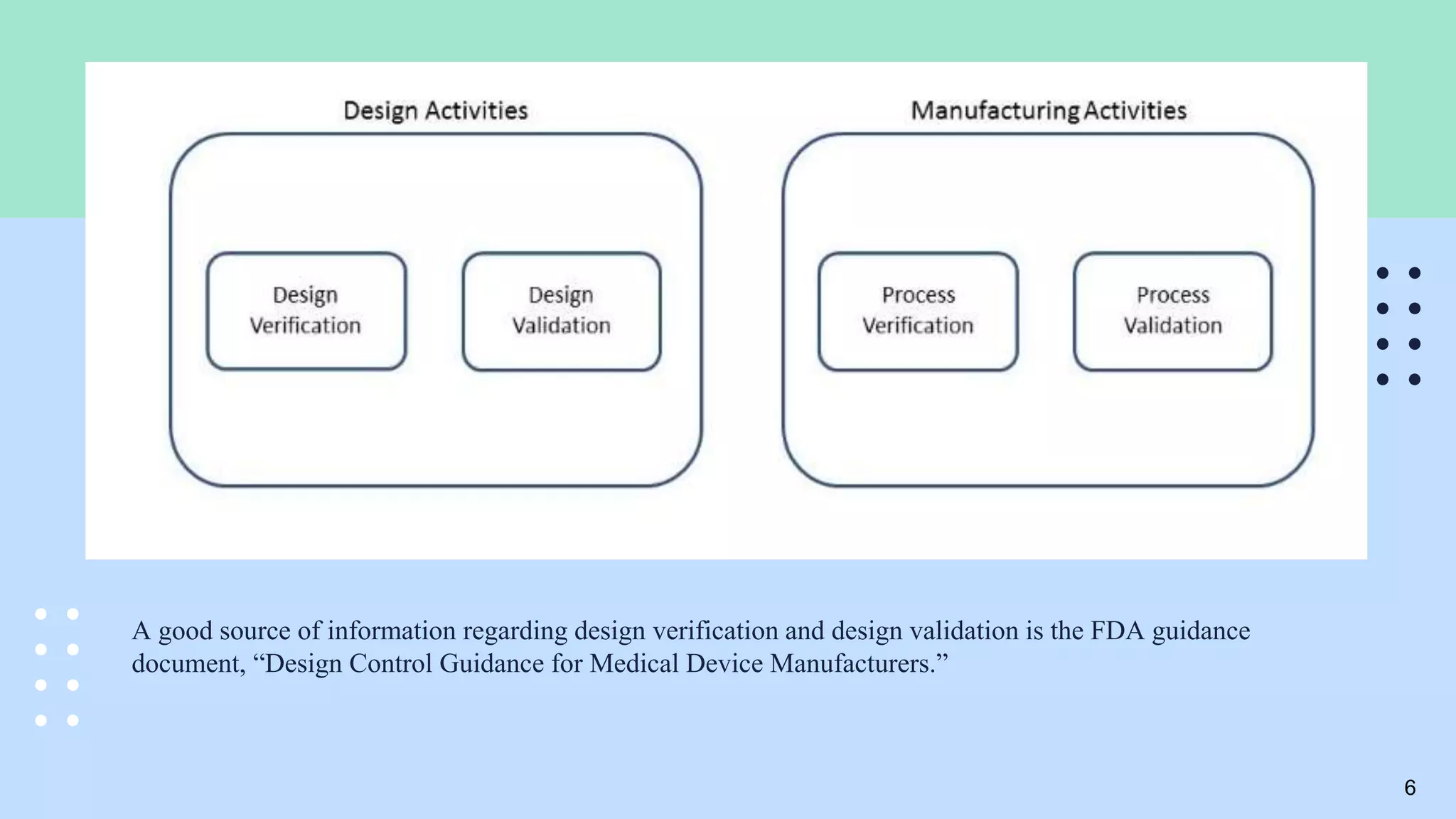
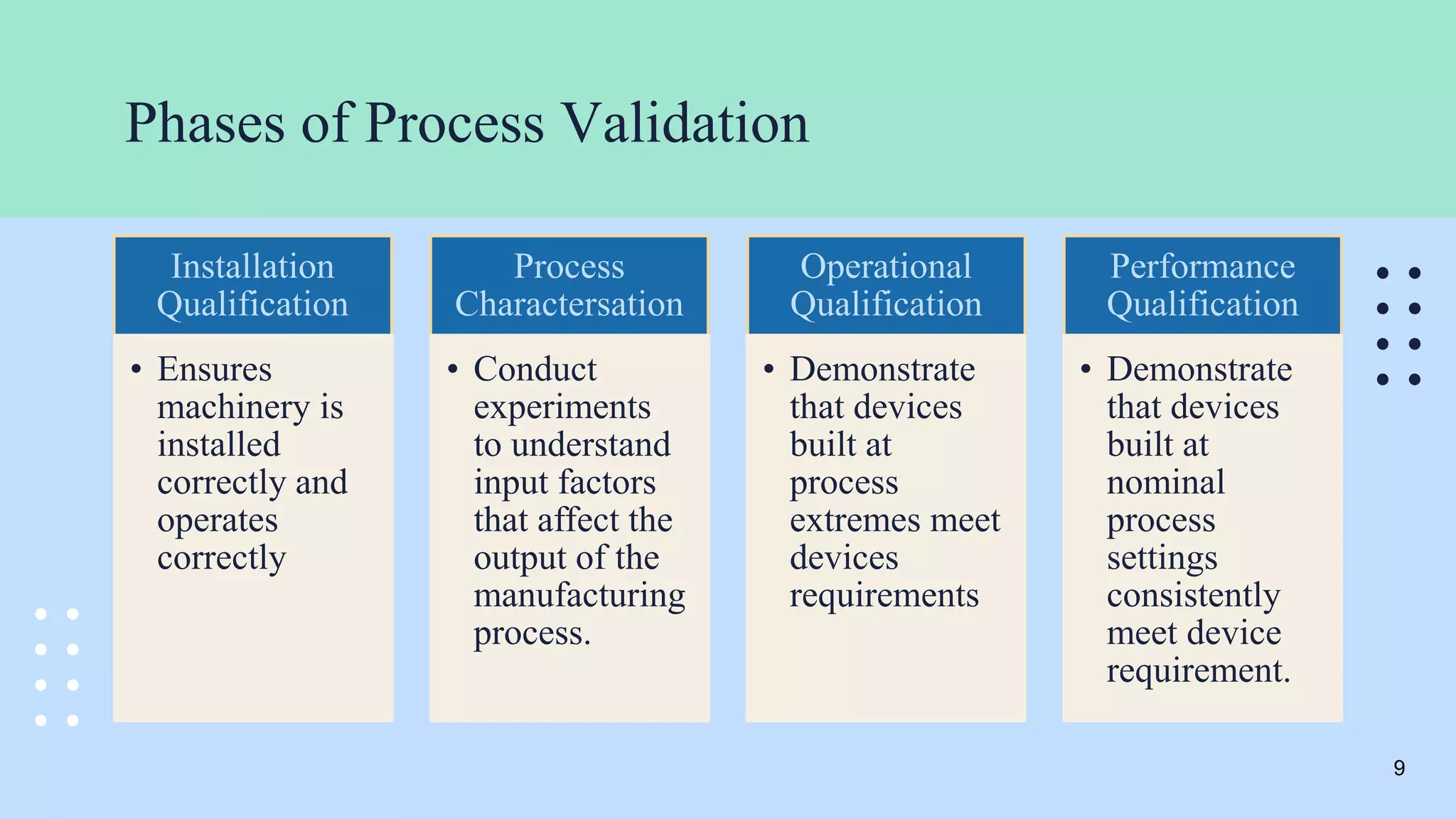
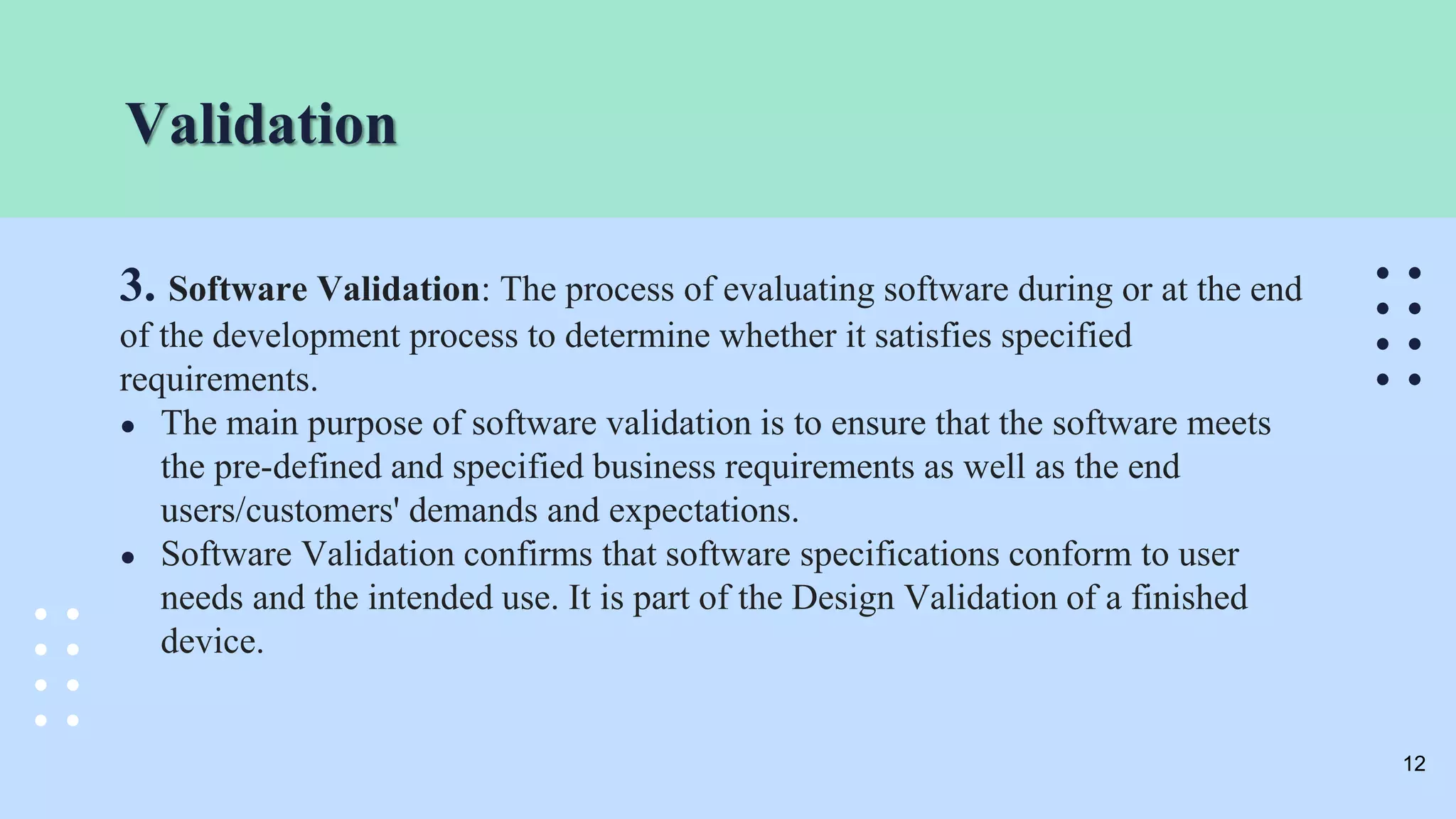
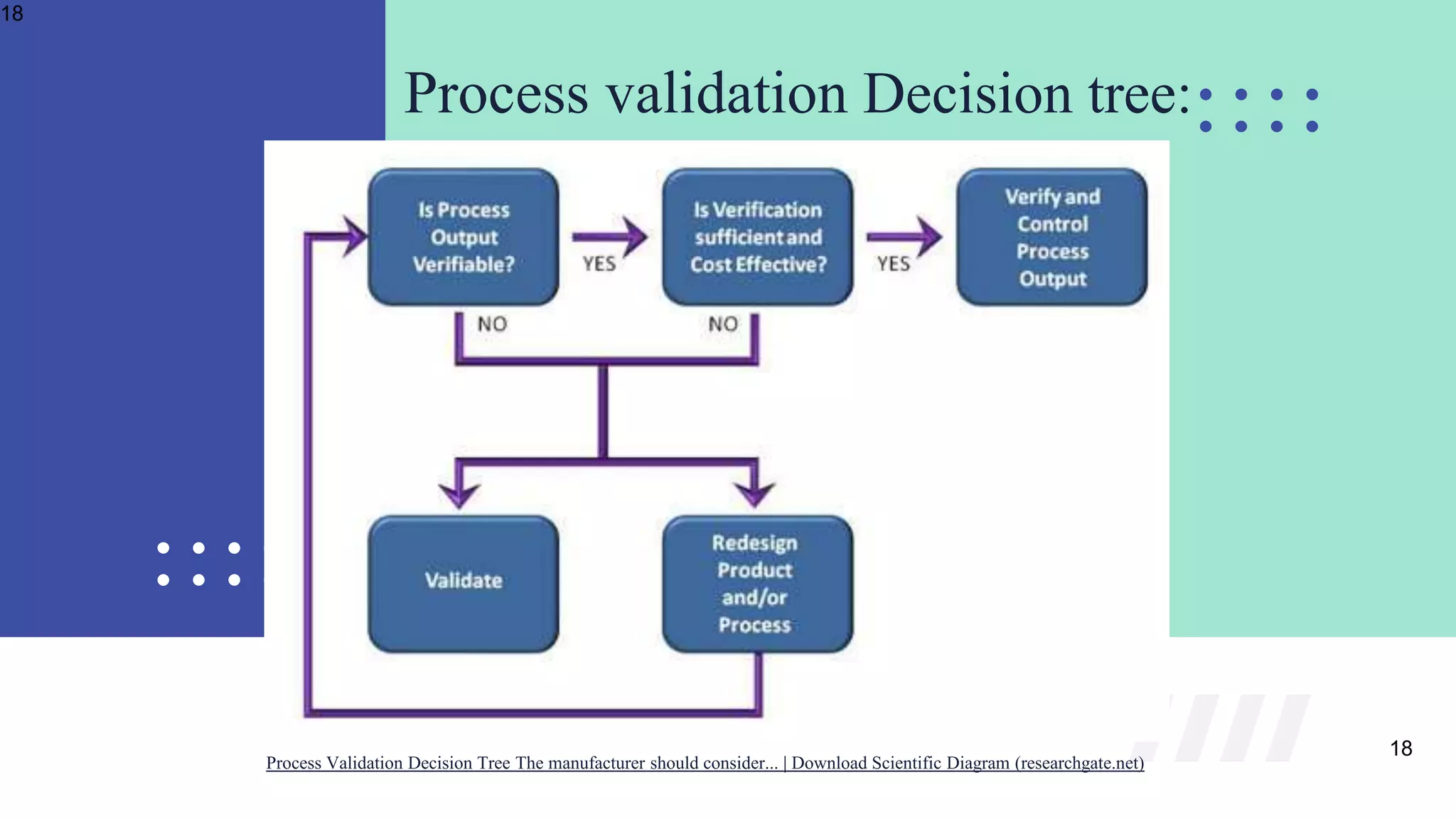
The document outlines the validation and verification processes for medical devices, emphasizing the importance of compliance with regulatory standards such as ISO 13485 and FDA requirements. It details the definitions and distinctions between validation and verification, as well as the phases of process validation including installation qualification, operational qualification, and performance qualification. Additionally, the document highlights the advantages of effective validation and verification, such as increased reliability and decreased risks to patients.