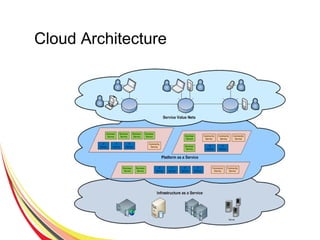
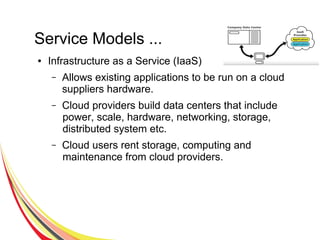
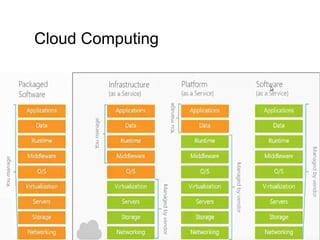
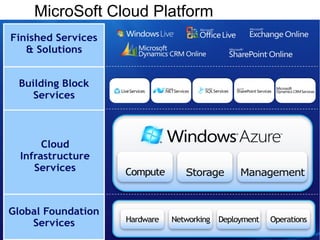
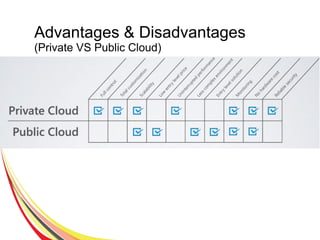
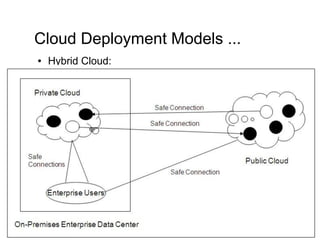
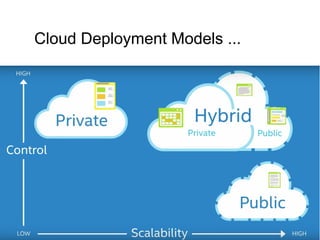
Cloud computing integrates software, hardware, and internet infrastructure, providing users with simple interfaces and on-demand services that are cost-effective compared to traditional data centers. It encompasses various service models such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages. Deployment models include private, public, and hybrid clouds, each with unique benefits and risks related to security, investment, and management.