This document provides an overview of ISO and ISO 9000 standards. It discusses:
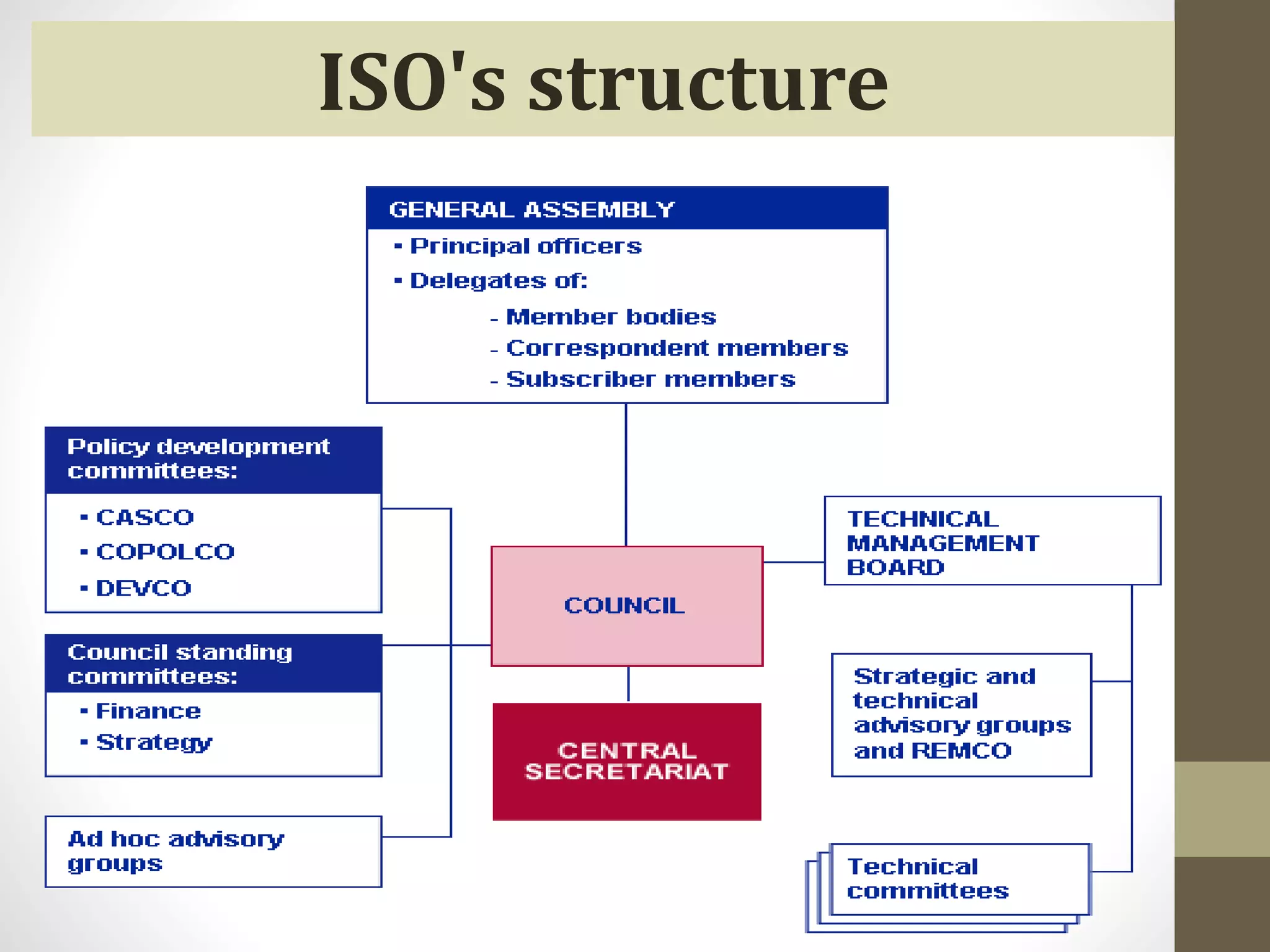
- The history and origins of ISO as an international organization for standardization.
