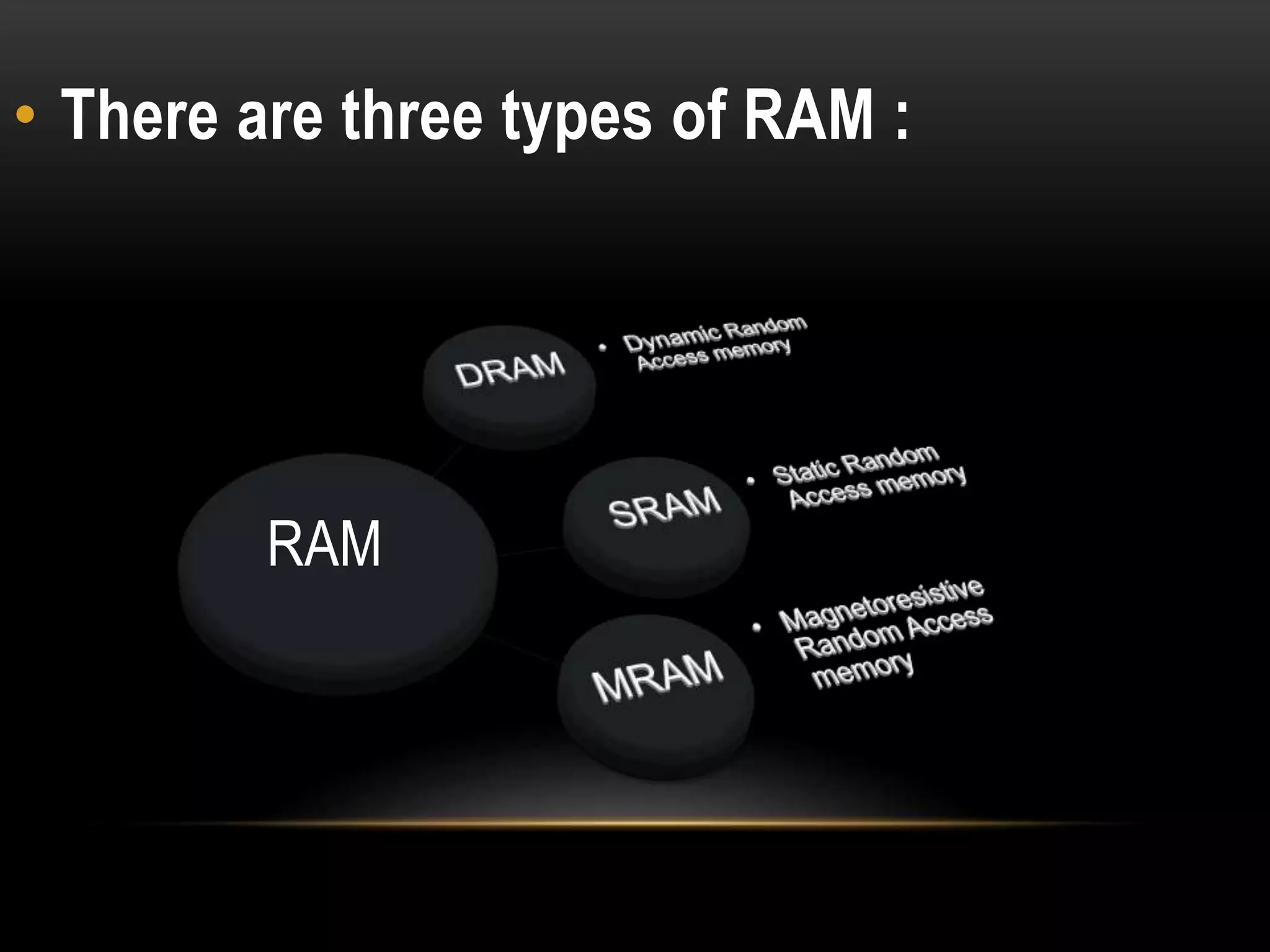
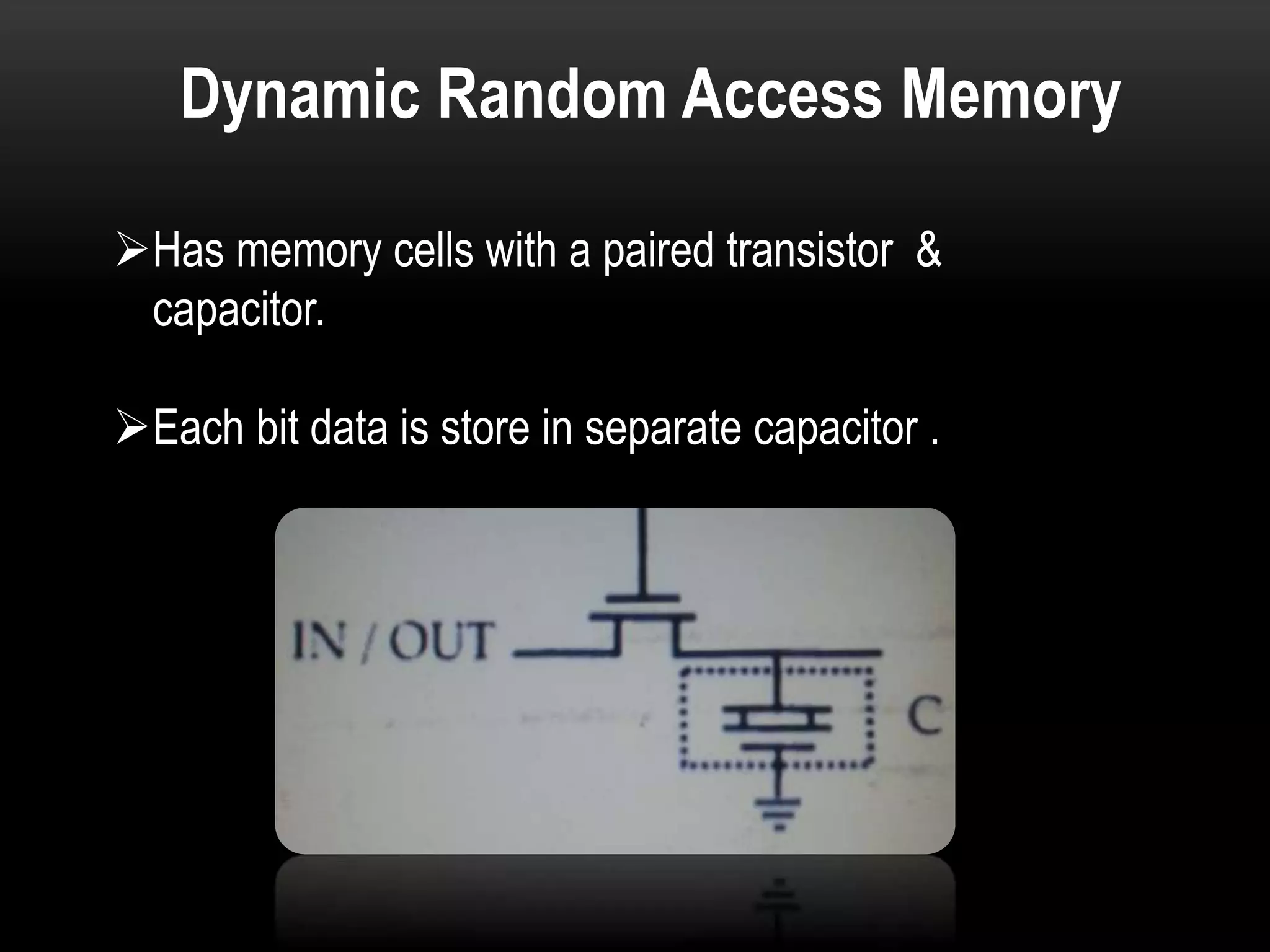
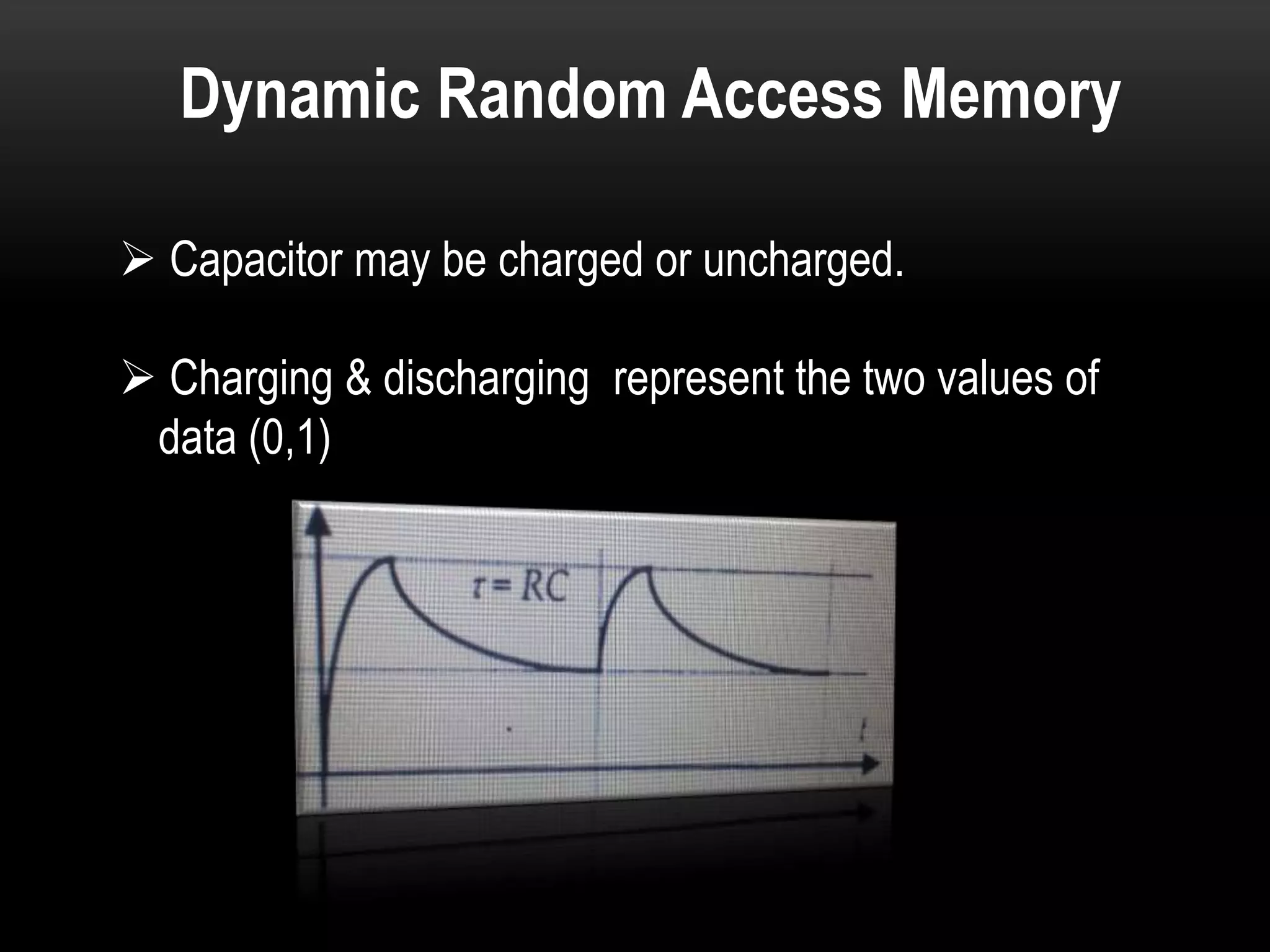
