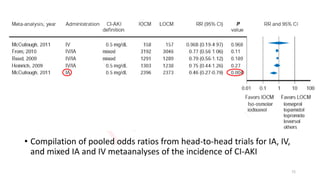
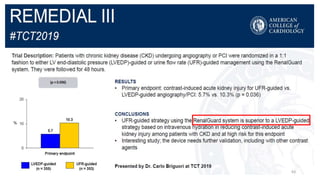
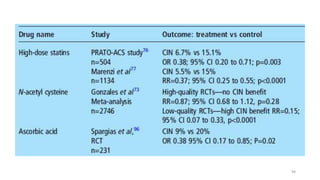
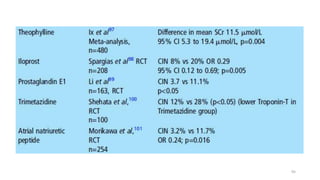
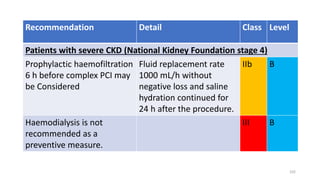
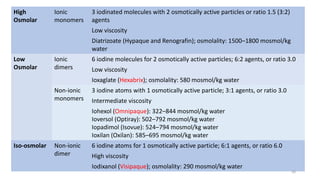
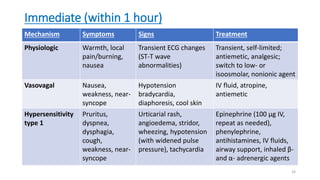
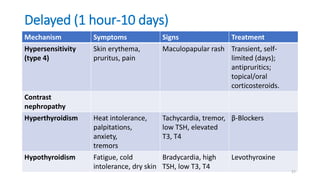
The document discusses the history and chemical properties of radiographic contrast agents, focusing on iodinated contrast agents, their mechanisms of action, and the risks associated with their use, particularly contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN). It outlines the differences between high, low, and iso-osmolar contrast media, detailing their physiological effects and adverse reactions. The document also addresses alternative agents like gadolinium and carbon dioxide, highlighting their application in imaging and safety concerns related to renal function.




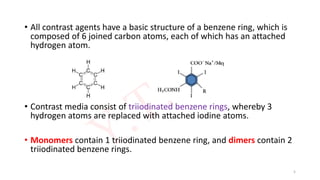





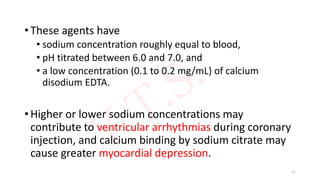

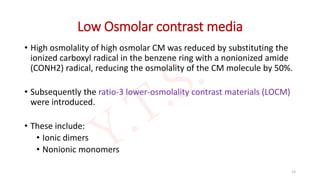












![INTRODUCTION
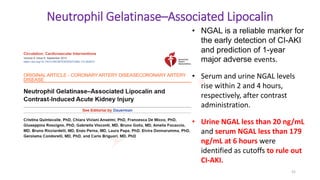
• Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN):
• responsible for one third of all hospital-acquired acute kidney injury
• affects between 1% and 2% of the general population and
• up to 50% of high-risk subgroups following coronary angiography (CAG)
or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
• Varying terminology to describe CIN has been used, e.g.,
• contrast-induced acute kidney injury [CI-AKI],
• contrast nephropathy,
• contrast-associated AKI.
Mehran R, Nikolsky E. Contrast-induced nephropathy: definition, epidemiology, and patients at risk.
Kidney Int Suppl 2006: S11–15
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contrast-inducednephropathy-220327123529/85/Contrast-induced-nephropathy-pptx-34-320.jpg)















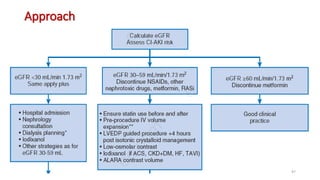
![Minimising contrast volume
• The maximal acceptable contrast dose (MACD) which is defined as
• “5 mL×body weight [kg])/baseline serum creatinine [mg/dL]”
• This value should not be exceeded.
• A single invasive approach should ideally be adopted, with CAG followed
by ad hoc PCI to reduce the risk of atheroembolic complications while
minimizing contrast volumes to <4 mL/kg or V/CrCl <3.7:1.
• A slight reduction in contrast volume was documented with the use of
an automated contrast injector system, although it did not impact the
occurrence of CI-AKI.
61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contrast-inducednephropathy-220327123529/85/Contrast-induced-nephropathy-pptx-61-320.jpg)