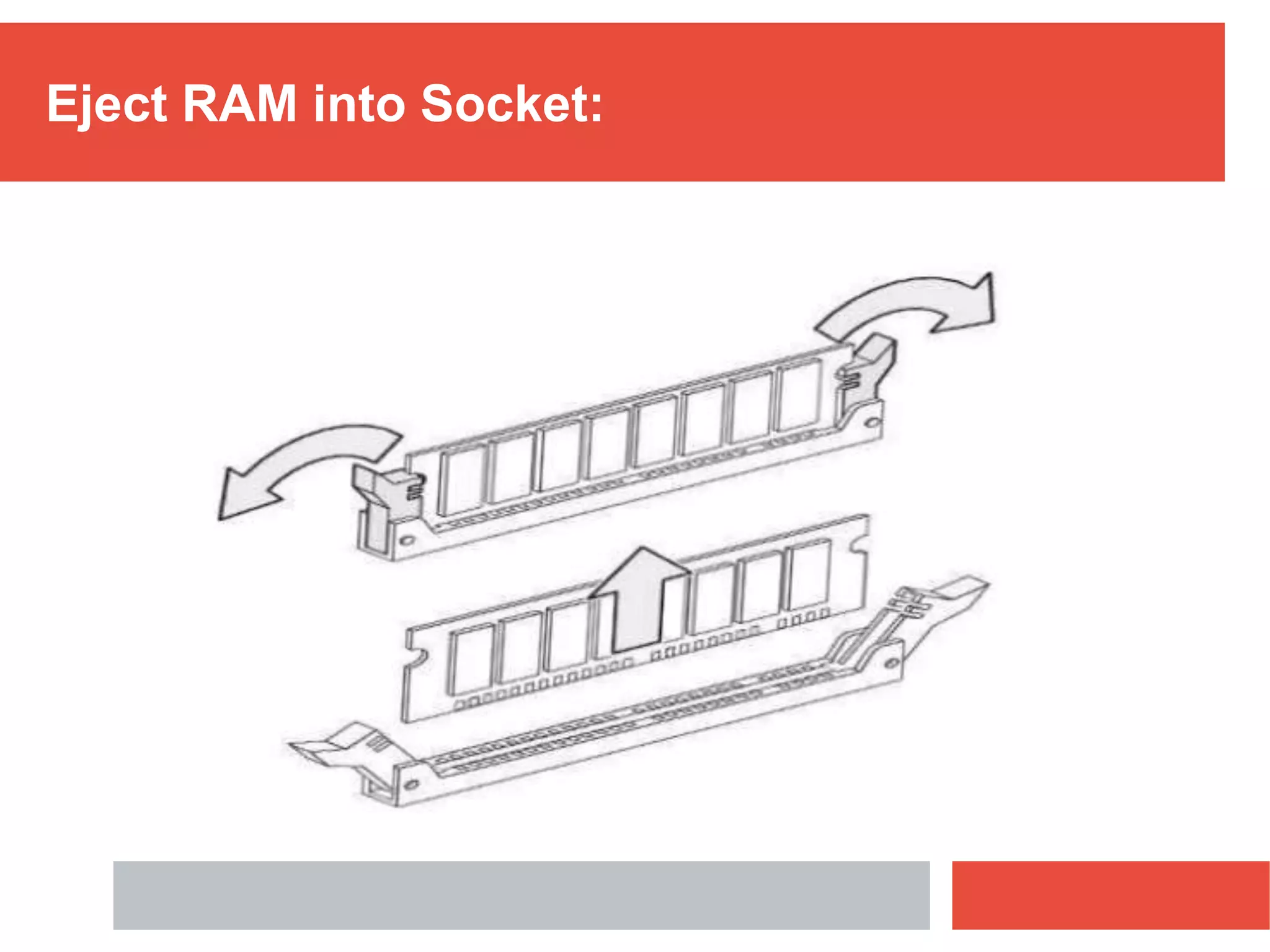
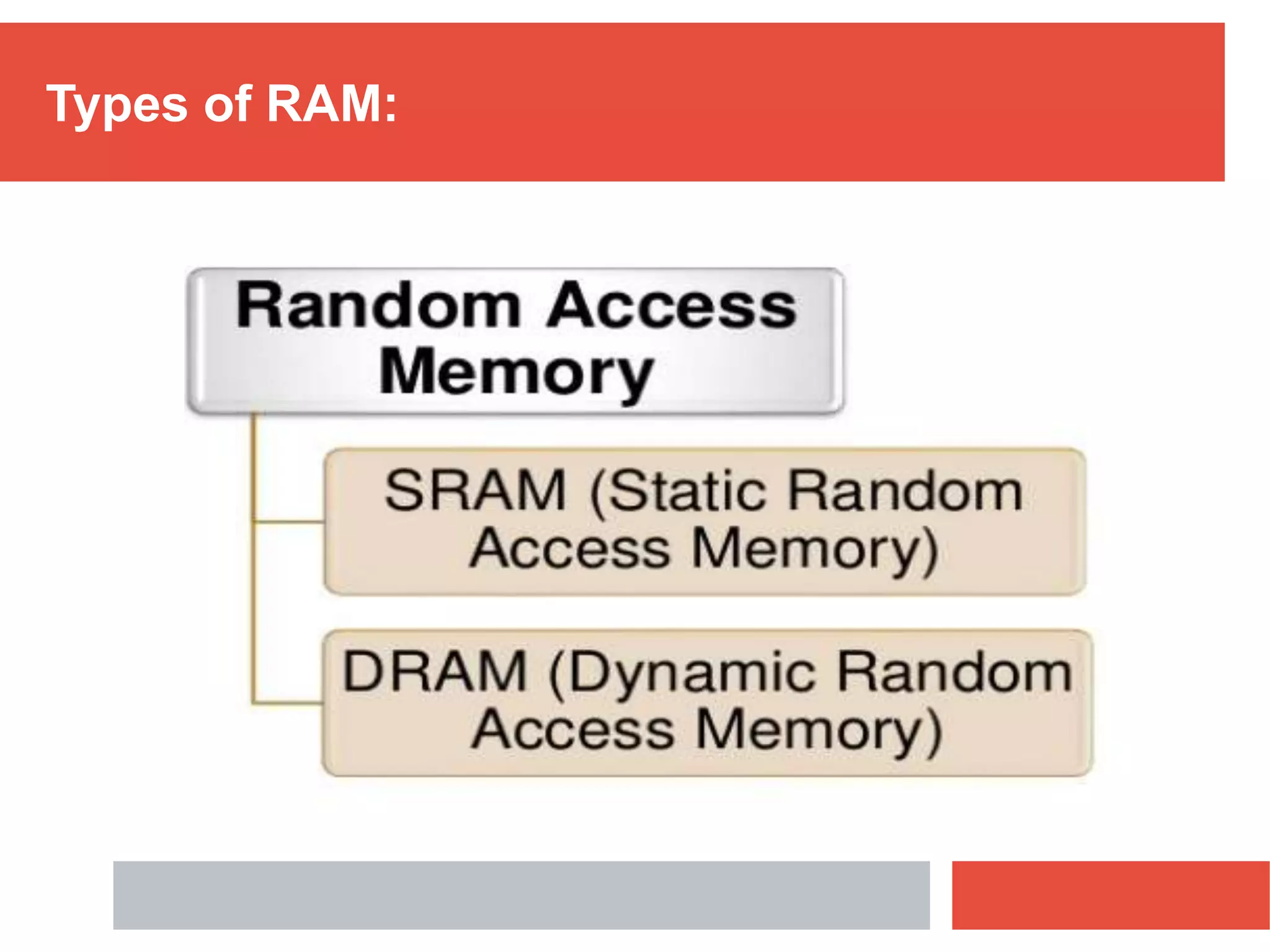
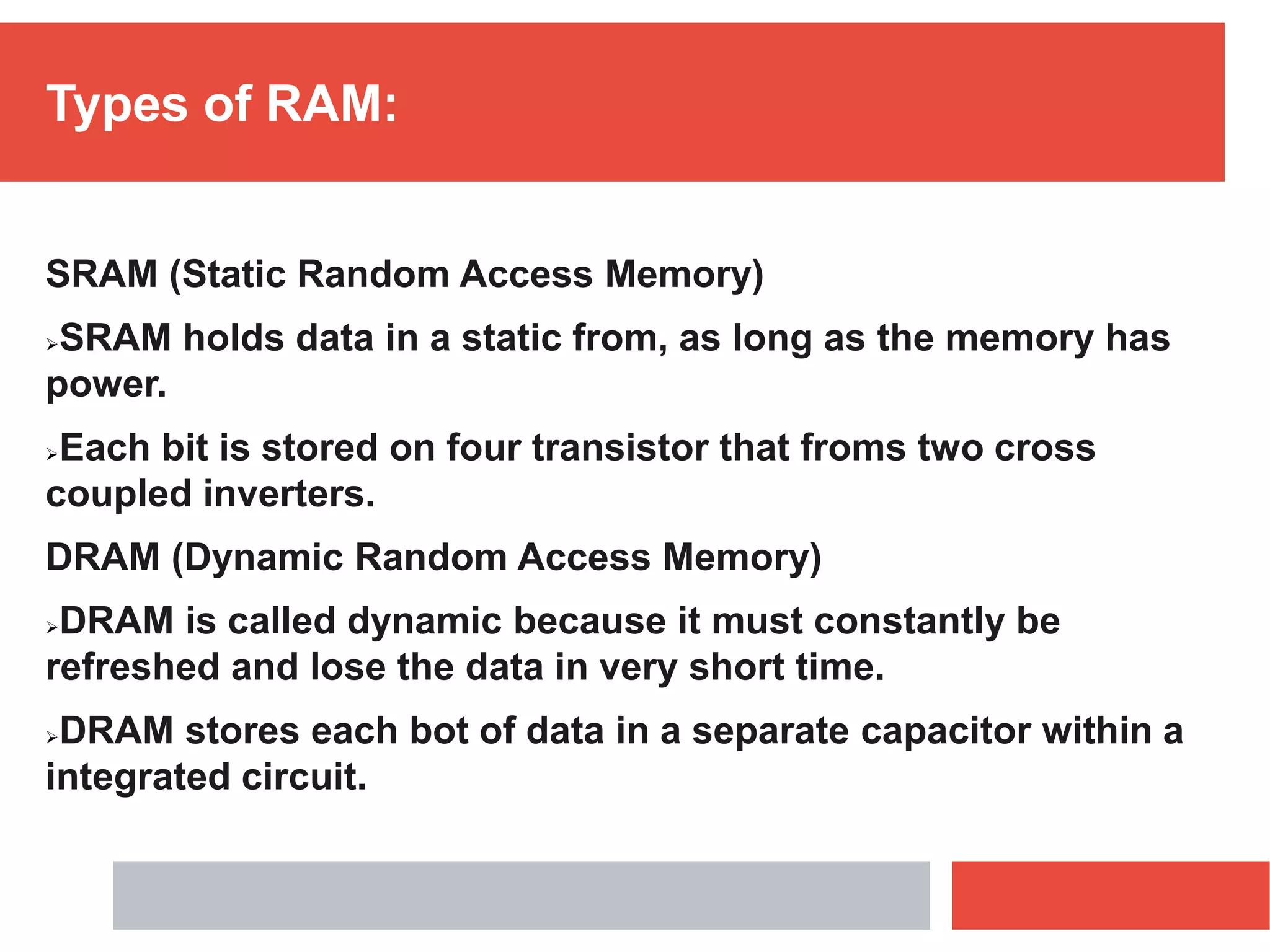
