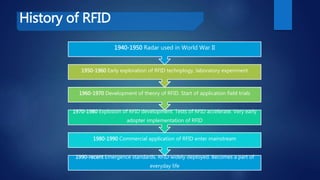
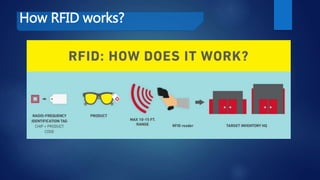
The document provides a comprehensive overview of RFID technology, including its history, current and future applications, benefits, and associated issues like privacy and security. It highlights how RFID improves inventory management and its potential future uses in sectors like smart factories and drone technology. The document concludes with advice for firms regarding the implementation of RFID and the need for appropriate legislative standards.