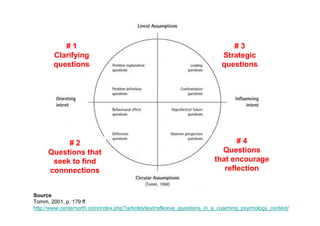
The document outlines various types of questions used in coaching psychology, categorized into strategic, clarifying, and reflective types. It emphasizes the importance of asking tailored questions to define problems, explore relationships, and provoke action. Additionally, it provides examples of questions for each type along with goals for their use in helping individuals reflect and find solutions.