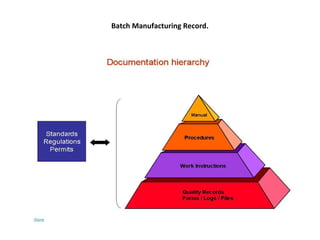
The document provides information on documentation practices in the pharmaceutical industry. It discusses why documentation is important, defining documentation as written evidence of activities. It states that regulatory bodies prioritize reviewing documents to verify activities. Good documentation practices, including systematic preparation and review of documents, are required to prevent errors and ensure compliance. Documentation provides records, traceability, and audit trails for investigation and review.