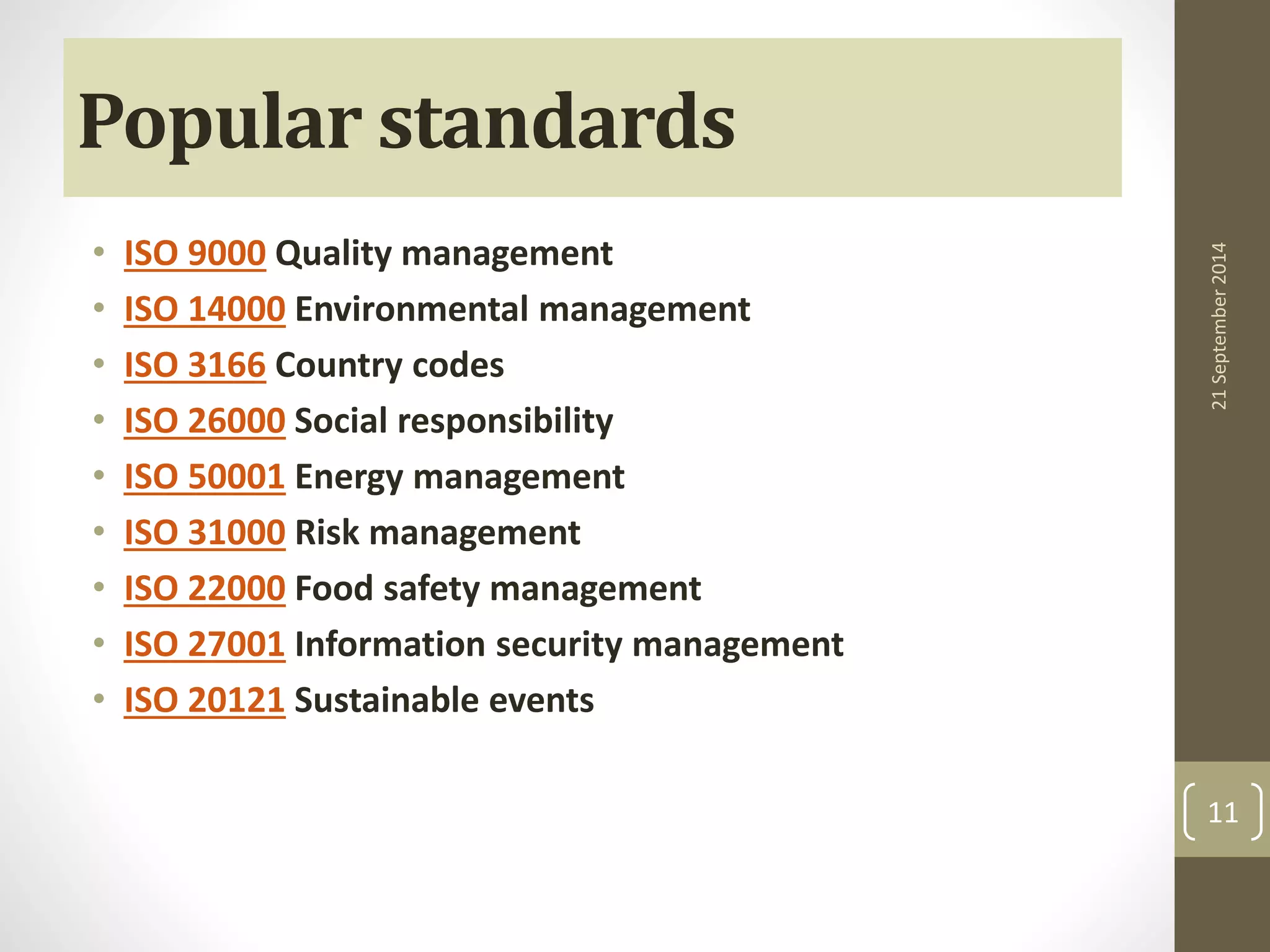
- An overview of the ISO 9000 family of quality management system standards, including the requirements of ISO 9001.