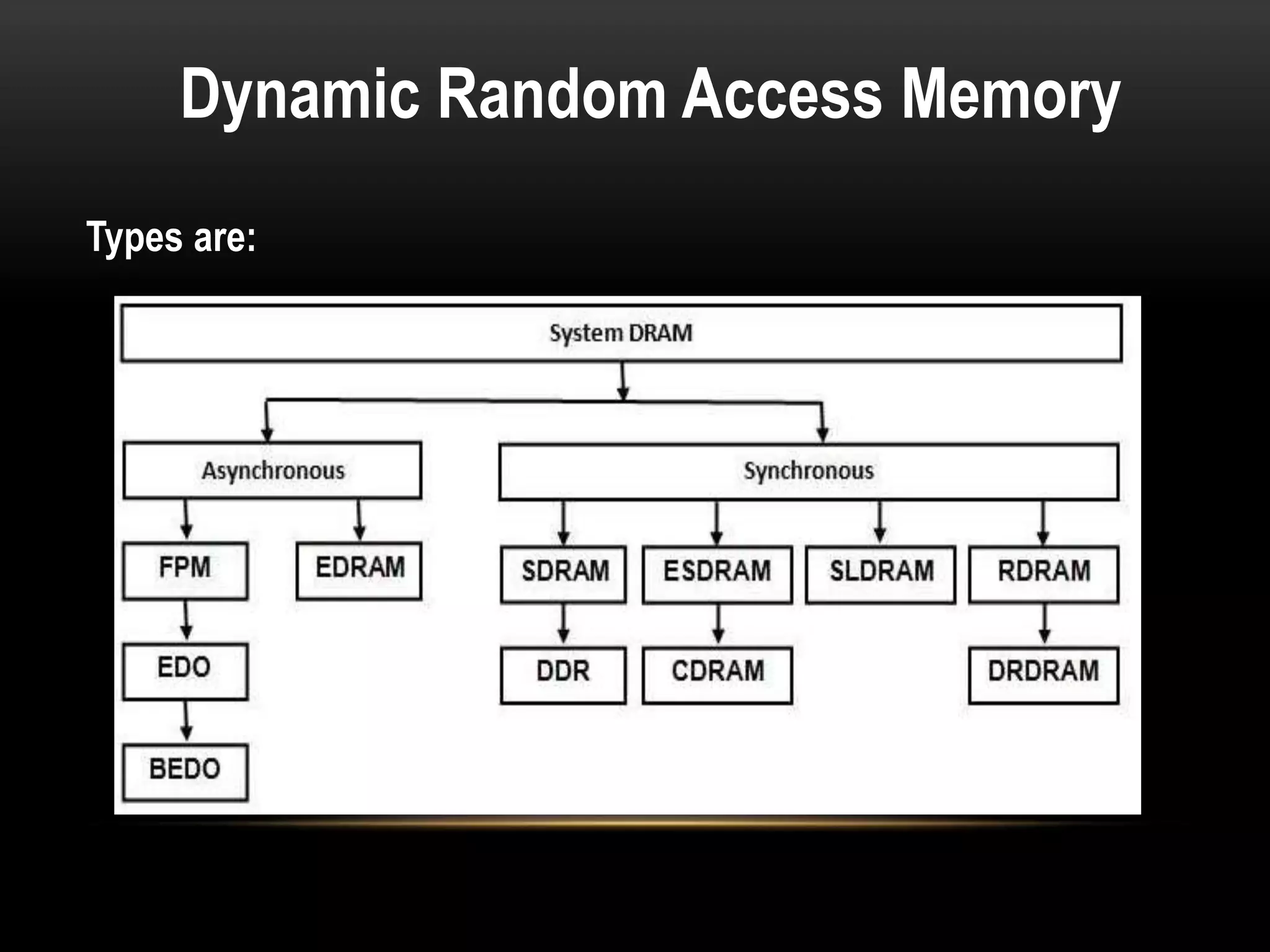
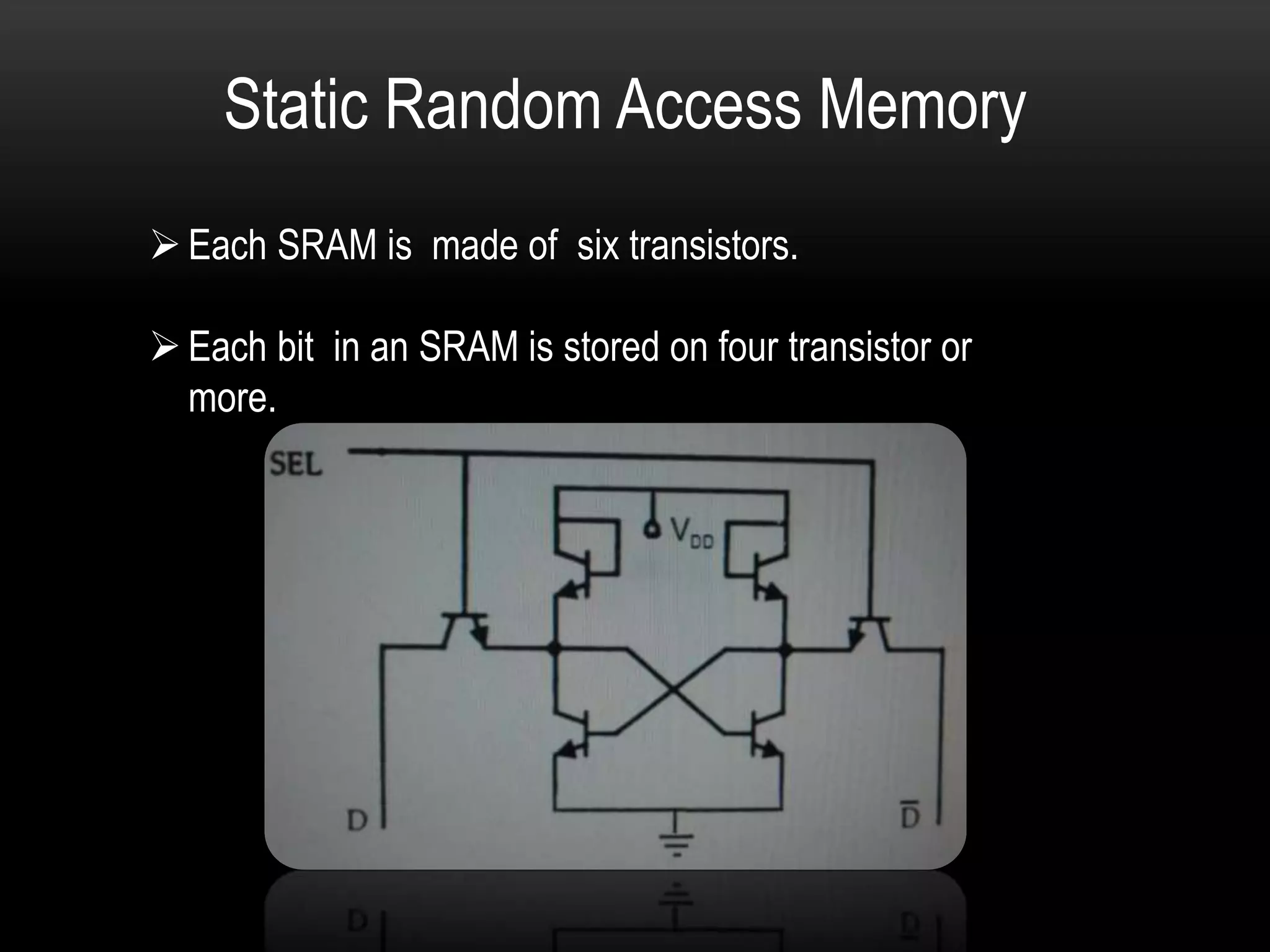
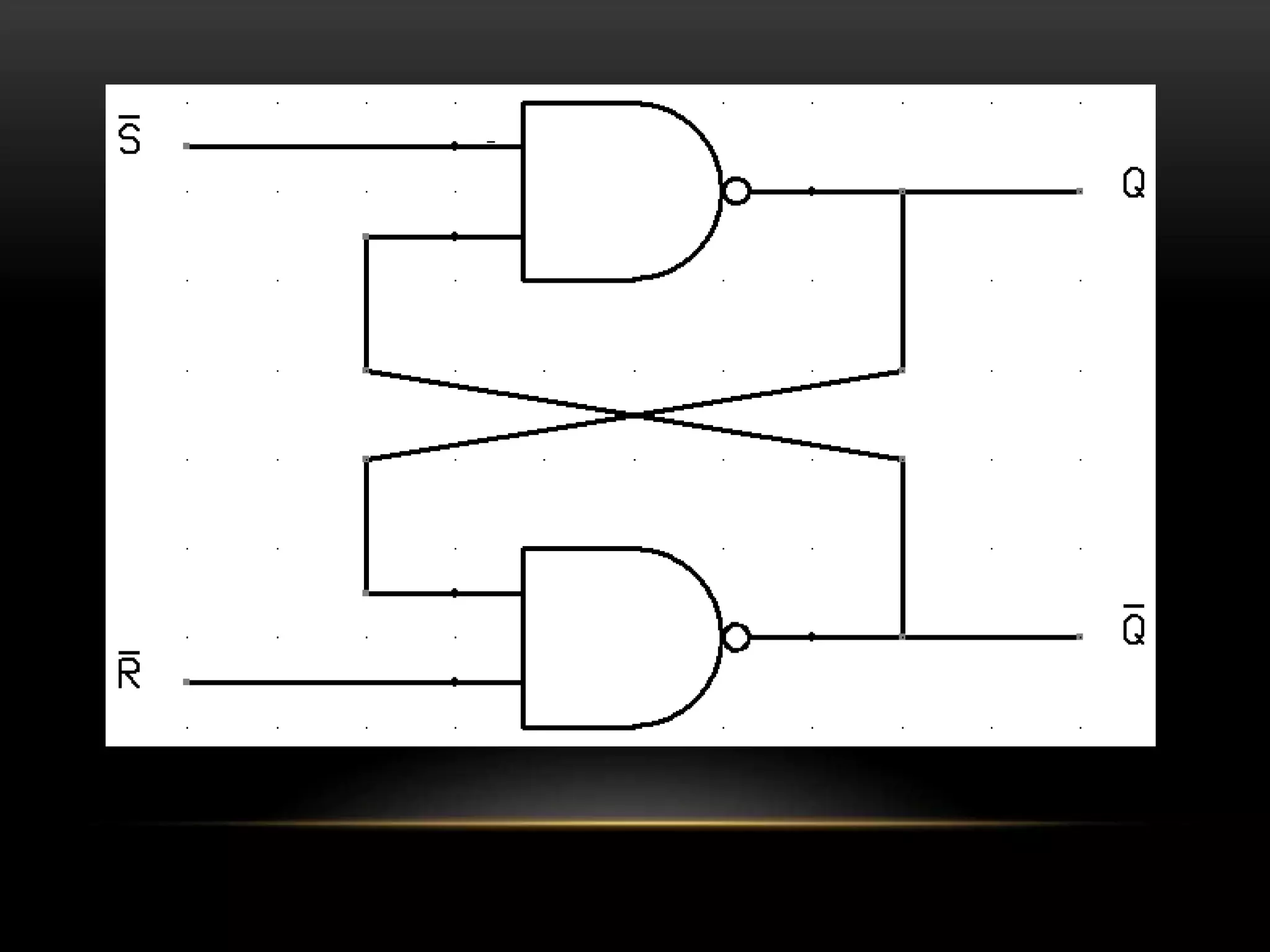
