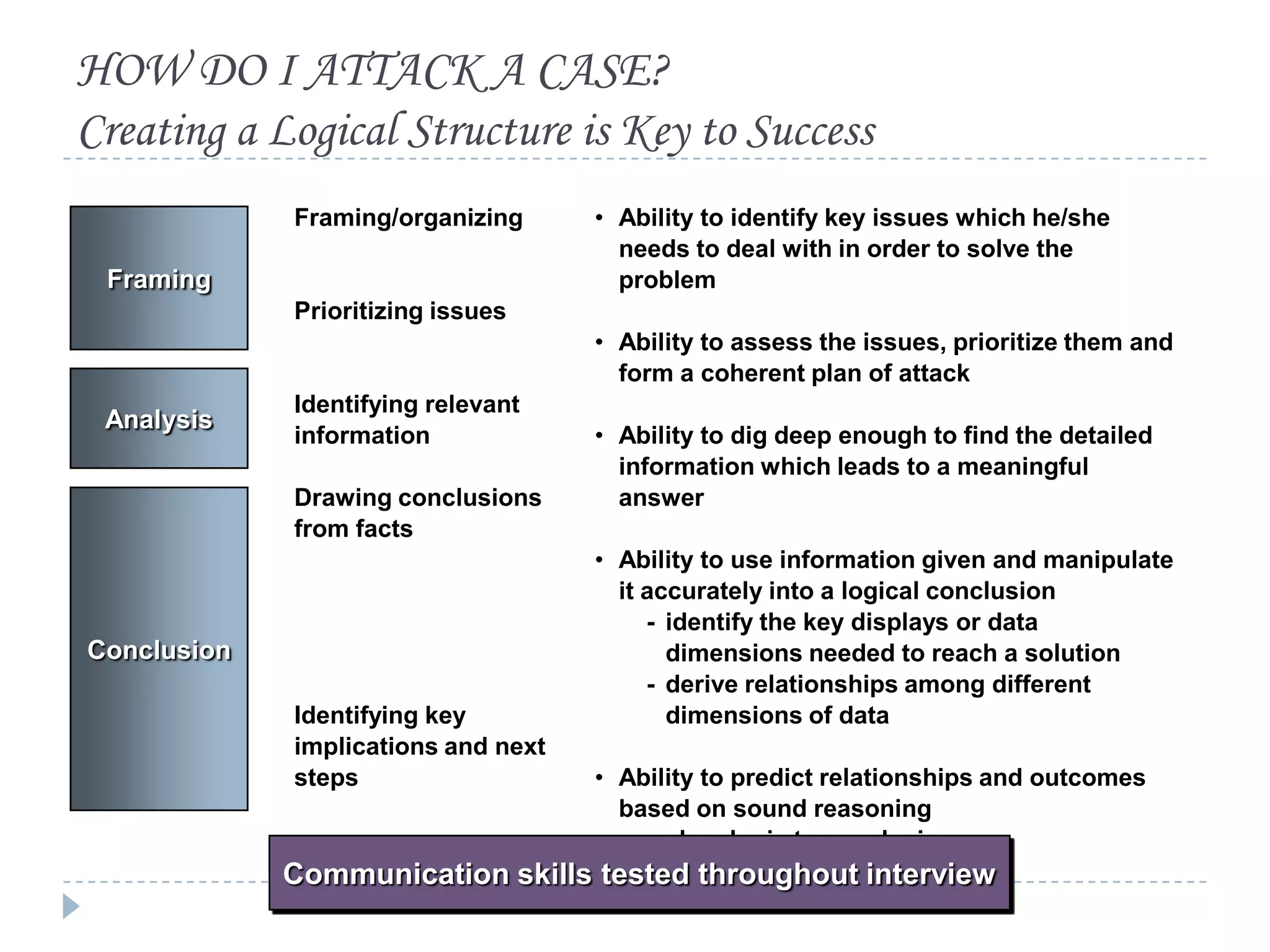
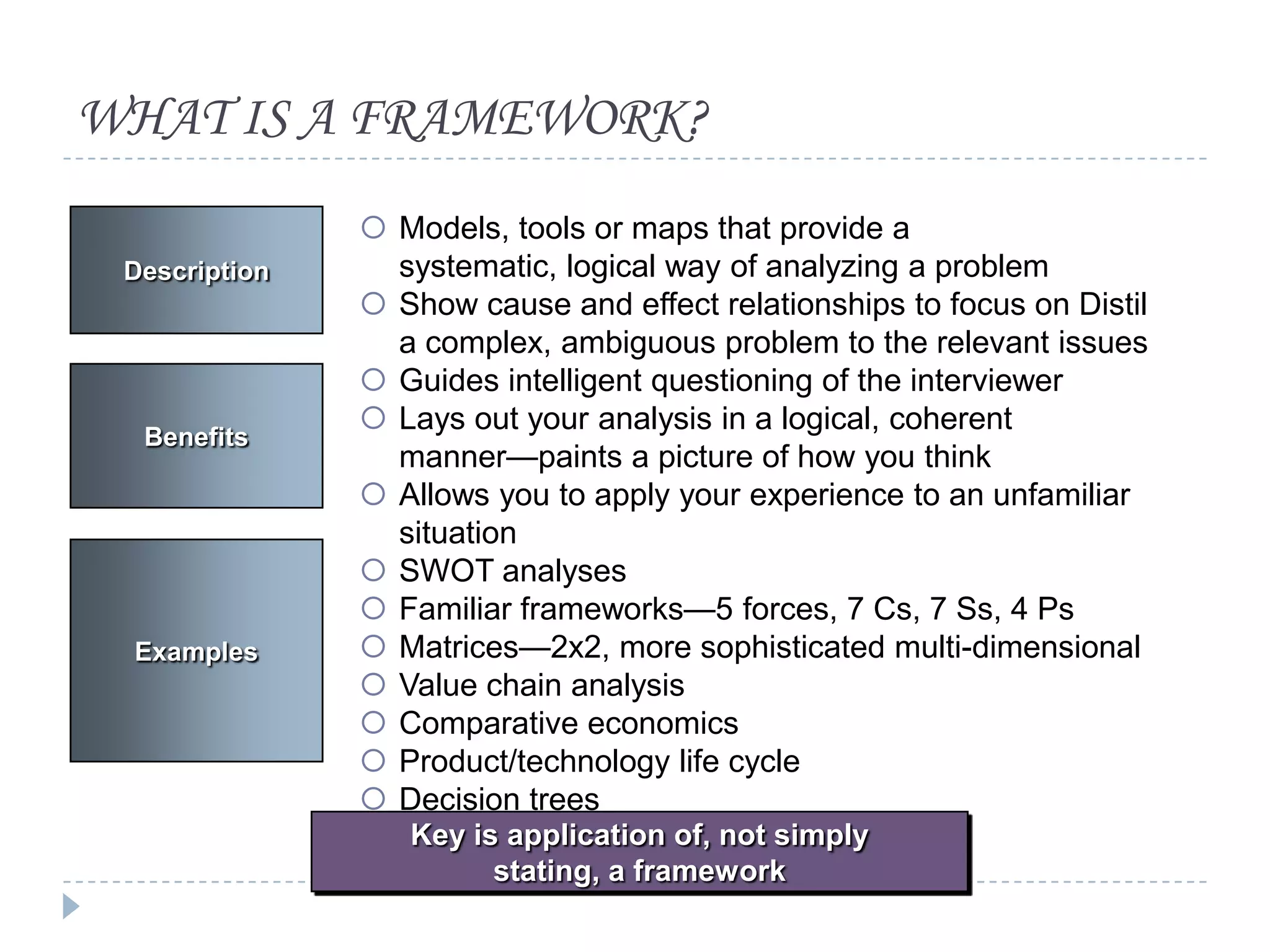
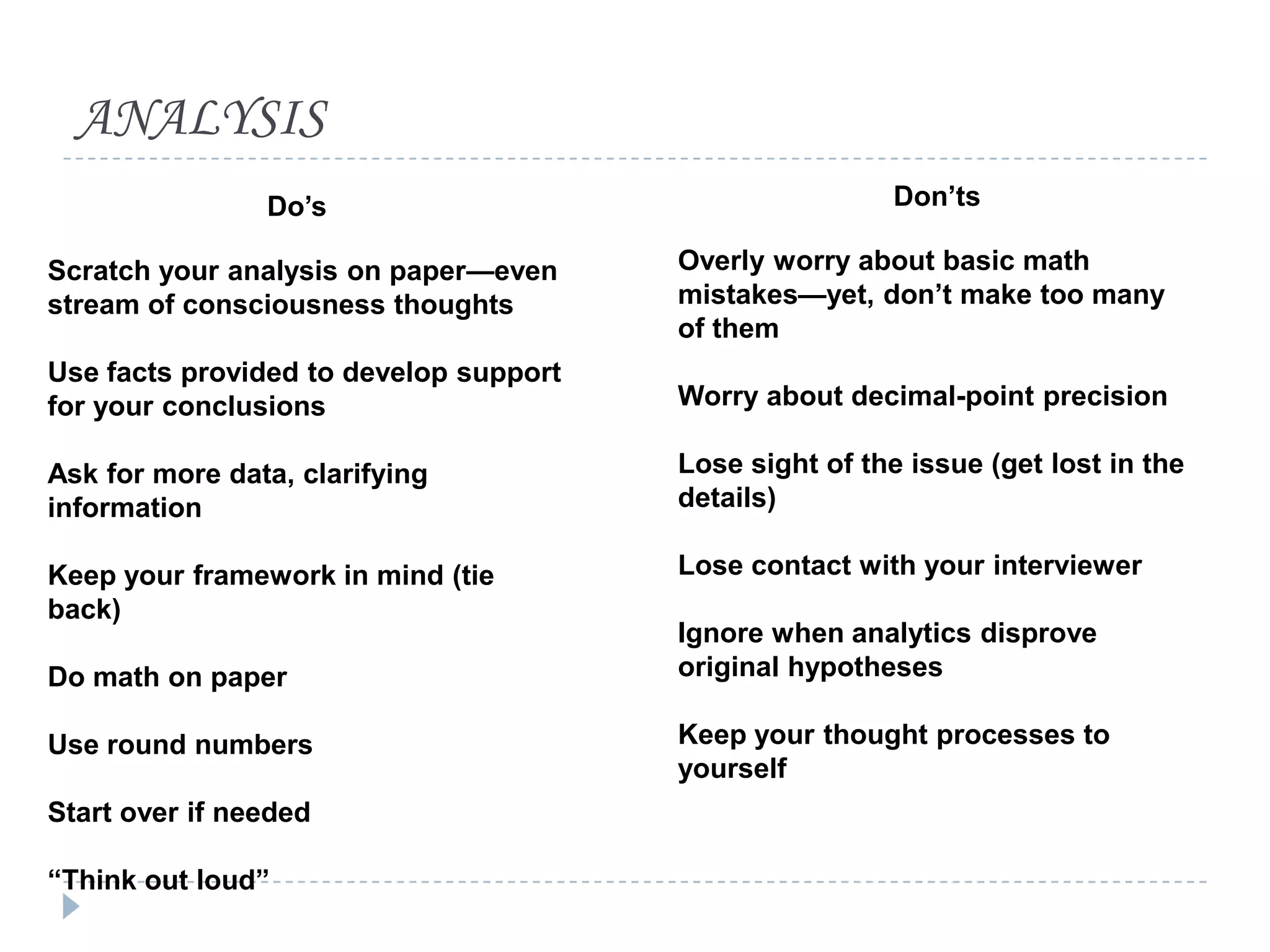