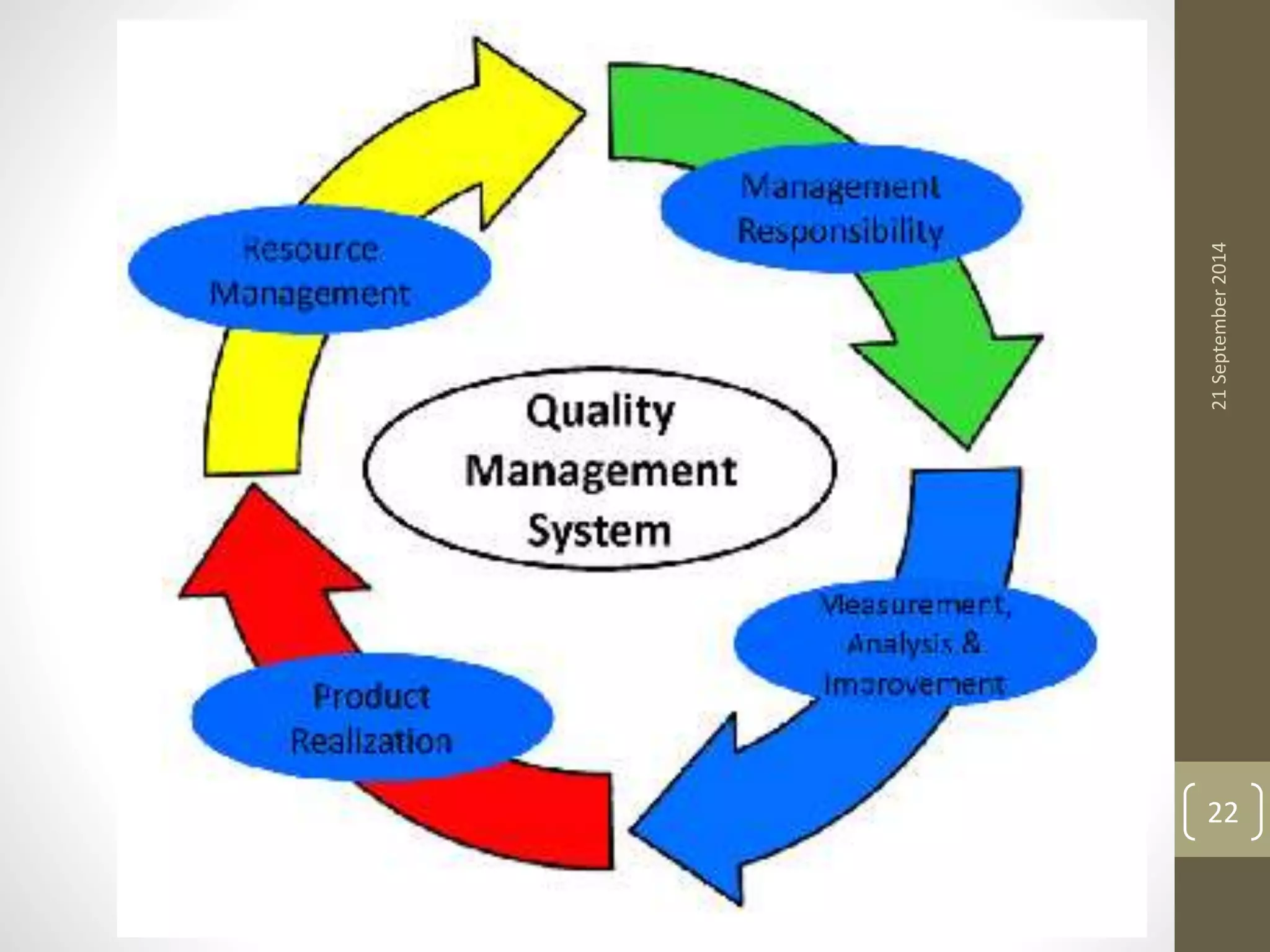
- The key elements required by the ISO 9000 standards, such as management responsibility, resource management, and process control.