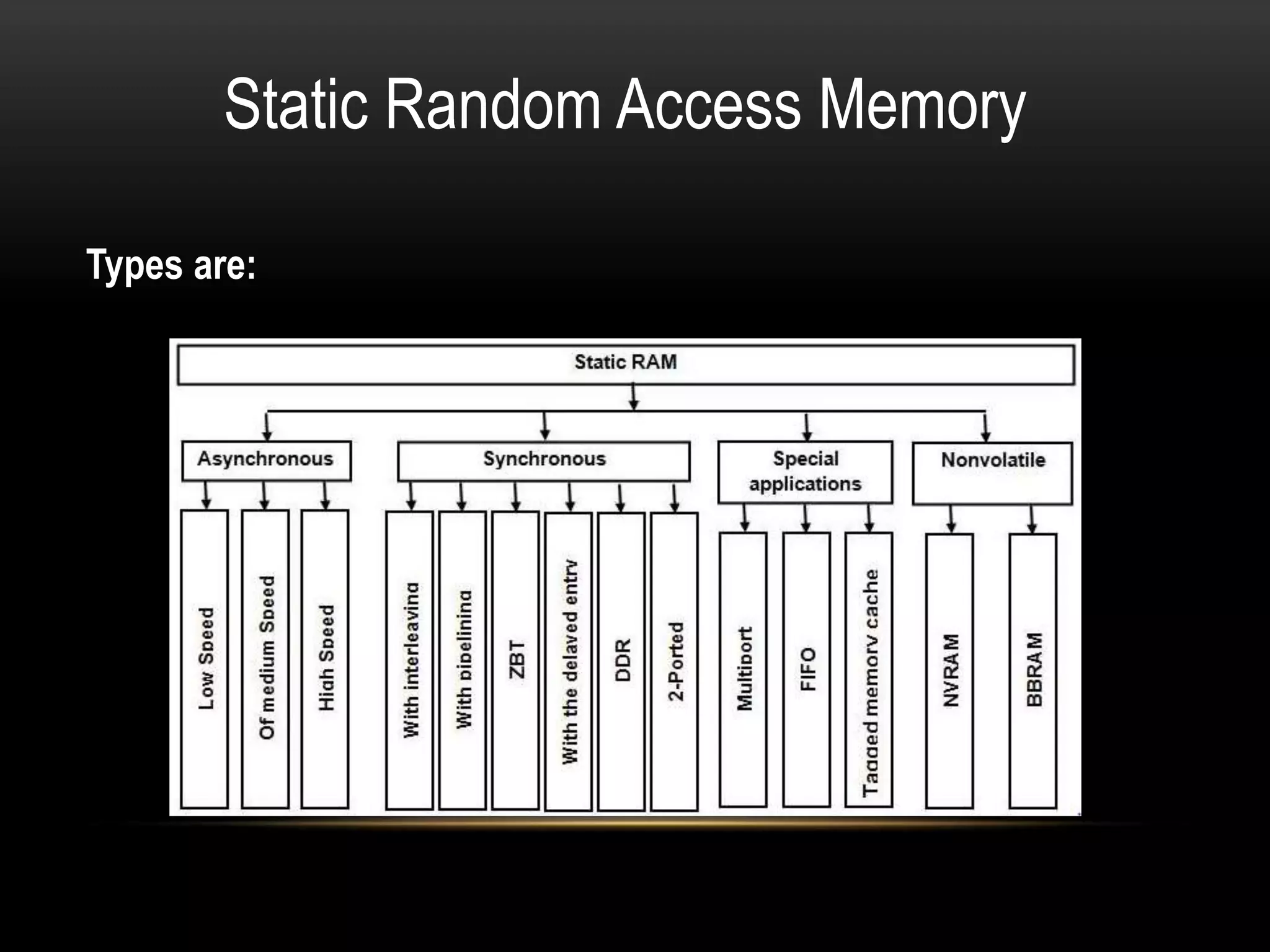
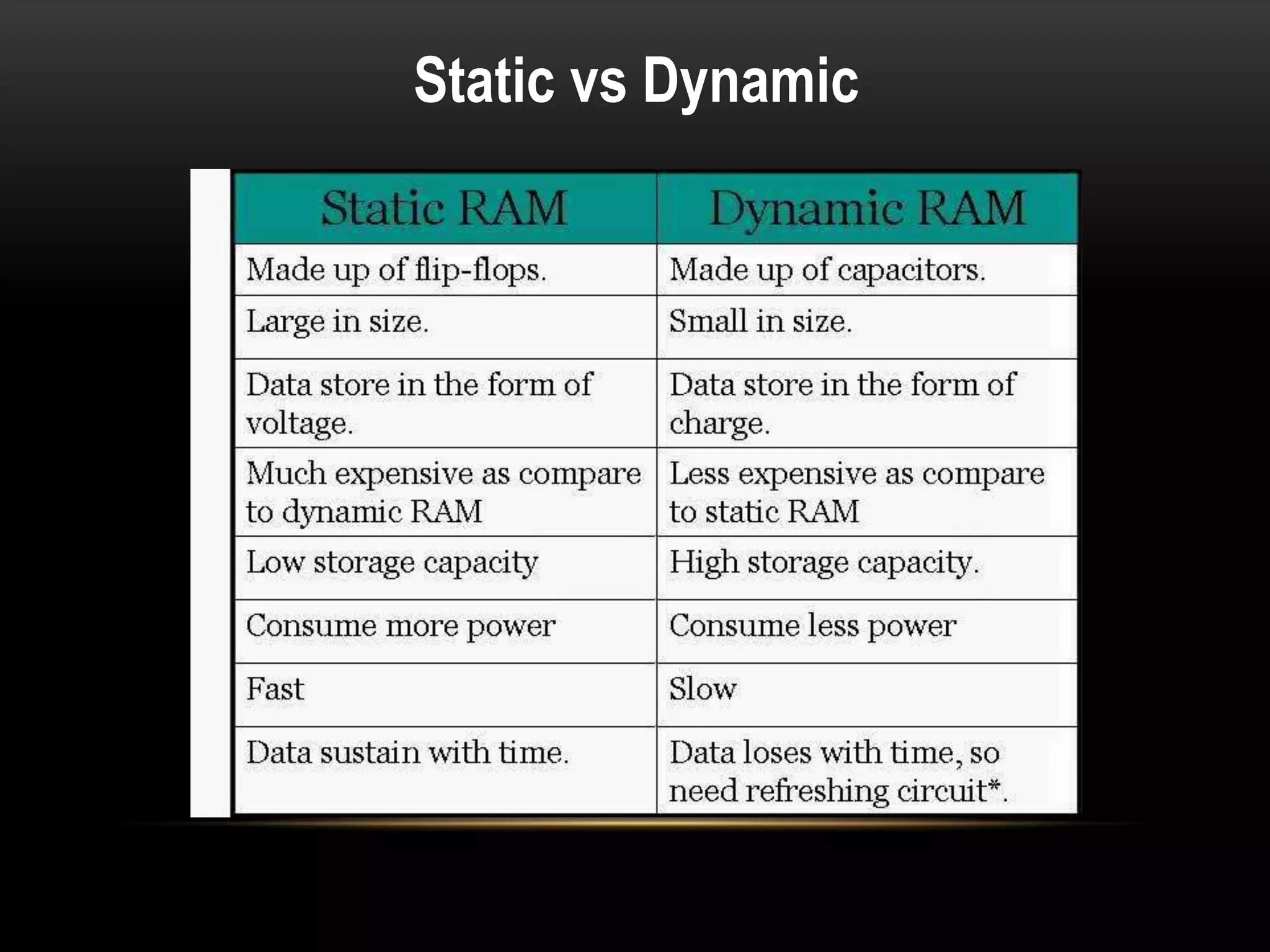
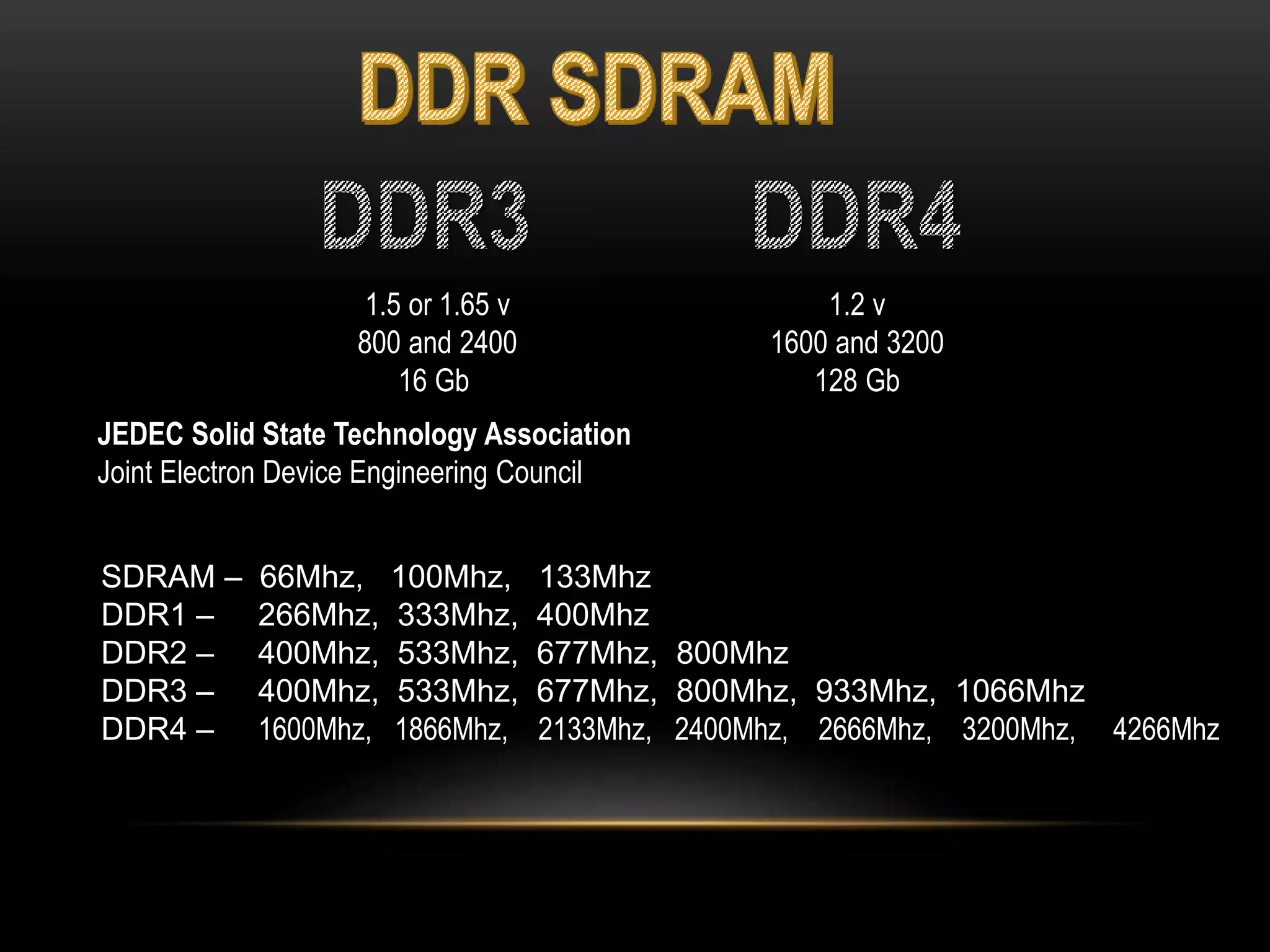
