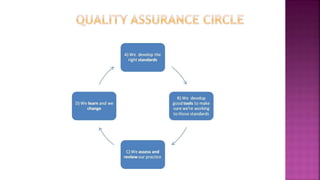
Quality assurance is a planned, proactive process focused on preventing defects during development through activities like process improvement. Quality control is a reactive process focused on identifying defects after development through testing and inspection. Quality assurance aims to improve processes, while quality control aims to check for defects in the final product before release. Responsibilities also differ, with quality assurance being a shared team responsibility and quality control handled by a dedicated testing team.