A queue is a first-in, first-out (FIFO) data structure where items are inserted at one end called the rear and removed from the other end called the front. Common applications include printer queues, bank lines, and computer input/output operations. The document discusses different implementations of queues including physical, single-step append-serve, and circular models. It also covers priority queues where items have priorities and are served according to those priorities.

![QUEUE
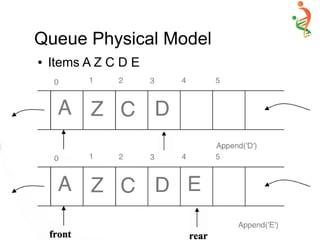
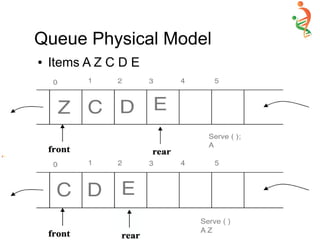
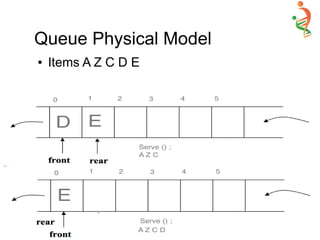
A queue is two ended data structure in which
items can be inserted from one end and taken out
from the other end. Therefore , the first item
inserted into queue is the first item to be taken out
from the queue. This property is called First in
First out [FIFO].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-150528091309-lva1-app6892/85/Queue-2-320.jpg)




![Queue Implementation In C++
● Template <class AnyType>
● Class Queue {
● Private:
– Int Size, Rear, Front;
– AnyType* Items;
● Public:
– Queue( ) { //default constructor
– Size =50; Rear = -1; Front = 0 //Front =0 is constant is Physical Model
– Items = new AnyType[Size];
● }
● Queue(int size) {
– Size=size; Rear = -1; Front = 0;
– Items = new AnyType[Size];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-150528091309-lva1-app6892/85/Queue-13-320.jpg)
![Queue Implementation In C++
● ~Queue ( ) {
– Delete [ ] Items; }
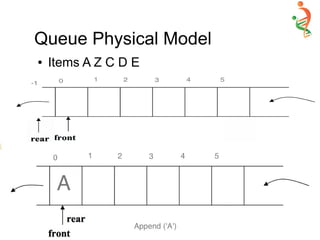
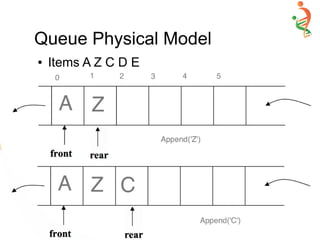
● Void Append (AnyType newItem) {
– If (!IsFull( ) )
● Items[++Rear ] = newItem;
– else
● Cout << “n Queue is Full … Append Failed”; }
● AnyType Server (void) {
– If (!IsEmpty ( ) )
● AnyType item =Item [Front]; // Same as item =item[0]
● for ( int i=0; i<Rear; i++ ) //Move each item one step forward
– Items[i] =Items [i+1];
● Rear --;
● Return item; }
– else
● Cout << “n Queue is empty … Serve failed”; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-150528091309-lva1-app6892/85/Queue-14-320.jpg)
![Queue Implementation In C++
● Int IsEmpty ( ) { return (Rear == -1 ) ; }
● Int IsFull ( ) { return (Rear == (Size-1) ); }
● Void Display( ) {
● Cout<< “n”;
● If (IsEmpty( ) )
– cout<<”Empty”;
● Else
– for(int i=Rear; i>=Front; i—)
● cout<<Items[i]<< “ “;
● }
● }; //end physical Model Queue class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-150528091309-lva1-app6892/85/Queue-15-320.jpg)
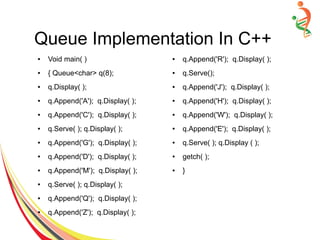
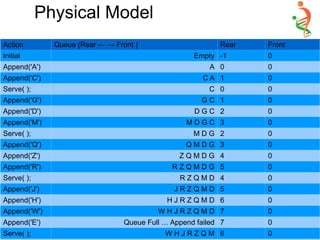