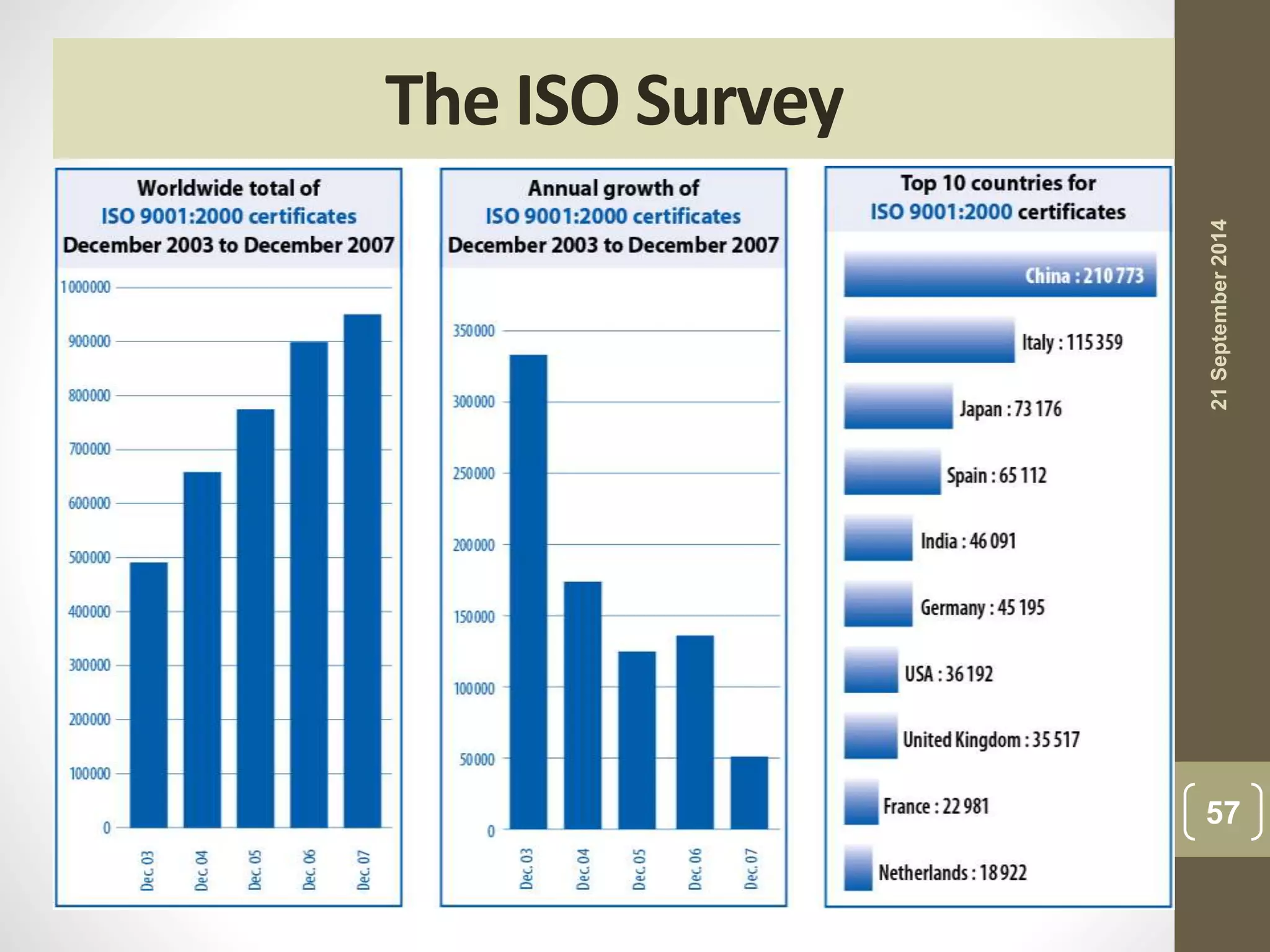
- The importance of ISO 9000 certification for companies, including helping to comply with customers and regulations, improve quality, and increase profitability.