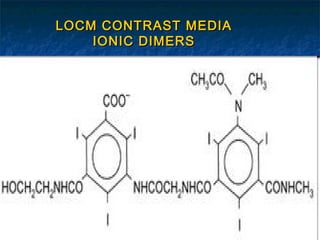
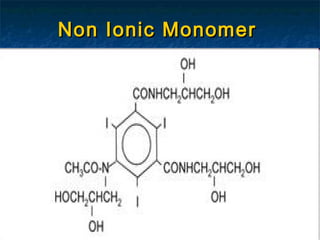
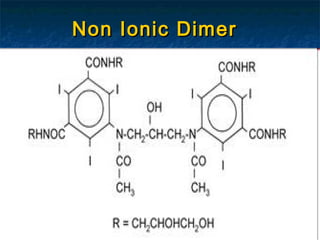
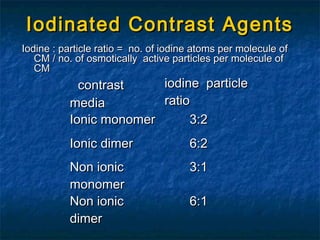
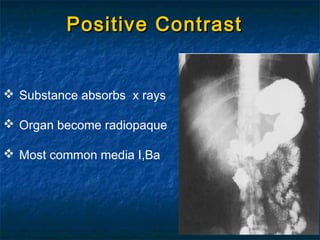
Contrast media are agents used to enhance the visibility of structures in medical imaging. There are several types including positive contrast media which make structures appear brighter on scans, and negative contrast media which make structures seem darker. Common contrast agents contain iodine and can be ionic monomers, ionic dimers, non-ionic monomers, or non-ionic dimers. While contrast imaging provides important medical information, the agents sometimes cause side effects from mild reactions like nausea to more severe issues like pulmonary edema. Care must be taken with patients having risk factors for complications.













![ Further classified on basis of % ofFurther classified on basis of % of
compound in the solution.eg. 30%, 70%compound in the solution.eg. 30%, 70%
[ UROGRAFFIN 76%][ UROGRAFFIN 76%]
Sodium is toxic to endothelium & BBB SoSodium is toxic to endothelium & BBB So
avoided in venography and cerebralavoided in venography and cerebral
angiography.angiography.
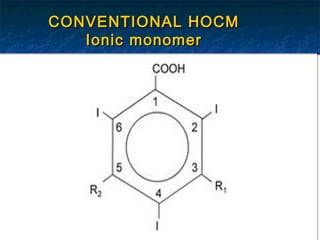
Ionic MonomerIonic Monomer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jayanti-150811061057-lva1-app6891/85/Contrast-Media-16-320.jpg)