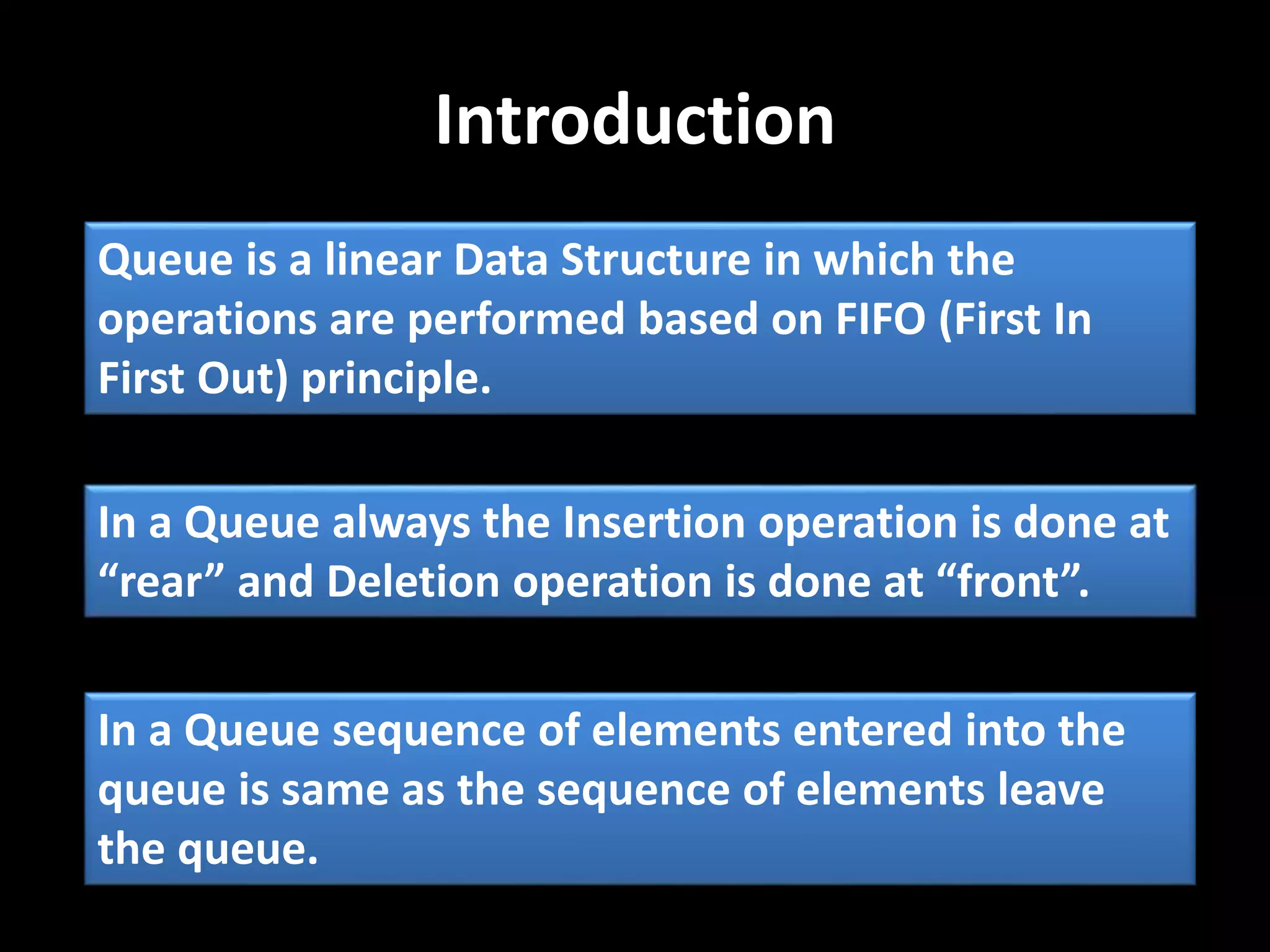
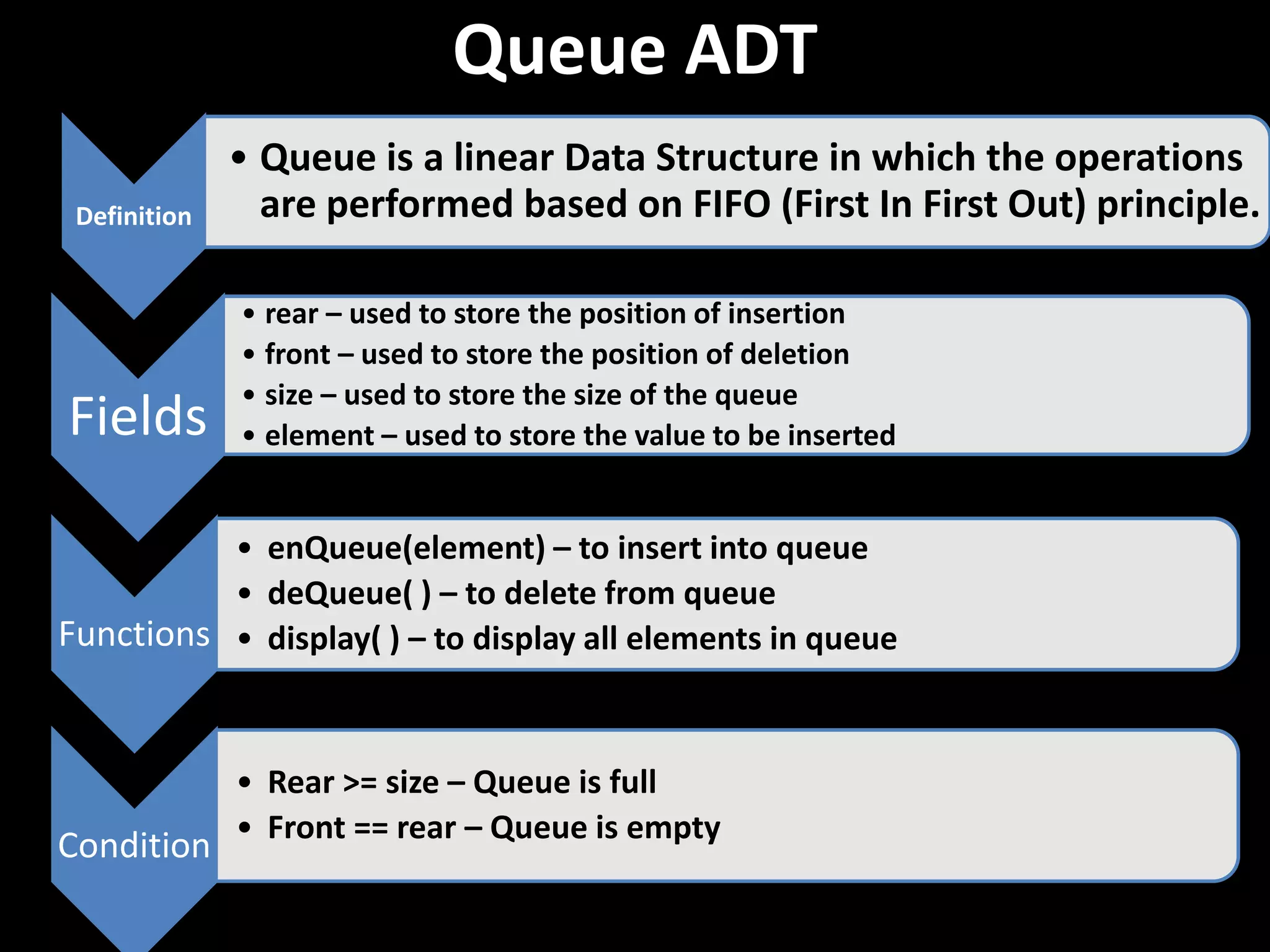
Queue is a linear data structure that follows the FIFO (First In First Out) principle where elements are inserted at the rear and deleted from the front. It has fields for the front and rear pointers and size, and functions to enqueue, dequeue, and display elements. Elements are inserted at the rear if space is available and deleted from the front, maintaining the order they entered the queue.