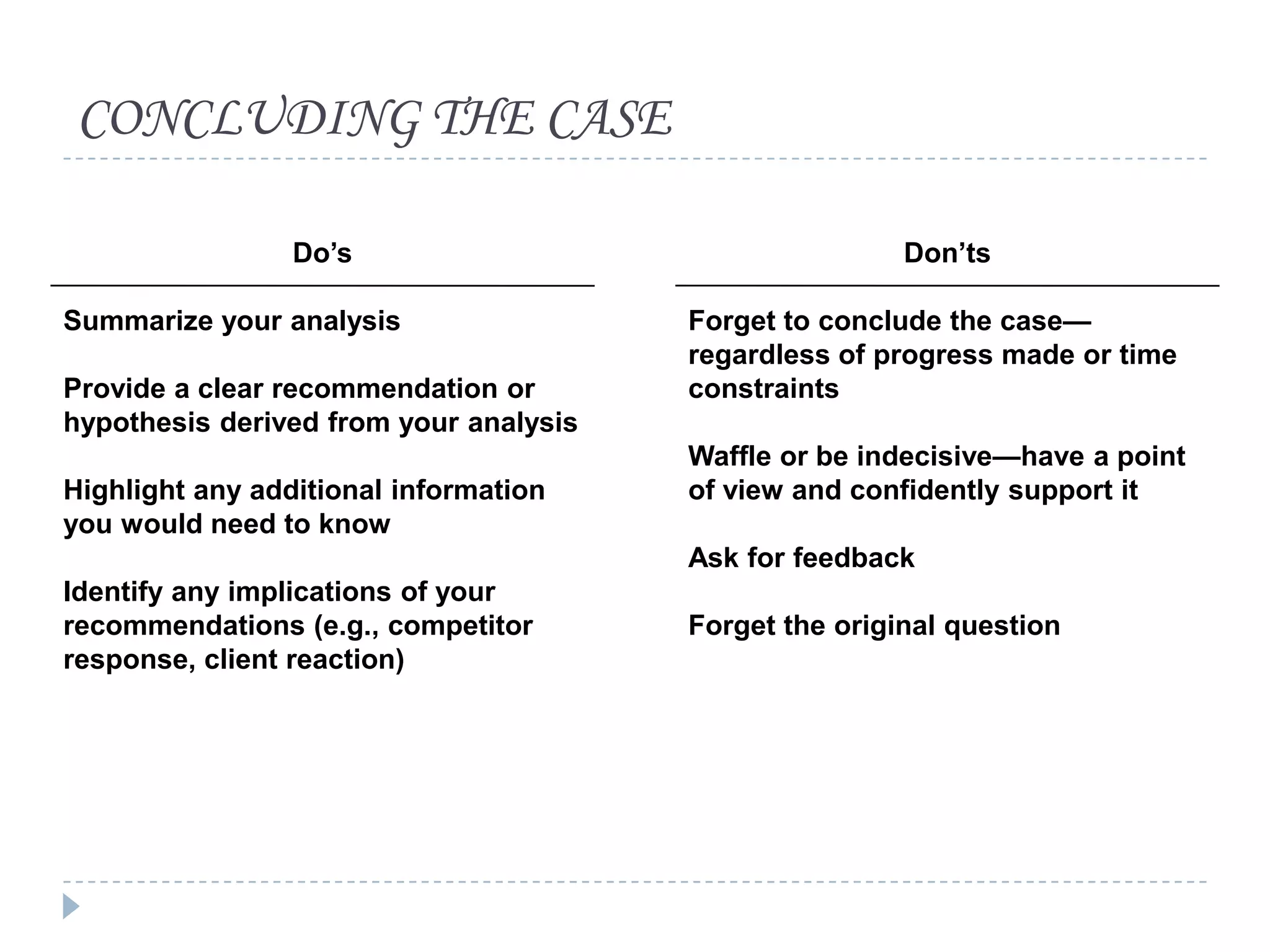
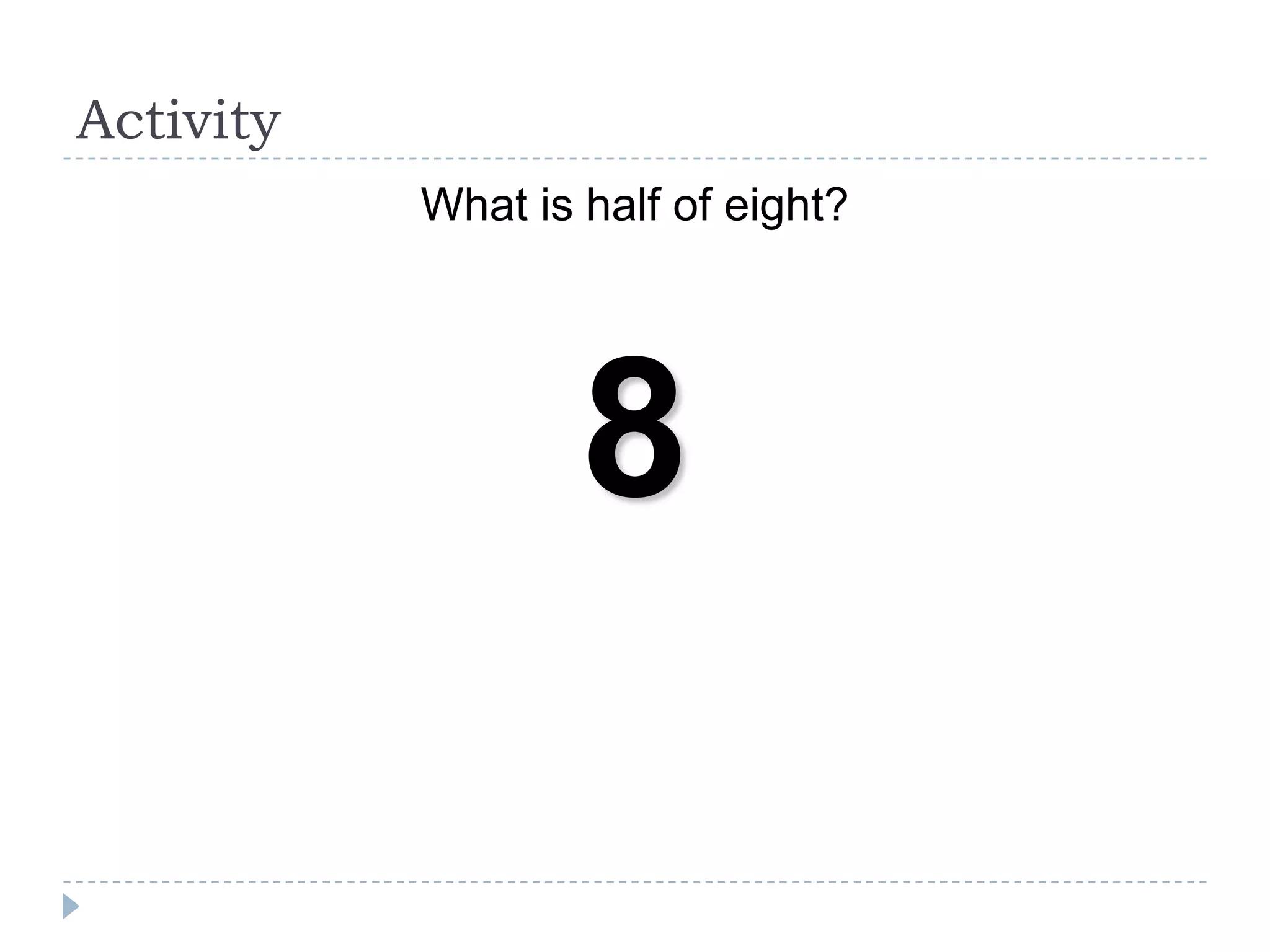The document presents a comprehensive overview of critical thinking and problem-solving skills, emphasizing their importance in various contexts such as interviews and everyday decision-making. It outlines key techniques, strategies for effective communication, and types of interview questions to expect, along with preparation tips for consulting case interviews. The goal is to cultivate critical thinkers who can analyze problems, think creatively, and derive logical conclusions.