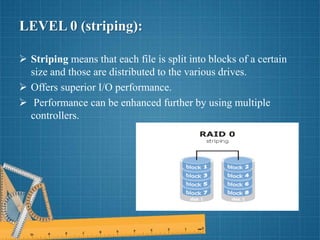
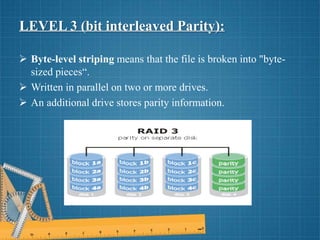
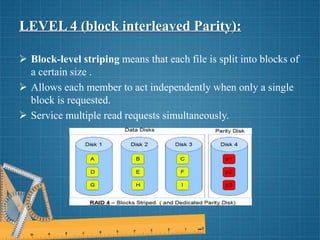
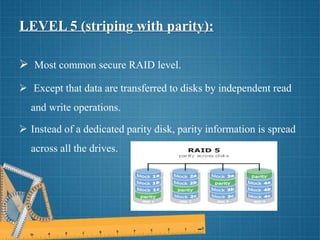
This document discusses different RAID levels for combining multiple disk drives into a logical unit for storage. It defines RAID and explains its purpose is to provide data redundancy, fault tolerance, increased storage capacity and performance. The document then covers RAID levels 0 through 5, describing their ideal uses, advantages, and disadvantages for striping, mirroring, parity and error correction approaches.