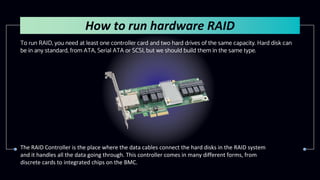
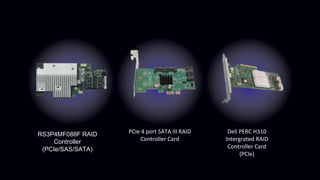
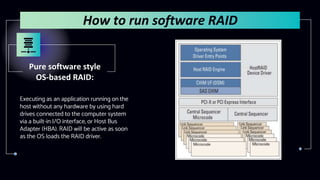
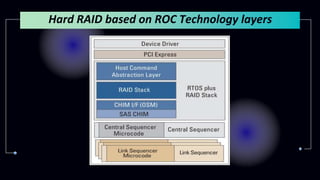
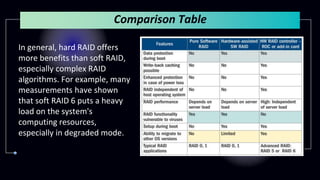
This document provides information about Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID). It defines RAID and explains that RAID allows data to be written across multiple disks for redundancy and increased speed. It then describes different RAID types (RAID 0, 1, 5, 10), their requirements, and pros and cons. RAID can be implemented through hardware or software solutions. Hardware RAID offers better performance but at higher cost than software RAID.