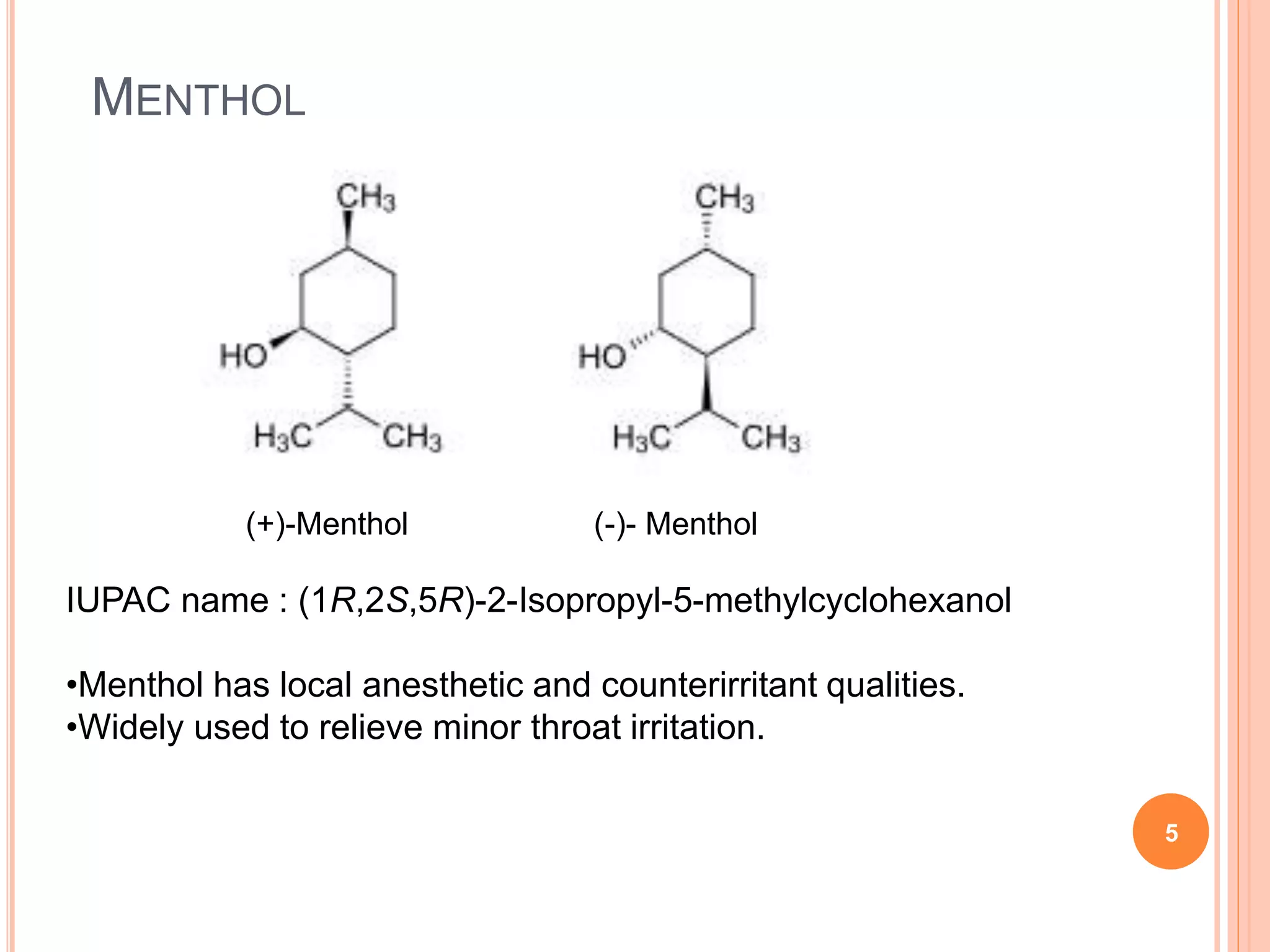
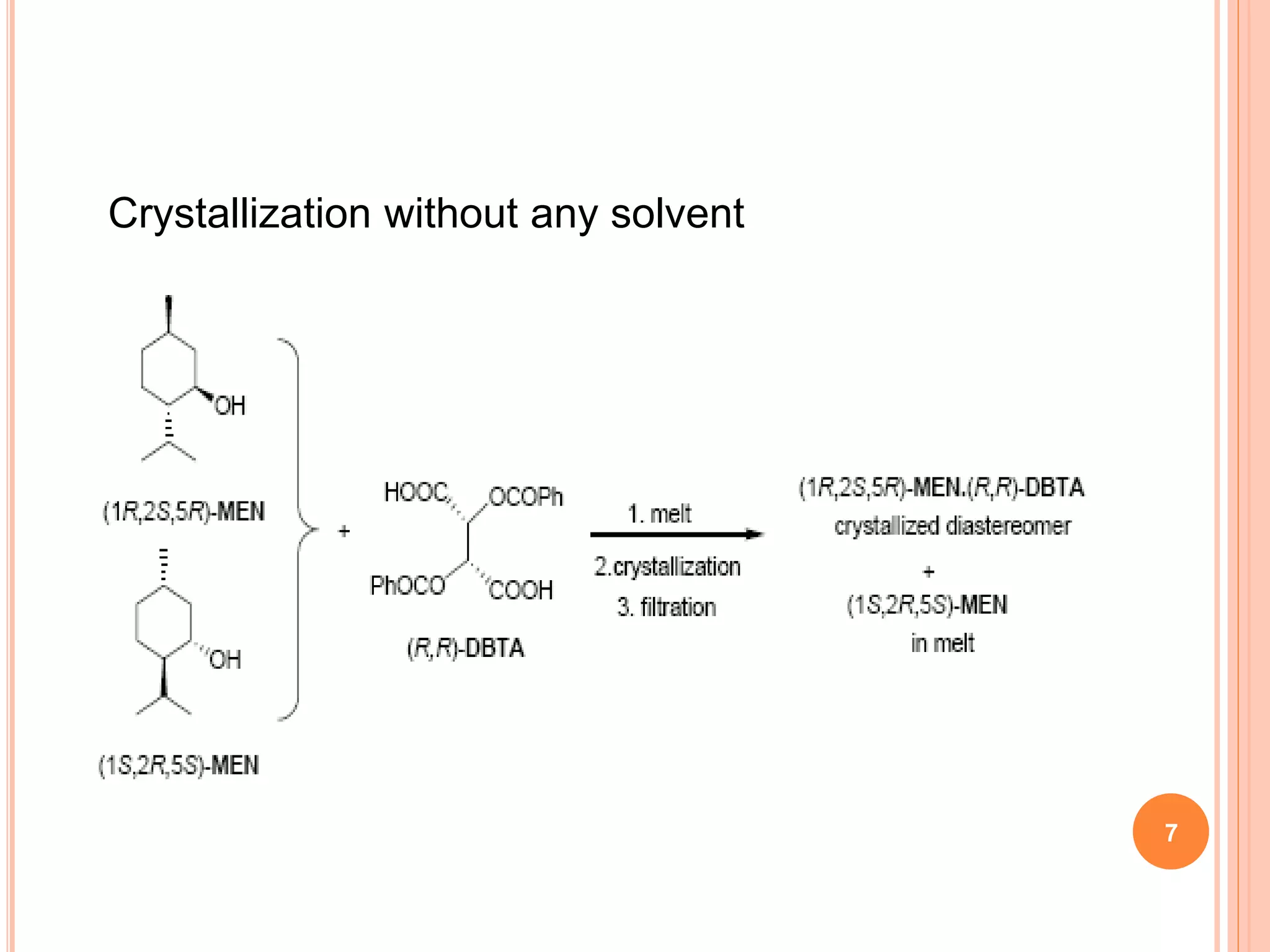
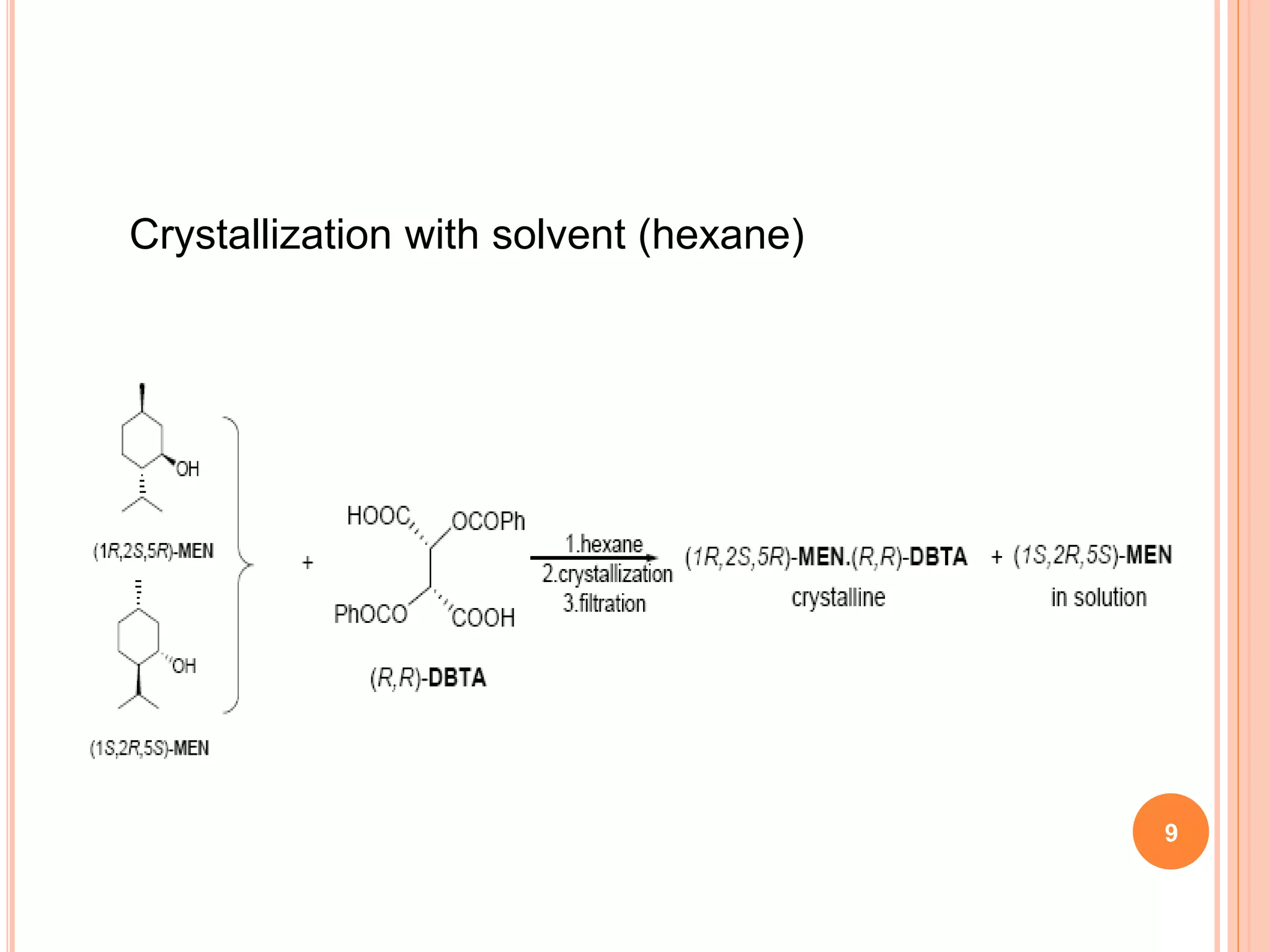
This document discusses the resolution of a racemic mixture of menthol. It begins by defining a racemic mixture as a solution containing equal amounts of both enantiomers of a compound. Common methods for separating the enantiomers include mechanical separation, biochemical separation, and forming diastereomeric salts with a resolving agent. For menthol specifically, the document describes two methods - crystallization without solvent and crystallization with hexane as the solvent. Both methods use (R,R)-DBTA as the resolving agent, which forms crystalline complexes that separate the (1R,2S,5R)-menthol enantiomer from the other.