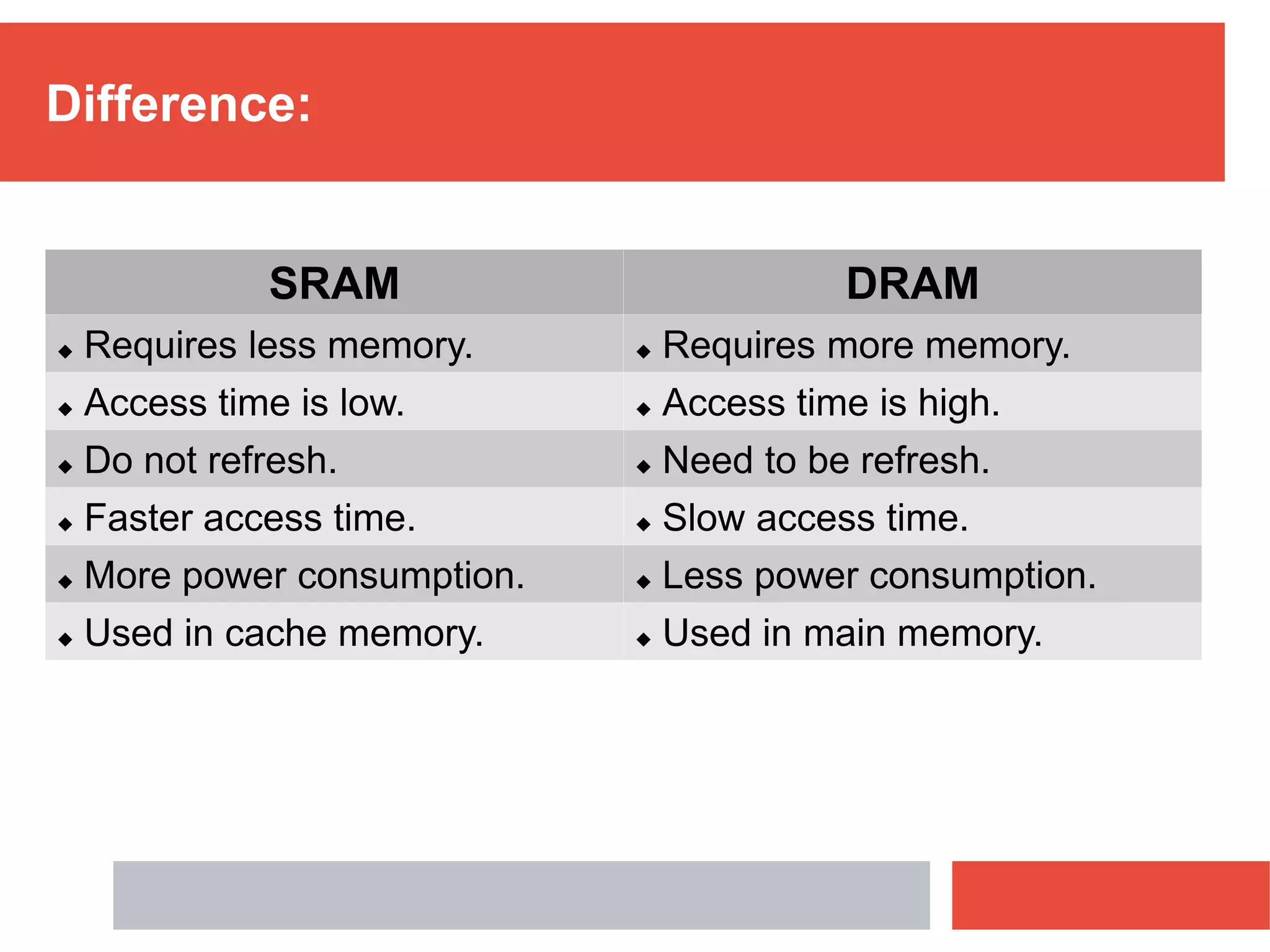
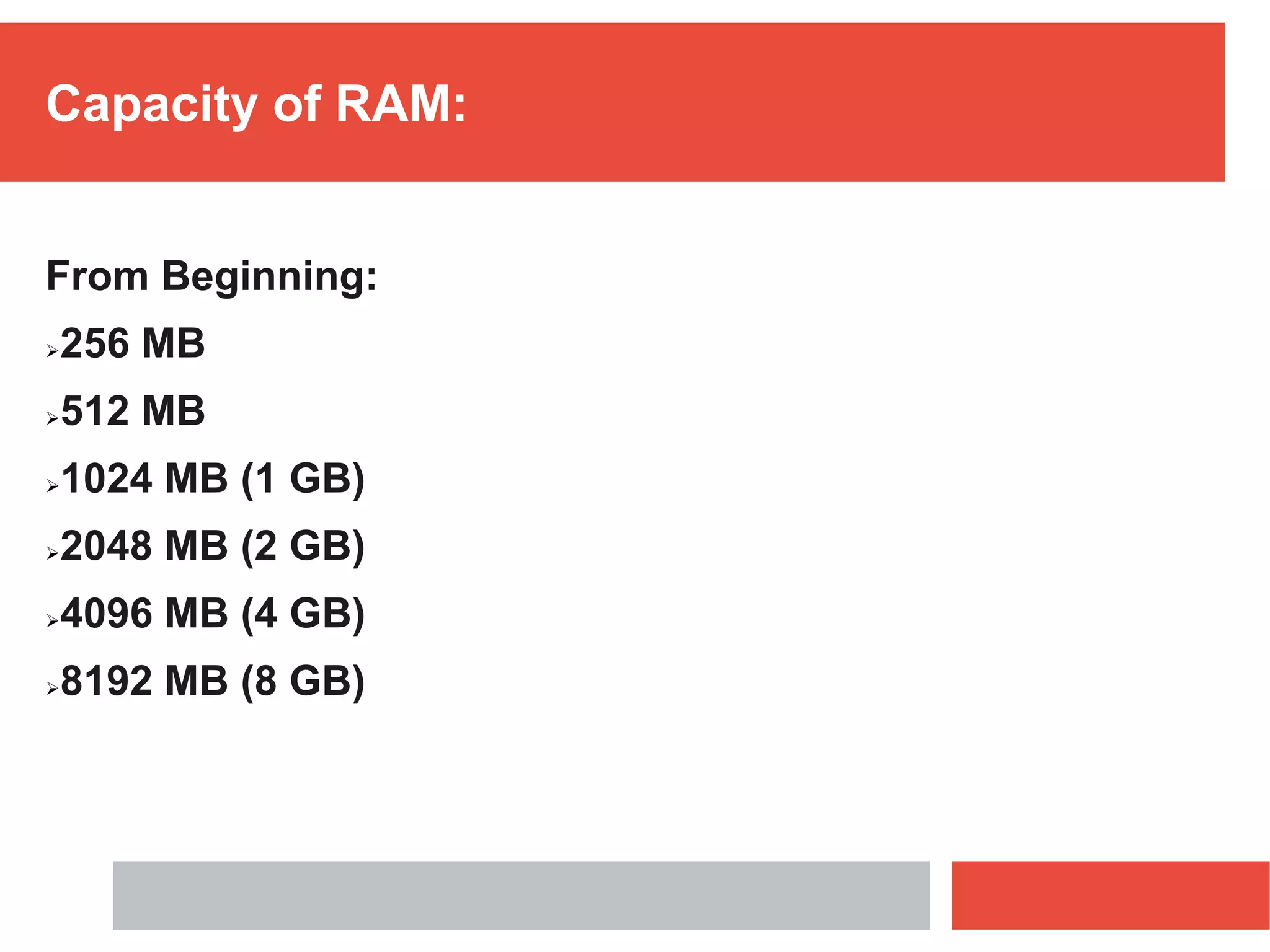
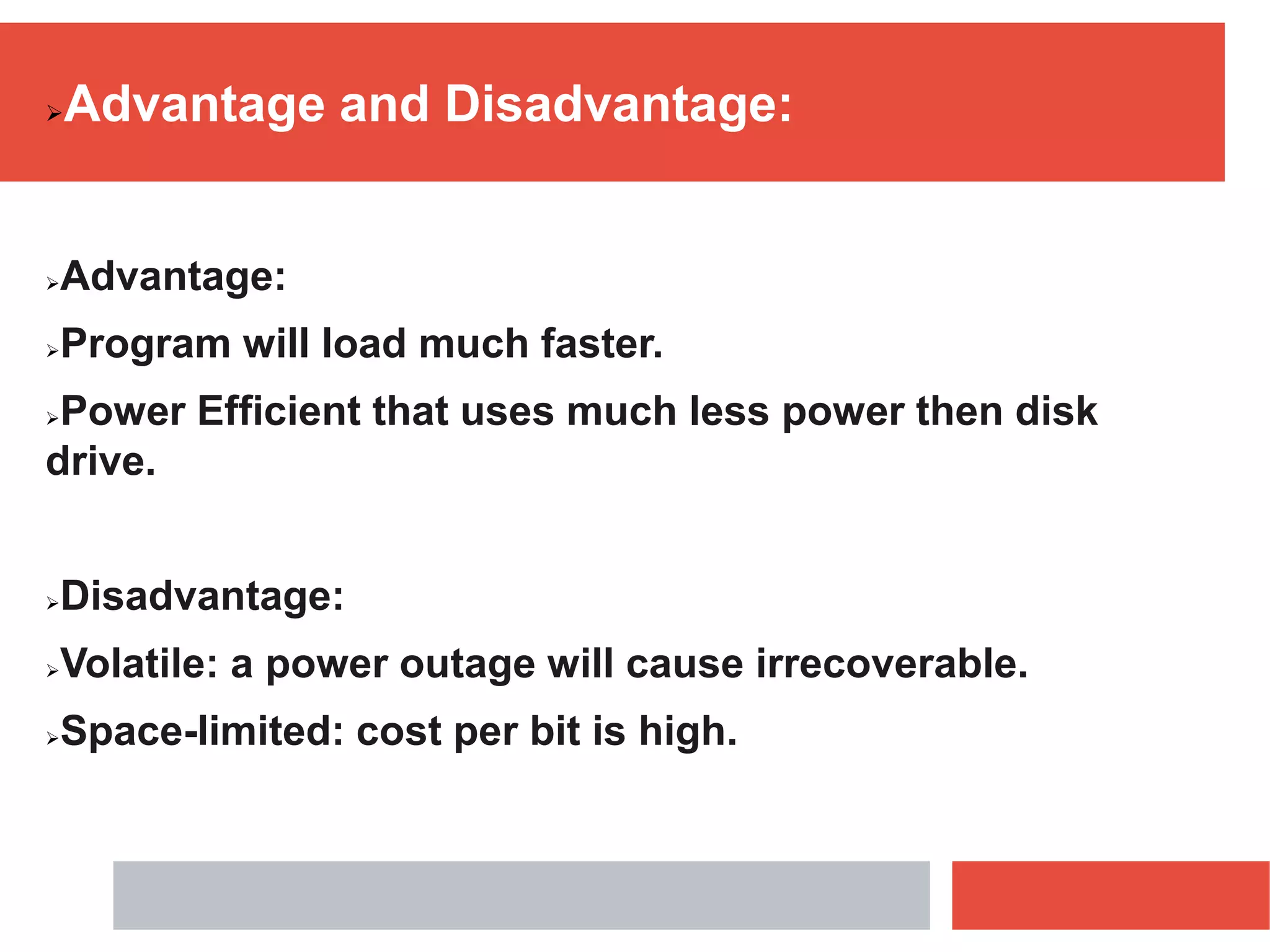
RAM is a type of volatile memory that is used as the main memory in a computer. It allows for fast random access to stored data. RAM was invented in 1968 by Robert Heath and consists of small memory chips arranged on a module. Data is stored temporarily in RAM when programs are opened, allowing for much faster access than reading from storage drives. The two main types are SRAM, which retains data as long as power is supplied, and DRAM, which must be regularly refreshed. RAM provides faster access times than other memory but has less storage capacity and is volatile.