1. The document introduces radio communication and its history, including early experiments by Maxwell, Hertz, Tesla, and Marconi in the late 19th century.
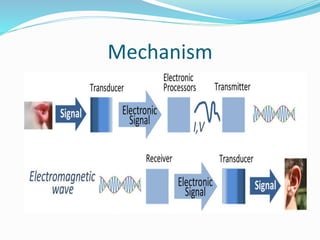
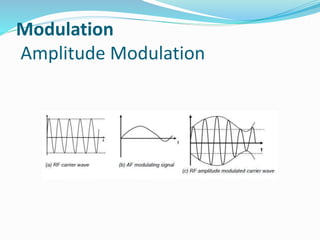
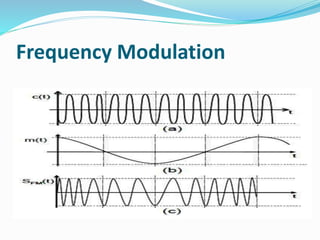
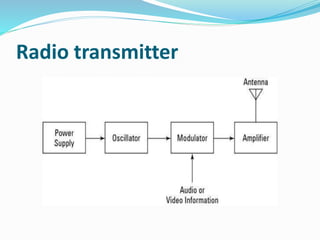
2. It describes the classification of radio waves by frequency range and the basic mechanisms, components, and uses of radio transmitters, receivers, and technology like amplitude modulation and frequency modulation.
3. Advantages of radio communication are its low cost and ability to transmit without wires, while disadvantages are low data rates and inability to transmit video or images. Future technologies discussed include cognitive radio networks.























![References
[1 ] Microphone IMAGE. Posted by Tom (2007). Houston’s
Clear Thinkers. Weblog [Online] August 22. Available
from:
http://blog.kir.com/archives/2007/08/sports_talk_rad.asp
[Accessed 22/01/11]
[ 2] National Astronauts and Space Administration. [Web
Definition] [Accessed 22/01/11] Available form:
http://science.hq.nasa.gov/kids/imagers/ems/radio.html
[3] National Astronauts and Space Administration(2010).
[Online Image] [Accessed 22/01/11] Available form:
http://science.hq.nasa.gov/kids/imagers/ems/radio.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicradiocommunicationoperation-130826212156-phpapp02-151006131609-lva1-app6891/85/Basic-radio-communication-29-320.jpg)

