Term paper
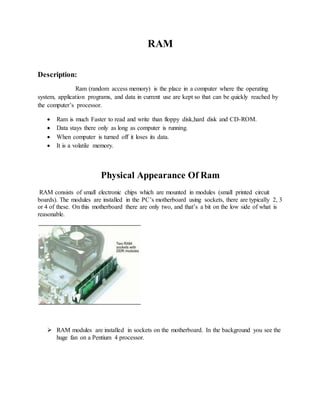
- 1. RAM Description: Ram (random access memory) is the place in a computer where the operating system, application programs, and data in current use are kept so that can be quickly reached by the computer’s processor. Ram is much Faster to read and write than floppy disk,hard disk and CD-ROM. Data stays there only as long as computer is running. When computer is turned off it loses its data. It is a volatile memory. Physical Appearance Of Ram RAM consists of small electronic chips which are mounted in modules (small printed circuit boards). The modules are installed in the PC’s motherboard using sockets, there are typically 2, 3 or 4 of these. On this motherboard there are only two, and that’s a bit on the low side of what is reasonable. RAM modules are installed in sockets on the motherboard. In the background you see the huge fan on a Pentium 4 processor.
- 2. Each RAM module is a rectangular printed circuit board which fits into the sockets on the motherboard: Fig. 512 MB DDR RAM module. On a module there are typically 8 RAM chips which are soldered in place. There can also be 16 if it is a double-sided module. Below is a single RAM chip: Fig. Figur130. A single RAM chip, a 256 megabit circuit. On the bottom edge of the module you can see the copper coated tracks which make electrical contact (the edge connector). Note also the profile of the module; this makes it only possible to install it one way round and in the right socket. Module or chip size All RAM modules have a particular data width, which has to match the motherboard, chipset, and ultimately the CPU. Modules using the two most common RAM types, SD and DDR RAM, are 64 bits wide.
- 3. Different Types Of Ram In the old days Back in the 1980’s, DRAM was used. This was dynamic RAM, which was relatively slow. It was replaced by FPM (Fast Page Mode) RAM which was also dynamic, only a bit faster. Originally, loose RAM chips were installed directly in large banks on the motherboard. Later people started combining the chips in modules. FPM RAM could not run any faster than 66 MHz, but that was fine for the system bus clock frequency in the original Pentium processors. After FPM came EDO RAM (Extended Data Out). EDO is a bit faster than FPM because the data paths to and from the RAM cells have been optimised. The gain was a 3-5 % improvement in bandwidth. The clock frequency could be increased to 75 MHz, but basically, EDO is not very different to FPM RAM. SDRAM The big qualitative shift came in around 1997, when SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM) began to break in. This is a completely new technology, which of course required new chipsets. SDRAM, in contrast to the earlier types of RAM, operatessynchronously with the system bus. Data can (in burst mode) be fetched on every clock pulse. Thus the module can operate fully synchronised with the bus – without so-called wait states (inactive clock pulses). Because they are linked synchronously to the system bus, SDRAM modules can run at much higher clock frequencies. The 100 MHz SDRAM (PC100) quickly became popular, and with new processors and chipsets, the speed was brought up to 133 MHz (PC133).
- 4. DDR RAM It is expensive to produce fast RAM chips. So someone hit on a smart trick in 1999-2000, which in one blow made normal RAM twice as fast. That was the beginning of DDR RAM (Double Data Rate). See the module in Fig. 131. In DDR RAM, the clock signal is used twice. Data is transferred both when the signal rises, and when it falls. This makes it possible to perform twice as many operations per clock pulse, compared to earlier RAM types: Timings DDR RAM exist in many versions, with different the clock frequencies and timings. The timing indicates how many clock cycles there are wasted, when the motherboard waits for the memory to deliver the requested data. With smaller numbers, we have better timings and the CPU having fewer idle clock cycles. The better timing, the more expensive the RAM module is. Rambus RAM Rambus Inc., as already mentioned, has developed a completely new type of RAM technology. Rambus uses a completely different type of chip, which are mounted in intelligent modules that can operate at very high clock frequencies. Here is a brief summary of the system: The memory controller delivers data to a narrow high-speed bus which connects all the RDRAM modules in a long series. The modules contain logic, which stores the data in the format the chips use. Data is written to one chip at a time, in contrast to SDRAM where it is spread across several chips.
- 5. The modules work at 2.5 volts, which is reduced to 0.5 volts whenever possible. In this way, both the build up of heat, and electromagnetic radiation can be kept down. They are encapsulated in a heat conducting, aluminium casing. Rambus RAM thus has a completely new and different design. The modules are only 16 bits wide. Less data is transferred per clock pulse, but the clock frequencies are much higher. As the advanced Rambus modules are quite costly to produce, the technology is on its way out of the market. (Reference Book: PC Architecture By B.Karbo)