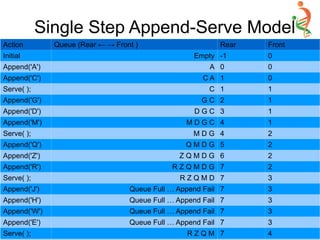
![AnyType Serve(void) {
if(!IsEmpty( ) )
Return Items[Front++] ;
else
cout<<”Queue is Empty... Serve failed”;
}
– int IsEmpty() { return (Front > Rear ); }
– Int IsFull( ) { return (Rear == (Size-1) }
Single Step Append-Serve Model
Implementation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-150528091309-lva1-app6892/85/Queue-20-320.jpg)
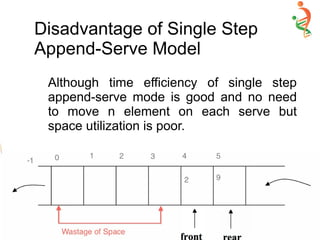
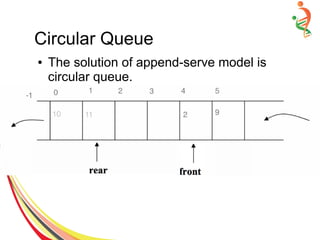
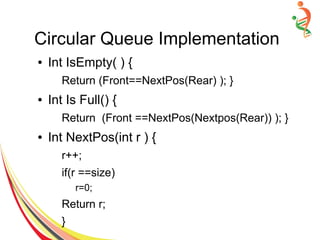
![Circular Queue Implementation
● AnyType Append(AnyType new Item) {
If (!IsFull() ) {
Rear++
if(Rear == Size)
Rear=0;
Items[Rear]= newItem;
}
else
cout<<”Queue is full … Append failed.”;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-150528091309-lva1-app6892/85/Queue-23-320.jpg)
![Circular Queue Implementation
● AnyType Serve(void) {
If (!IsEmpty( ) {
AnyType item =Items[Front];
Front++;
If (Front ==Size)
Front=0;
Return item;
}
else
cout<<”Queue is Empty … serve failed”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-150528091309-lva1-app6892/85/Queue-24-320.jpg)
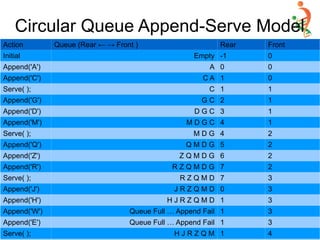
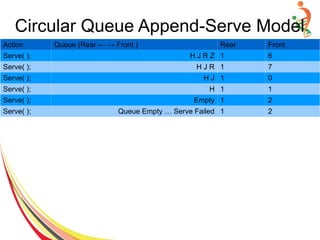
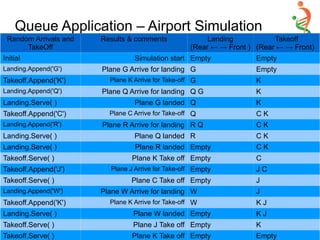



![Priority Queue Implementation
# include <iostream.h>
● #include <conio.h>
● Template <class AnyType>
● Struct Item {
– AnyType Item;
– Int priority;
● Template <class AnyType>
● Class MaxPriorityQueue {
● private:
– int Size, Rear, Front;
– Item<AnyType>* Items;
● Public:
– MaxPriorityQueue ( ) //default constructor
– Size=50;
– Rear = -1
– Front = 0 //Always 0 in physical model
Items= new Item<AnyType>[Size];
}
● MaxPriorityQueue(int size) {
– Size = size;
– Rear = -1 ;
– Front = 0; //Always 0 in physical model
– Items = new Item<AnyType>[Size];
– }
● ~MaxpriorityQueue ( ) { delete[ ] Items; }
● Void Place(Item<AnyType> newItem) {
– if(IsEmpty( ) ) {
● Items [ ++Rear] = newItem;
– }
–](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-150528091309-lva1-app6892/85/Queue-32-320.jpg)
![Priority Queue Implementation
if(!IsFull( ) ) {
Int i, putAt;
– For (i=Rear; i>=Front; i - - ) //Find where to
put item
if(newItem.priority <= Item[i].priority )
Break;
– PutAt=++ i //position where to put new item
– Rear ++;
– For (i=Rear; i>putAt; i-- ) //move item to
create space
● Item[i]=Items[ i -1];
– Items[putAt] = newItem;
– }
– Else
● cout<< “n Priority queue is Full. Place
failed “
● } // ending “} “ of place function
AnyType Serve(void) {
– if(!IsEmpty ( ) ) {
● AnyType item=Items[Front].Item;
● //same as item = item[ 0 ]
● for(int i=0; i<Rear; i++)
– Items[i] =Items[ i+1];
● Rear--;
● return item;
}
– else
– cout<<”nQueue is Empty... Serve failed”;
– }
– Int IsEmpty ( ) { return (Rear ==-1); }
– Int IsFull ( ) {return (Rear == (Size-1 ) ); }
– void Display( ) {
– cout<<endl <<Front<<' ' <<Rear<<' ' << “ “;
– If (IsEmpty( ) )
● cout<<”Empty”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-150528091309-lva1-app6892/85/Queue-33-320.jpg)
![Priority Queue Implementation
– void Display( ) {
– cout<<endl <<Front<<' ' <<Rear<<' ' << “ “;
– If (IsEmpty( ) )
● cout<<”Empty”;
– else
● for(int i<Rear; i>=Front; i—)
– cout<<Item[i].Item<< ' ';
– }
– }; //end Physical model max priority Queue
class
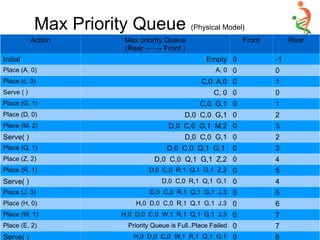
– void main( ) {
– MaxpriorityQueue<char> q(8);
– Item<char> Items[ ] = { {'A', 0}, {'C', 0}, {'G', 1},
{'D', 0}, {'M', 2}, {'Q', 1},
{'Z', 2}, {'R', 1}, {'J', 3},
{'H', 0}, {'W', 1},{'E', 2}};
q.Display ( );
q.Place(Items[0]); q.Display( );
q.Place(Items[1]); q.Display( );
q.Serve( ) ;
q.Place(Items[2]); q.Display( );
q.Place(Items[3]); q.Display( );
q.Place(Items[4]); q.Display( );
q.Serve( );
q.Place(Items[5]); q.Display( );
q.Place(Items[6]); q.Display( );
q.Place(Items[7]); q.Display( );
q.Serve( );
q.Place(Items[8]); q.Display( );
q.Place(Items[9]); q.Display( );
q.Place(Items[9]); q.Display( );
q.Place(Items[9]); q.Display( );
● q.Serve( );
● getch ( ); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-150528091309-lva1-app6892/85/Queue-34-320.jpg)