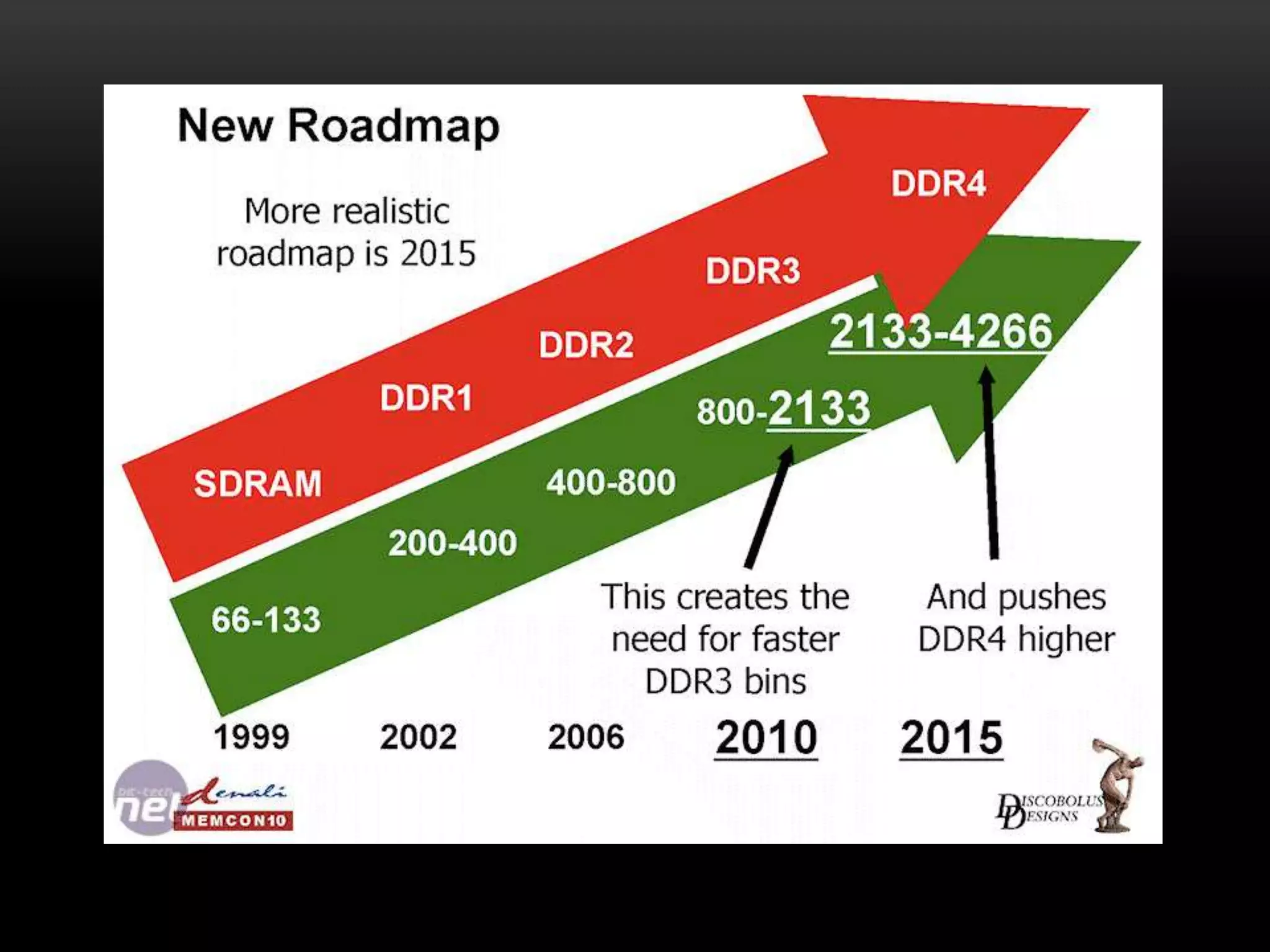
There are three main types of RAM: Dynamic RAM (DRAM), Static RAM (SRAM), and Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM). DRAM stores each bit in a separate capacitor and transistor, while SRAM uses multiple transistors per cell without capacitors. MRAM uses magnetic charges instead of electrical charges, providing greater storage capacity, lower power consumption, and faster access times than other RAM types. RAM technology has advanced from SDRAM to DDR1, DDR2, DDR3, and now DDR4, with increasing speeds and capacities over time.