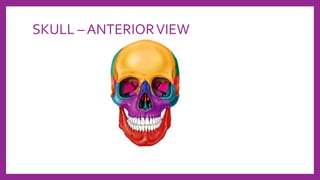
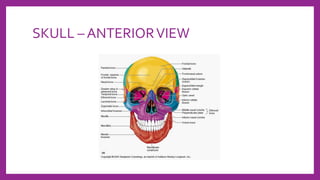
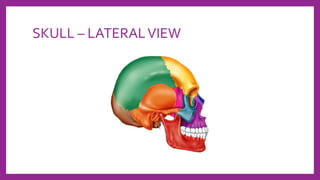
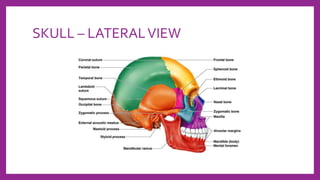
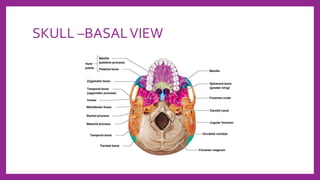
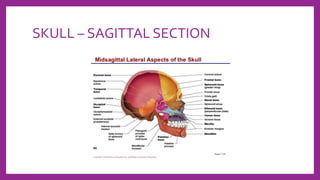
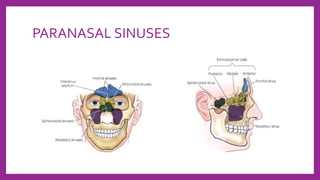
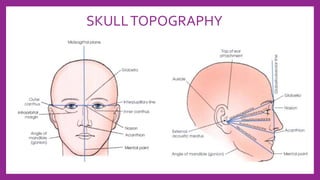
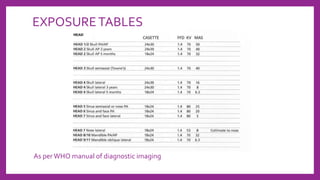
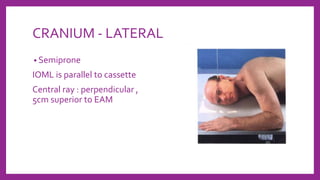
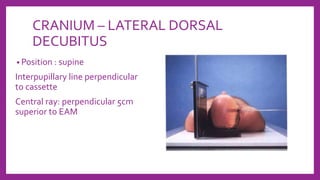
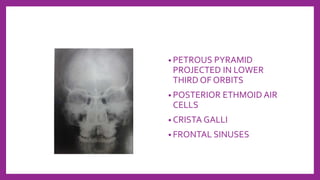
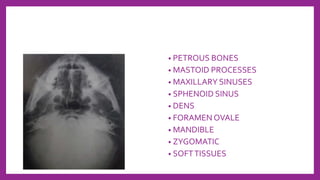
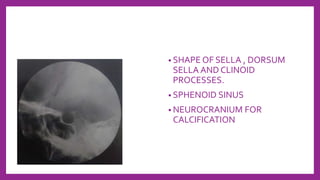
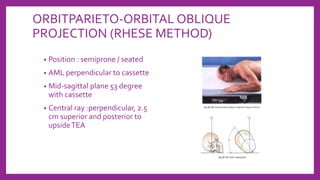
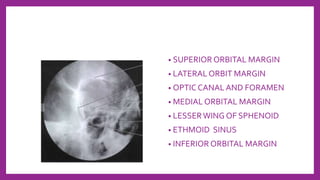
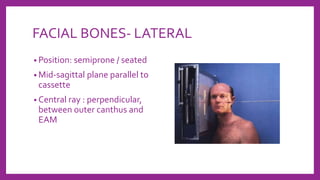
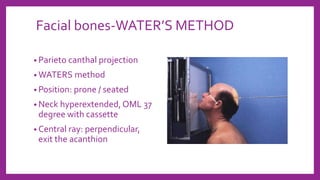
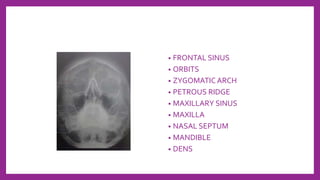
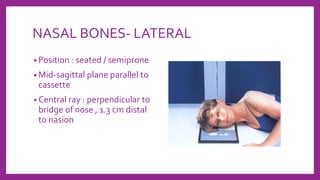
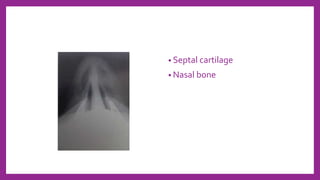
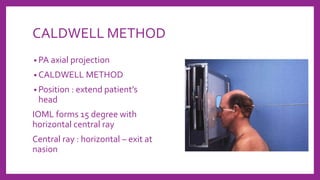
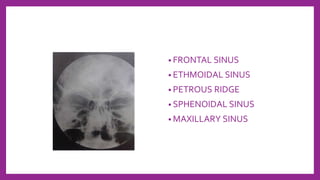
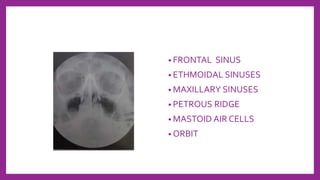
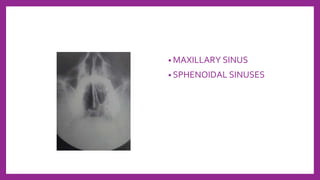
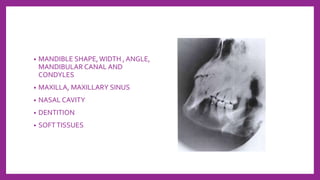
