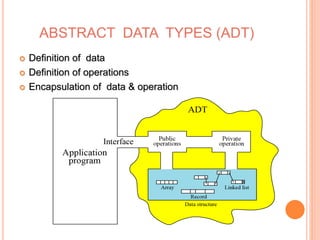
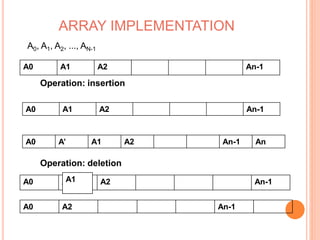
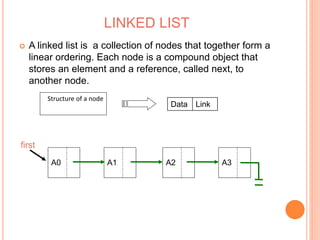
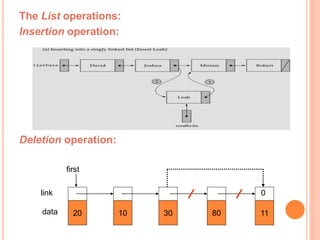
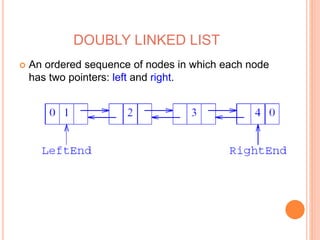
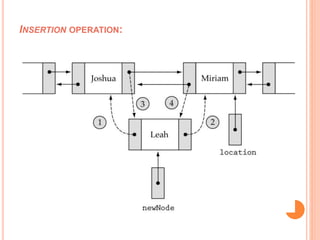
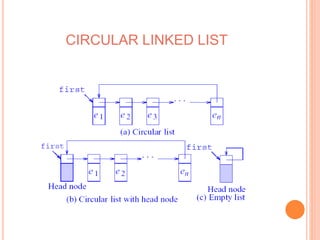
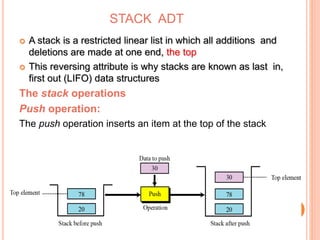
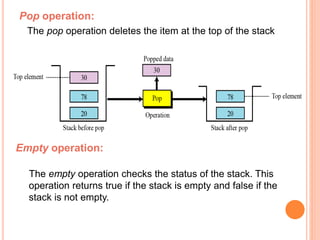
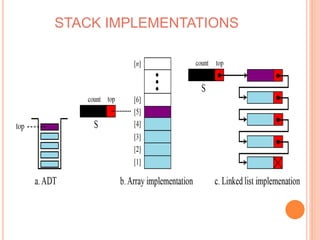
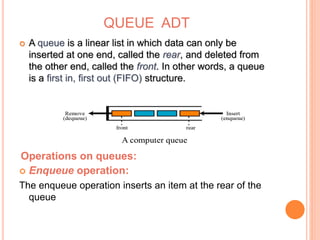
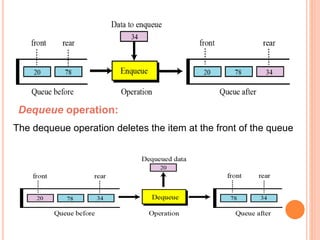
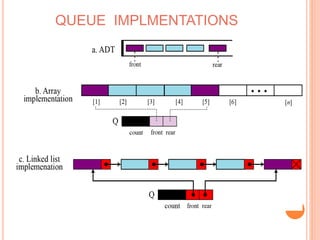
This document defines and compares common data structures like lists, stacks, and queues. It describes their abstract definitions, common operations, and different implementation methods. Lists can be implemented with arrays or linked nodes and support insertion, deletion, and retrieval of elements. Stacks and queues follow last-in first-out and first-in first-out rules respectively.