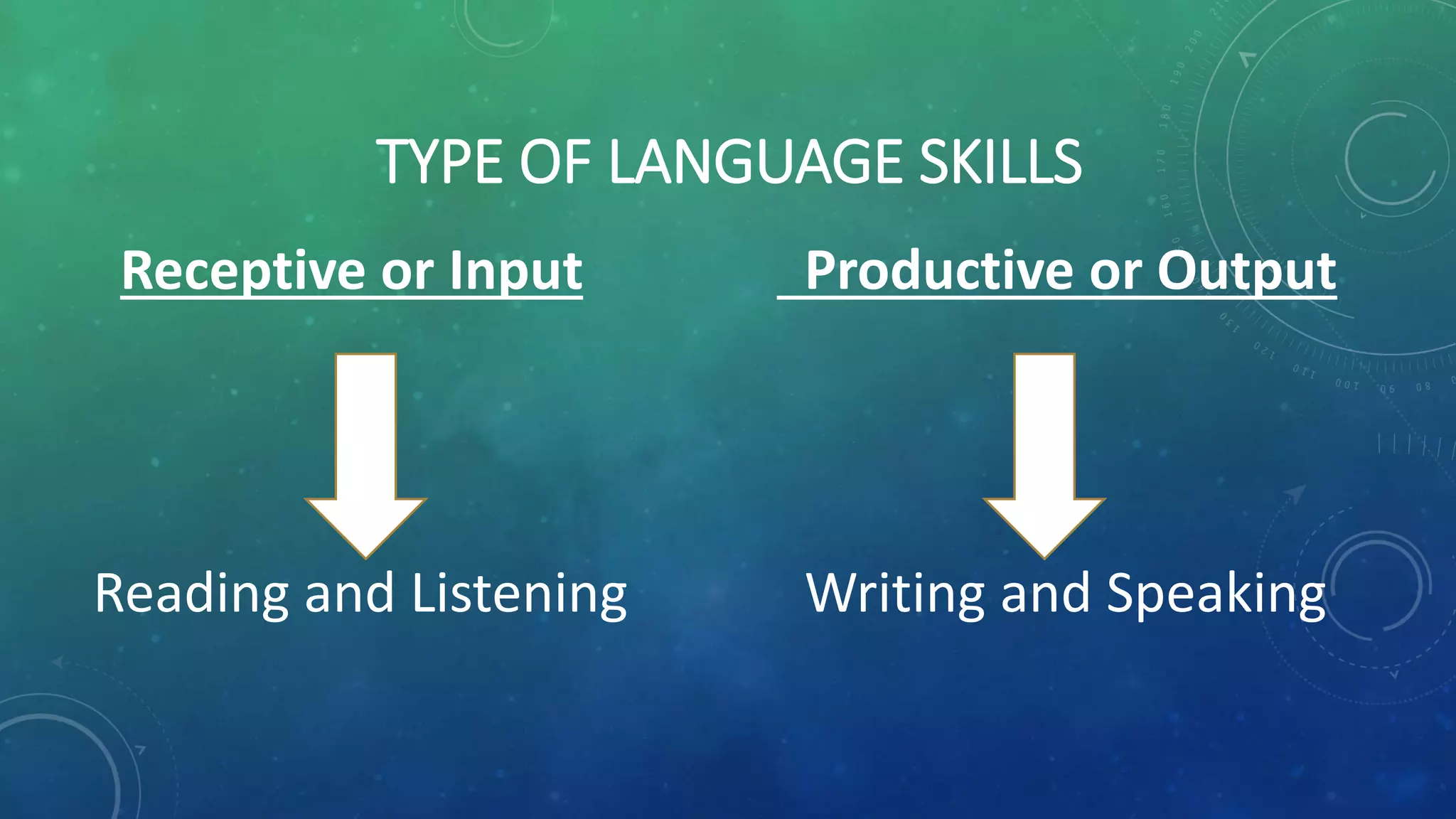
The document discusses the four main language skills of English - listening, speaking, reading, and writing. It categorizes listening and reading as receptive or input skills, while speaking and writing are productive or output skills. For each skill, the document provides information on when they are used, their importance, common issues, and solutions to improve them. The overall purpose is to outline and explain the four core language skills needed to develop proficiency in English.