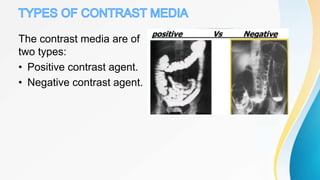
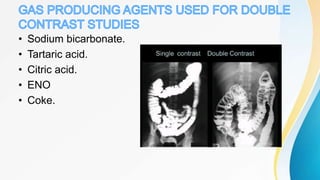
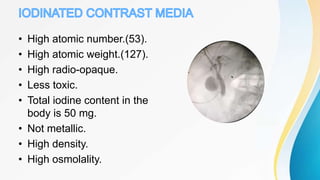
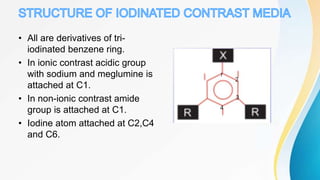
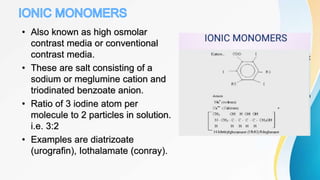
This document discusses the history and use of contrast media and emergency drugs for radiology procedures. It begins by outlining the early discoveries of contrast agents from the 1890s to the 1920s. It then describes how contrast agents are administered and their properties like osmolality and viscosity. The document discusses common contrast agents like barium, iodine-based agents, and categorizes them as high vs low osmolar. It outlines risks of contrast media and expected adverse reaction rates. The document concludes by listing emergency equipment needed to treat potential severe reactions.