This document discusses the components and functions of permanent way and track for railways. It includes:
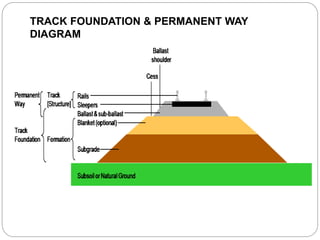
1. The layers of the track structure including rails, sleepers, ballast, and sub-ballast which form the track bed and distribute load to reduce stress on the subgrade.
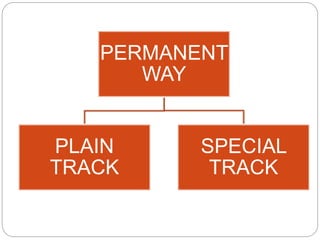
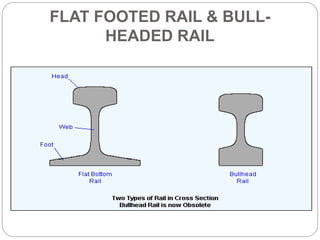
2. Details of rails, sleepers, ballast, and gauge and their purposes in guiding trains, bearing loads, maintaining alignment, and allowing for drainage.
3. Rail fastenings like fish plates and bolts which hold rails to sleepers to distribute load over a large area and firmly attach rails.