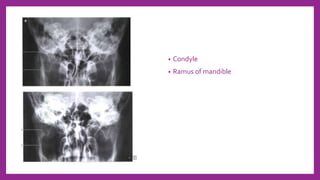
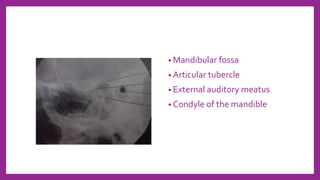
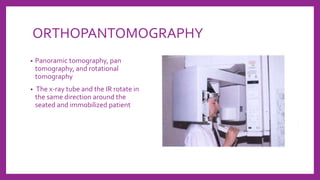
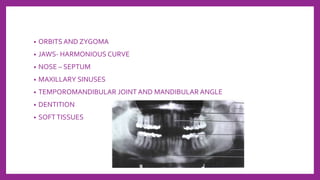
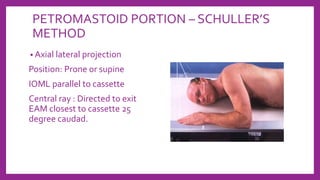
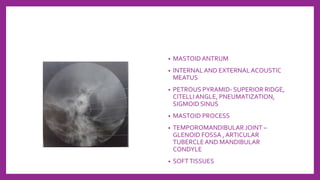
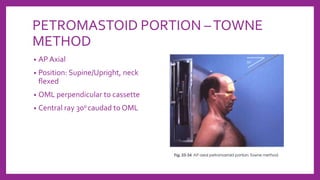
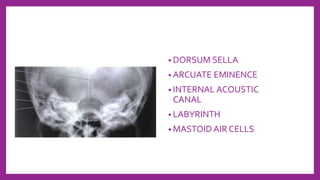
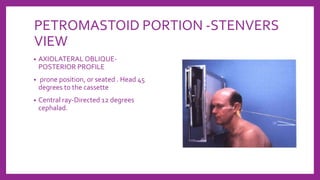
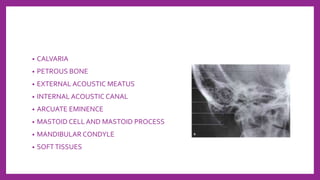
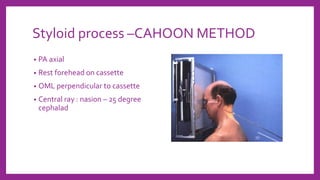
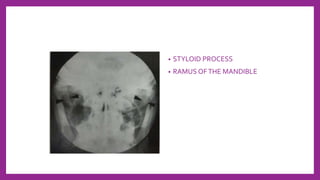
This document provides information on various radiological techniques and views for imaging the skull. It discusses different projections for visualizing the entire skull, specific bones like the nasal bones, paranasal sinuses, mandible, zygomatic arch, and petromastoid portion. It also covers tomosynthesis techniques like orthopantomography. For each view, it provides details on patient positioning, central ray angulation, and anatomical structures visible. The document aims to guide radiologists in proper technique and checklist items for interpreting skull radiographs.