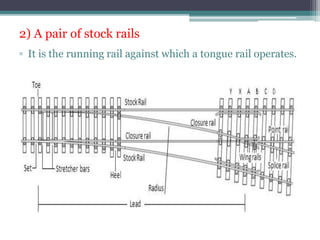
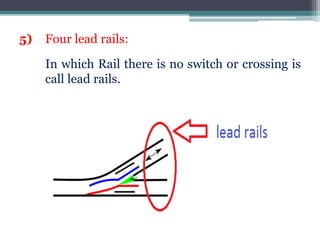
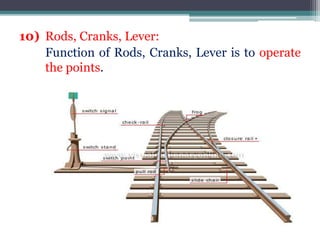
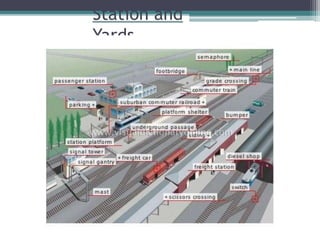
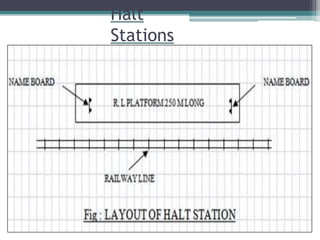
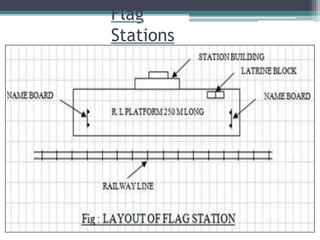
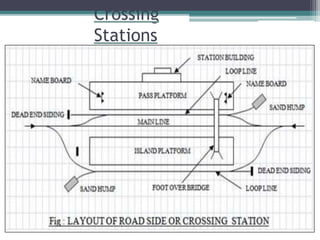
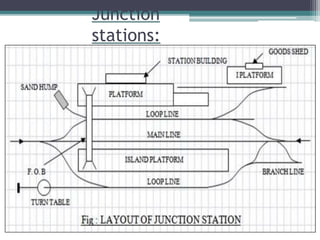
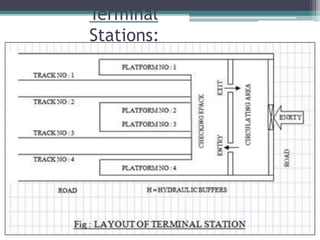
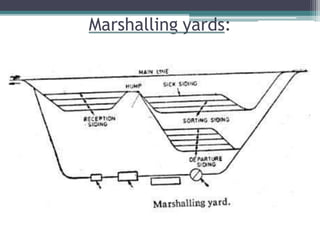
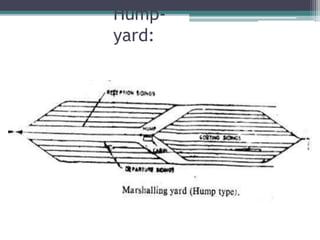
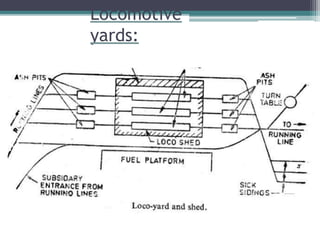
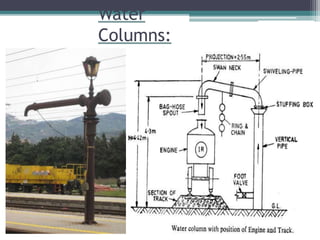
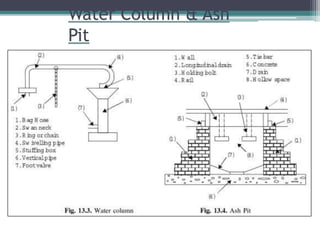
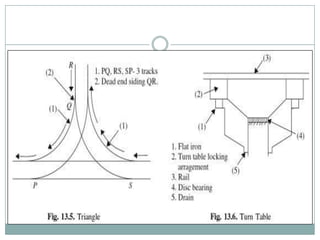
This document discusses various aspects of railway track components and infrastructure. It describes points and crossings which allow trains to divert from one track to another. It then discusses turnouts, their components like stock rails, crossings, and operating mechanisms. The document covers different types of stations like wayside, junction and terminal stations. It also discusses railway yards for passengers, goods, and locomotives along with their key facilities.




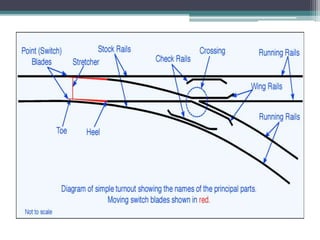
![1) A pair of Points (Switches):
A switch, turnout or [set of] points is a
mechanical installation enabling railway
trains to be guided from one track to another.
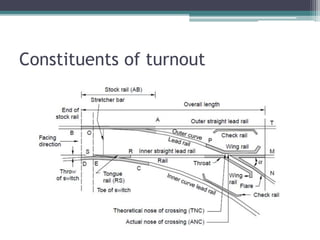
• Tongue Rail:
▫ It is a tapered movable rail, made of high-carbon or
manganese steel to withstand wear.
▫ At its thicker end, it is attached to a running rail.
▫ A tongue rail is also called a switch rail.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-6pointscrossingsandyards-200615103730/85/Chapter-6-Points-crossings-and-yards-7-320.jpg)