Embed presentation
Downloaded 118 times



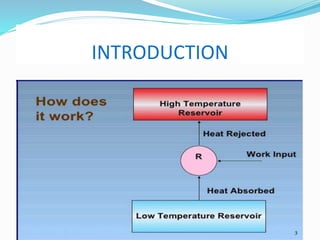






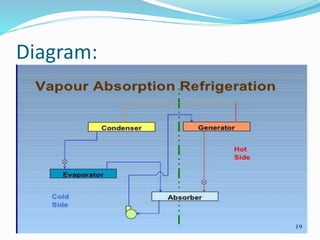


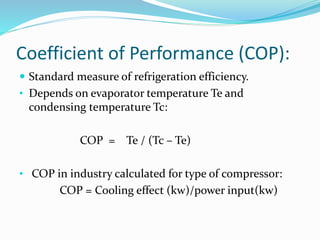
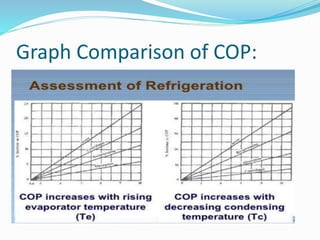


The document provides an overview of refrigeration systems, focusing on vapour compression and absorption refrigeration methods, along with their advantages. It details the types of refrigerants used, specifically chlorinated fluorocarbons, and introduces key concepts like the assessment of cooling effects and the coefficient of performance (COP). The content includes equations and measures related to refrigeration efficiency and performance assessment.
















