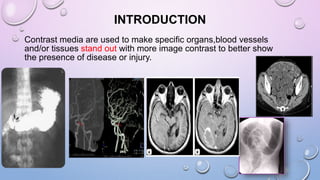
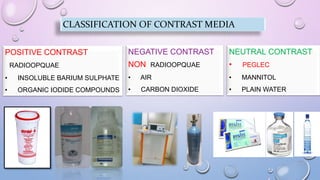
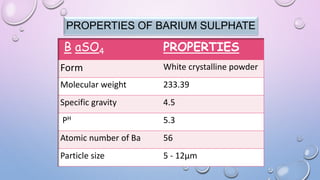
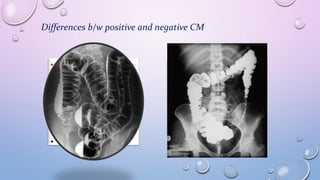
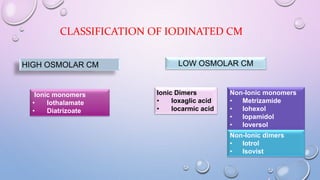
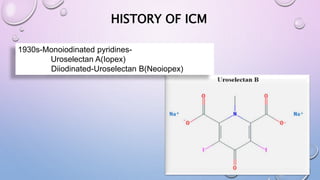
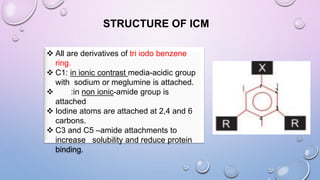
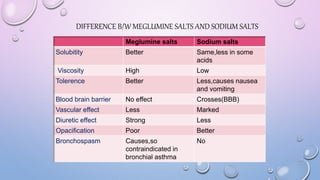
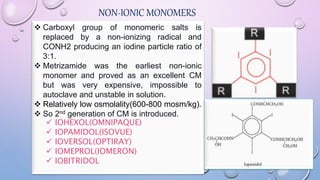
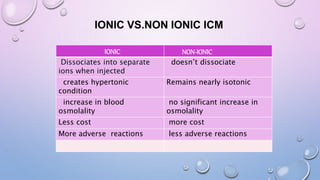
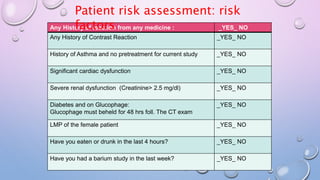
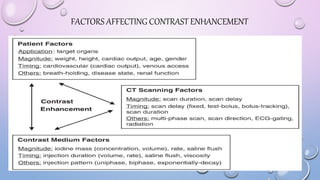
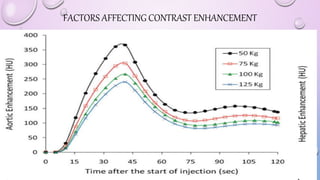
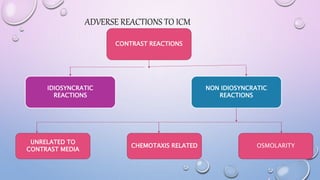
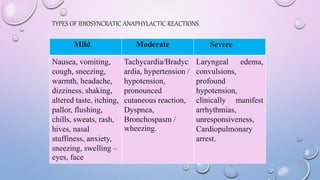
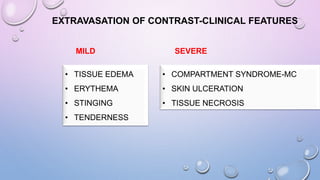
This document provides an overview of contrast media used in medical imaging, including barium sulfate, iodinated contrast media, and gas agents. It discusses the classification, properties, administration, and adverse reactions of different contrast types. Barium sulfate is described as the preferred oral and rectal contrast due to its insolubility, inertness, and ability to coat the gastrointestinal mucosa. Iodinated contrast media are classified based on osmolality, ionicity, and iodine content. Water-soluble iodinated contrasts are preferred over oil-based agents. An ideal contrast is outlined as having properties like water solubility, chemical stability, biological inertness, and renal excretion.