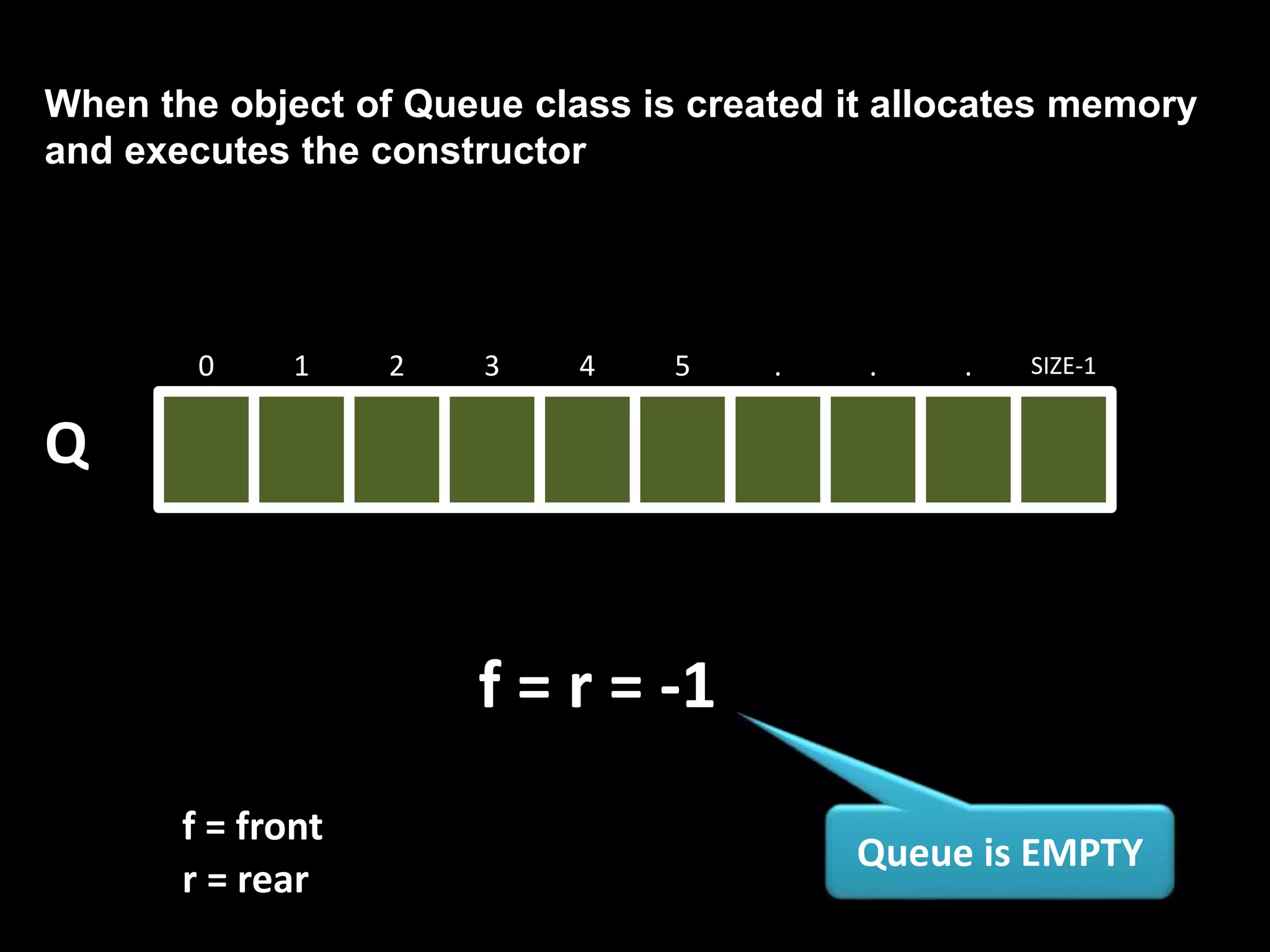
![class Queue
{
int *Q, front, rear, size;
public:
Queue()
{
cout<<“Enter the Queue size:”;
cin>>size;
Q = new int[size];
front=rear=-1;
}
void qInsert(int);
void qDelete();
void qDisplay();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queuebyrajanikanth-150421003800-conversion-gate02/75/Queue-by-rajanikanth-4-2048.jpg)
![Insertion
Q
enQueue( int element )
{
if( rear != size-1)
{
rear ++;
Q[rear] = element;
}
}
else
cout<< “Queue is full !!!”;
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 20 30 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queuebyrajanikanth-150421003800-conversion-gate02/75/Queue-by-rajanikanth-6-2048.jpg)
![Deletion
Q
deQueue( )
{
if( front != rear )
{
front ++;
Cout<<“nElement removed : ”<<Q[front];
}
}
else
cout<< “Queue is empty !!!”;
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 20 30 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queuebyrajanikanth-150421003800-conversion-gate02/75/Queue-by-rajanikanth-7-2048.jpg)
![Display
Q
if( front != rear )
{
for(int i=front+1; i<=rear, i++)
cout<<Q[front]<<“t”;
}
}
else
cout<< “Queue is empty !!!”;
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 20 30 40
display( )
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queuebyrajanikanth-150421003800-conversion-gate02/75/Queue-by-rajanikanth-8-2048.jpg)