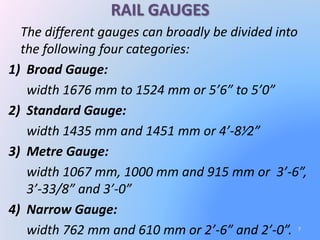
The document discusses rail gauges and types of rails used in railway tracks. It defines rail gauge as the minimum perpendicular distance between the inner faces of two rails. Key factors that affect rail gauge choice include traffic volume, development needs, speed requirements, construction costs, and terrain. Common gauges range from broad gauge over 5 feet wide to narrow gauge under 2.5 feet. The document also describes the functions of rails in providing a continuous, level surface for train movement and load distribution. The three main types of rails discussed are double headed, bull headed, and flat footed (Vignoles) rails, with the latter now comprising around 90% of tracks worldwide due to advantages like reduced costs and greater stiffness.