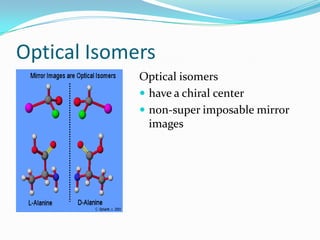
1. Chirality refers to molecular compounds that are non-superimposable on their mirror images and thus exist as two enantiomers. Recognition of chirality in compounds is important in pharmacology.
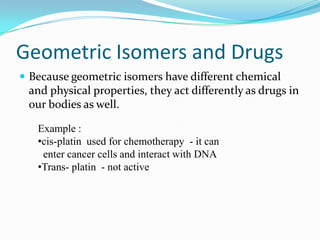
2. Many drugs are chiral, and their enantiomers may have different pharmacological effects ranging from no activity to distinct activities. This is due to biological molecules like receptors being chiral.
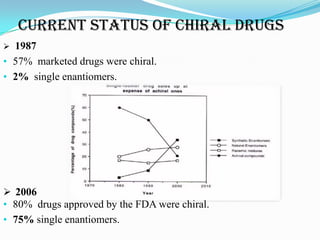
3. There has been a shift in drug development from racemic drug mixtures to single enantiomers due to issues like thalidomide and differences in enantiomer activity and side effects. Many current drugs have been redeveloped as single enantiomers.











![Arthur r. Cushny & “ChirAl”
Pharmacology
1866 - 1926
• (-)-Hyoscyamine almost exactly twice as
active as atropine [( )- hysocyamine]
(1904).
• (-)-Adrenaline twice the potency of ( )-adrenaline as a
vasoconstrictor (1908). (-)-enantiomer 12-15 fold more potent
than (+)-adrenaline on sympathetic vessels (1909).
• Biological Relations of Optically Isomeric Substances (1926).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chiraldrugs-140415094412-phpapp01/85/Chiral-drugs-14-320.jpg)